Molecular Development - Ribonucleic acid: Difference between revisions
(Created page with "{{Header}} ==Introduction== thumb|Amphibian oocyte transcription File:Epigenetics cartoon.jpg|thumb|Epigenetics mechanisms<ref><p...") |
mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
[[File:Epigenetics cartoon.jpg|thumb|Epigenetics mechanisms<ref><pubmed>16688142</pubmed></ref>]] | [[File:Epigenetics cartoon.jpg|thumb|Epigenetics mechanisms<ref><pubmed>16688142</pubmed></ref>]] | ||
The original "RNA family" consisted of just 3 main members; transfer RNA (tRNA), ribosomal RNA (rRNA) and messenger RNAs (mRNA). Involved in gene expression through protein translation (synthesis). | The original "RNA family" consisted of just 3 main members; transfer RNA (tRNA), ribosomal RNA (rRNA) and messenger RNAs (mRNA). Involved in gene expression through protein translation (synthesis). | ||
In recent years this RNA family, shown in the table below, has been expanded to include newly identified members: small nuclear RNA (snRNA) , small nucleolar RNA (snoRNA), and short regulatory RNA (piwi-associated RNA (piRNA), endogenous short-interfering RNA (endo-siRNA) and microRNA (miRNA) and now long non-coding RNA (lncRNA). Each of these new family members has a range of potential roles in development and differentiation. | In recent years this RNA family, shown in the table below, has been expanded to include newly identified members: small nuclear RNA (snRNA) , small nucleolar RNA (snoRNA), and short regulatory RNA (piwi-associated RNA (piRNA), endogenous short-interfering RNA (endo-siRNA) and microRNA (miRNA) and now long non-coding RNA (lncRNA). Each of these new family members has a range of potential roles in development and differentiation. | ||
| Line 9: | Line 10: | ||
<center>''Draft template page - content to be added.''</center> | <center>''Draft template page - content to be added.''</center> | ||
[[Molecular_Development_-_microRNA|microRNA]] | |||
{{Molecular Links}} | {{Molecular Links}} | ||
| Line 32: | Line 37: | ||
|- | |- | ||
! RNA Class !! Acronym !! Roles !! Examples !! Reviews | ! RNA Class !! Acronym !! Roles !! Examples !! Reviews | ||
|- | |||
| transfer RNA || tRNA || carry amino acid in cell cytoplasm to ribosome || || PMID 24966867 | |||
|- | |- | ||
| messenger RNA || mRNA || transcribed from DNA in cell nucleus and relocate to cytoplasm for translation on the ribosome|| Example | | messenger RNA || mRNA || transcribed from DNA in cell nucleus and relocate to cytoplasm for translation on the ribosome|| Example | ||
|- | |- | ||
| ribosomal RNA|| rRNA || structural RNA that allow the assembly of ribosomal proteins in the cytoplasm into ribosomal subunits required for protein translation | | ribosomal RNA || rRNA || structural RNA that allow the assembly of ribosomal proteins in the cytoplasm into ribosomal subunits required for protein translation|| Example | ||
|- | |- | ||
| small nuclear RNA || snRNA || involved in cell nucleus RNA splicing|| | | small nuclear RNA || snRNA || involved in cell nucleus RNA splicing|| || PMID 23980890 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| small nucleolar RNA || snoRNA || modify other small RNAs (rRNAs and tRNAs) || box C/D snoRNAs and the box H/ACA || | | small nucleolar RNA || snoRNA || modify other small RNAs (rRNAs and tRNAs) || box C/D snoRNAs and the box H/ACA || PMID 21664409 PMID 19446021 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| microRNA || miRNA || post-transcriptional regulator of gene expression|| | | microRNA || miRNA || post-transcriptional regulator of gene expression|| || PMID 25128264 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| endogenous short-interfering RNA || endo-siRNA || short regulatory RNA || | | endogenous short-interfering RNA || endo-siRNA || short regulatory RNA || mainly characterised in plants || PMID 22578318 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| piwi-associated RNA || piRNA || short regulatory RNA || | | piwi-associated RNA || piRNA || short regulatory RNA || || PMID 18032451 PMID 22103557 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| long non-coding RNA || ncRNA || non-coding RNA greater than 200bp in length may have different roles in signalling, protein processing and differentiation || | | long non-coding RNA || ncRNA || non-coding RNA greater than 200bp in length may have different roles in signalling, protein processing and differentiation || || PMID 24829860 | ||
|} | |} | ||
Revision as of 11:17, 15 September 2014
| Embryology - 20 Apr 2024 |
|---|
| Google Translate - select your language from the list shown below (this will open a new external page) |
|
العربية | català | 中文 | 中國傳統的 | français | Deutsche | עִברִית | हिंदी | bahasa Indonesia | italiano | 日本語 | 한국어 | မြန်မာ | Pilipino | Polskie | português | ਪੰਜਾਬੀ ਦੇ | Română | русский | Español | Swahili | Svensk | ไทย | Türkçe | اردو | ייִדיש | Tiếng Việt These external translations are automated and may not be accurate. (More? About Translations) |
Introduction
The original "RNA family" consisted of just 3 main members; transfer RNA (tRNA), ribosomal RNA (rRNA) and messenger RNAs (mRNA). Involved in gene expression through protein translation (synthesis).
