Musculoskeletal System - Tendon Development: Difference between revisions
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
| | | | ||
* '''Connecting muscles to tendons: tendons and musculoskeletal development in flies and vertebrates'''<ref><pubmed>20699295</pubmed></ref> "The formation of the musculoskeletal system represents an intricate process of tissue assembly involving heterotypic inductive interactions between tendons, muscles and cartilage. An essential component of all musculoskeletal systems is the anchoring of the force-generating muscles to the solid support of the organism: the skeleton in vertebrates and the exoskeleton in invertebrates. Here, we discuss recent findings that illuminate musculoskeletal assembly in the vertebrate embryo, findings that emphasize the reciprocal interactions between the forming tendons, muscle and cartilage tissues. We also compare these events with those of the corresponding system in the Drosophila embryo, highlighting distinct and common pathways that promote efficient locomotion while preserving the form of the organism." | * '''Connecting muscles to tendons: tendons and musculoskeletal development in flies and vertebrates'''<ref><pubmed>20699295</pubmed></ref> "The formation of the musculoskeletal system represents an intricate process of tissue assembly involving heterotypic inductive interactions between tendons, muscles and cartilage. An essential component of all musculoskeletal systems is the anchoring of the force-generating muscles to the solid support of the organism: the skeleton in vertebrates and the exoskeleton in invertebrates. Here, we discuss recent findings that illuminate musculoskeletal assembly in the vertebrate embryo, findings that emphasize the reciprocal interactions between the forming tendons, muscle and cartilage tissues. We also compare these events with those of the corresponding system in the Drosophila embryo, highlighting distinct and common pathways that promote efficient locomotion while preserving the form of the organism." | ||
* Slowdown promotes muscle integrity by modulating integrin-mediated adhesion at the myotendinous junction <ref><pubmed>20110313</pubmed></ref> | * '''Slowdown promotes muscle integrity by modulating integrin-mediated adhesion at the myotendinous junction''' <ref><pubmed>20110313</pubmed></ref> | ||
|} | |} | ||
==Histology== | ==Histology== | ||
Revision as of 20:17, 3 May 2012
Introduction
This page describes skeletal tendon development, during formation of the connective tissue connection muscle to bone.
The origins of some muscles and tendons in the head differ from those found in the remained of the body.
See also notes Connective Tissue Development.
Some Recent Findings
|
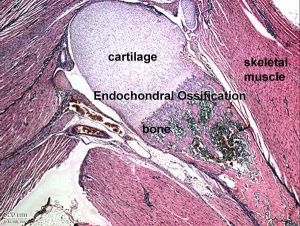
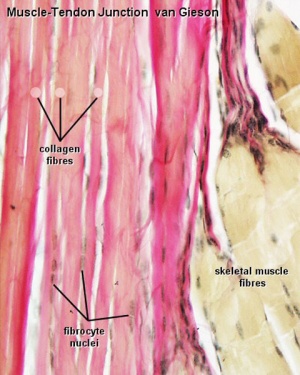
Histology
References
Reviews
Articles
<pubmed>12705871</pubmed>
Search PubMed
Search Pubmed: Tendon Development | myotendinous junction development
Additional Images
Terms
External Links
External Links Notice - The dynamic nature of the internet may mean that some of these listed links may no longer function. If the link no longer works search the web with the link text or name. Links to any external commercial sites are provided for information purposes only and should never be considered an endorsement. UNSW Embryology is provided as an educational resource with no clinical information or commercial affiliation.
Glossary Links
- Glossary: A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | Numbers | Symbols | Term Link
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, April 19) Embryology Musculoskeletal System - Tendon Development. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/Musculoskeletal_System_-_Tendon_Development
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G