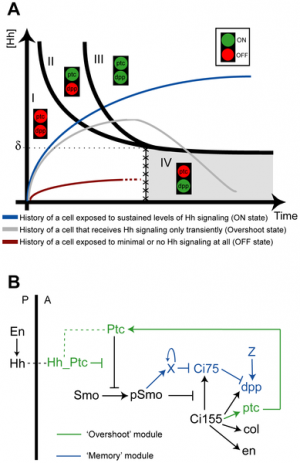
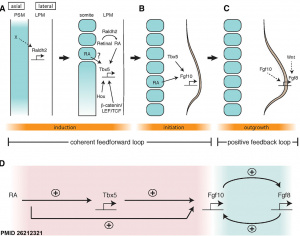
Molecular Development - Signaling: Difference between revisions
mNo edit summary |
mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 48: | Line 48: | ||
{| | {| | ||
| {{Bmp family collapsetable}} | |||
| {{Sox family collapsetable}} | | {{Sox family collapsetable}} | ||
| {{Tbx family collapsetable}} | | {{Tbx family collapsetable}} | ||
Revision as of 14:10, 16 January 2018
| Embryology - 16 Apr 2024 |
|---|
| Google Translate - select your language from the list shown below (this will open a new external page) |
|
العربية | català | 中文 | 中國傳統的 | français | Deutsche | עִברִית | हिंदी | bahasa Indonesia | italiano | 日本語 | 한국어 | မြန်မာ | Pilipino | Polskie | português | ਪੰਜਾਬੀ ਦੇ | Română | русский | Español | Swahili | Svensk | ไทย | Türkçe | اردو | ייִדיש | Tiếng Việt These external translations are automated and may not be accurate. (More? About Translations) |
Introduction
In current years we have turned from wanting to merely describe the events of embryogenesis, to a desire to understand the mechanisms of development. These notes are intended to introduce a number of different mechanisms at the cellular level and factors that form structures within the embryo. These cellular dynamic and physical interactions form basic tissue structures of epithelia, connective tissues and features such as tubes.
Membrane Receptors Signaling between cells, cells and matrix, tissues, and systemically, is key to the developmental and differentiation process. While there are a large number of known methods of signaling these all fall into a few broad classes. Signaling also depends upon having an initial source for the signal and cells which can interpret the signal. To see how these mechanisms are employed you should look at embryo axes formation or the specific pages within each set of notes that refer to early development or system development (these pages are listed on Molecular Development homepage).
Some signals act internally (More? cell cycle) or over a short distance (between ajoining cells or to the cell itself), others act in a distance dependent manner (changing concentration of the signal will alter the response), others act by cascading (signaling from one cell to the next, to the next), and finally some signals act at a distance (between one tissue and a distant cell population).
Signaling in many cases precedes any observable change in cell shape and motility. Please note as an introduction the notes below have been extensively simplified. More details can be gained by clicking on the specific links below.
| Factor Links: AMH | hCG | BMP | sonic hedgehog | bHLH | HOX | FGF | FOX | Hippo | LIM | Nanog | NGF | Nodal | Notch | PAX | retinoic acid | SIX | Slit2/Robo1 | SOX | TBX | TGF-beta | VEGF | WNT | Category:Molecular |
Molecular Factors
- BMP - Bone Morphogenetic Protein
- hCG - human Chorionic Gonadotropin
- FGF - Fibroblast Growth Factor
- FOX - Forkhead bOX
- HIPPO
- HOX - Homeobox
- PAX - "paired" (prd) with a box (homeodomain) domain.
- NANOG - Tír na nÓg ("Land of the Young")
- NOTCH
- RA - Retinoic Acid
- SHH - Sonic HedgeHog
- SIX
- Slit2/Robo1
- SOX
- TBX
- TGF-beta - Transforming Growth Factor - beta
- VEGF - Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor
- WNT - Wingless and iNT
|
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Factor Links: AMH | hCG | BMP | sonic hedgehog | bHLH | HOX | FGF | FOX | Hippo | LIM | Nanog | NGF | Nodal | Notch | PAX | retinoic acid | SIX | Slit2/Robo1 | SOX | TBX | TGF-beta | VEGF | WNT | Category:Molecular |
Mechanisms
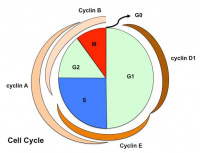
- cell cycle- position in cell cycle, proliferative rate, post-mitotic
- time- position in cell cycle, cell death (apoptosis)
- adhesive interactions- cell/cell, cell/extracellular matrix
- transcription factors- Hox, bHLH, zinc finger,
- protein growth factors- VEGF, FGF, NGF, GDNF, TGFb
- steroidal growth factors- RA, TH,
- extracellular matrix proteins- Wnt7a, laminin, fibronectin
- ion signaling- calcium
References
Reviews
<pubmed></pubmed>
<pubmed></pubmed> <pubmed></pubmed>
Articles
Search PubMed
Search Pubmed: molecular development signals
Glossary Links
- Glossary: A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | Numbers | Symbols | Term Link
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, April 16) Embryology Molecular Development - Signaling. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/Molecular_Development_-_Signaling
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G