In recent years this RNA family, shown in the table below, has been expanded to include newly identified members: small nuclear RNA (snRNA) , small nucleolar RNA (snoRNA), and short regulatory RNA (piwi-associated RNA (piRNA), endogenous short-interfering RNA (endo-siRNA) and microRNA (miRNA) and now long non-coding RNA (lncRNA). Each of these new family members has a range of potential roles in development and differentiation.
| Factor Links: AMH | hCG | BMP | sonic hedgehog | bHLH | HOX | FGF | FOX | Hippo | LIM | Nanog | NGF | Nodal | Notch | PAX | retinoic acid | SIX | Slit2/Robo1 | SOX | TBX | TGF-beta | VEGF | WNT | Category:Molecular |
Some Recent Findings
|
RNA Classes
| RNA Class | Acronym | Roles | Examples | Reviews |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| transfer RNA | tRNA | carry amino acid in cell cytoplasm to ribosome | PMID 24966867 | |
| messenger RNA | mRNA | transcribed from DNA in cell nucleus and relocate to cytoplasm for translation on the ribosome | Example | |
| ribosomal RNA | rRNA | structural RNA that allow the assembly of ribosomal proteins in the cytoplasm into ribosomal subunits required for protein translation | Example | |
| small nuclear RNA | snRNA | involved in cell nucleus RNA splicing | PMID 23980890 | |
| small nucleolar RNA | snoRNA | modify other small RNAs (rRNAs and tRNAs) | box C/D snoRNAs and the box H/ACA | PMID 21664409 PMID 19446021 |
| microRNA | miRNA | post-transcriptional regulator of gene expression | PMID 25128264 | |
| endogenous short-interfering RNA | endo-siRNA | short regulatory RNA | mainly characterised in plants | PMID 22578318 |
| piwi-associated RNA | piRNA | short regulatory RNA | PMID 18032451 PMID 22103557 | |
| long non-coding RNA | ncRNA | non-coding RNA greater than 200bp in length may have different roles in signalling, protein processing and differentiation | PMID 24829860 |
RNA nucleotides
Ribonucleic acid (RNA) consists of 4 nucleotides:
- Adenine (A)
- Cytosine (C)
- Guanine (G)
- Uracil (U)
- Links: Molecular Development
Epigenetics
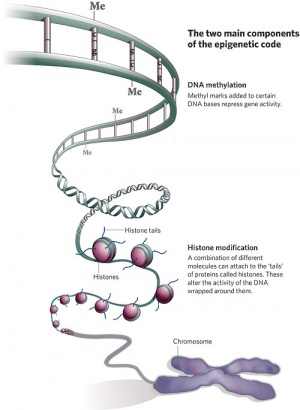
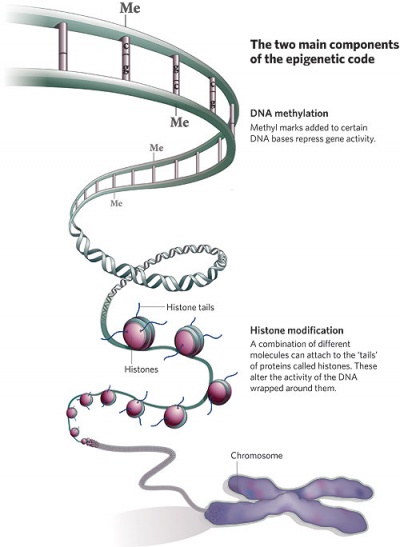
| Epigenetics as the name implies, is the inheritance mechanisms that lie outside the DNA sequence of our genes.
One of the initial discoveries was the effects of DNA methylation upon gene expression and then modifications of nucleosomal histones. This DNA methylation, usually associated with 5-methylcytosine (m5C), leads to transcriptional silencing in vertebrates.
|
|
References
Terms
External Links
External Links Notice - The dynamic nature of the internet may mean that some of these listed links may no longer function. If the link no longer works search the web with the link text or name. Links to any external commercial sites are provided for information purposes only and should never be considered an endorsement. UNSW Embryology is provided as an educational resource with no clinical information or commercial affiliation.
- NHGR- The ENCODE Project ENCyclopedia Of DNA Elements
- Foldit - Amino Acids
Glossary Links
- Glossary: A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | Numbers | Symbols | Term Link
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, April 20) Embryology Molecular Development - Ribonucleic acid. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/Molecular_Development_-_Ribonucleic_acid
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G