Main Page: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 84: | Line 84: | ||
! Author Comments | ! Author Comments | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [[File: | | [[File:Mark_Hill.jpg|50px]] | ||
Shown below is the original embryology main page content links, I removed this in the latest update to simplify the opening page appearance, but this also removed the google visibility. | Shown below is the original embryology main page content links, I removed this in the latest update to simplify the opening page appearance, but this also removed the google visibility. | ||
Revision as of 09:01, 19 November 2012
Friday April 19 2024
Introduction
Welcome to the new site designed to allow interactive development of Embryology resources and information.
|
Site Map - where the content is located |
|
New - what is new on this Wiki |
|
Contributors - who has contributed |
Bookmark with: http://php.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology
Total number of views: Template:NUMBEROFVIEWS
Start Here
This is the Main Page of the website, clicking the top lefthand icon or the menu item will always bring you to here.
There are several different ways to find what you are looking for: click the major topic on the large left hand image, the Site Map also links to major topic sections, the Category option will show related materials, or simply use the search box.

|
Designed to update the original and popular UNSW Embryology website. You should find this new site easier to navigate and search. I am always happy to receive feedback on your learning experience. |
UNSW Embryology content has been derived under a number of different copyright restrictions, therefore do not assume that you can reuse content found on this current site without permission. Click on images and movies to get descriptions and full copyright information.
|
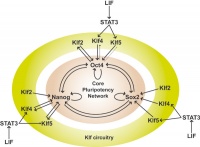
The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 2012 was awarded jointly to Sir John B. Gurdon and Shinya Yamanaka "for the discovery that mature cells can be reprogrammed to become pluripotent"
(More? Yamanaka Factors | Induced Stem Cells | Stem Cells) |
| Author Comments | |
|---|---|

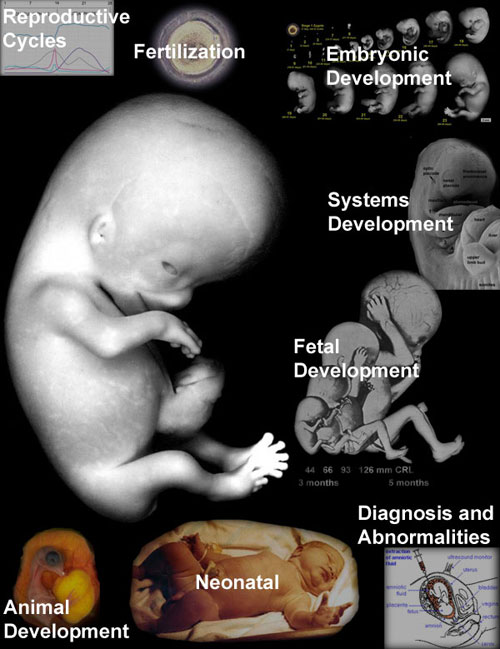
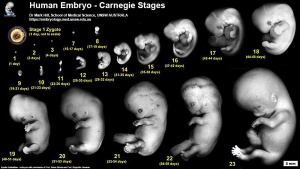
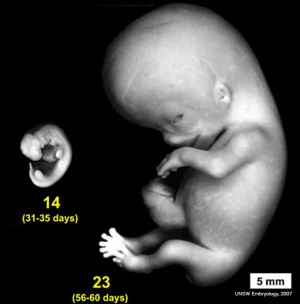
Shown below is the original embryology main page content links, I removed this in the latest update to simplify the opening page appearance, but this also removed the google visibility. Human Embryology
MoviesMovies There are many different animations showing developmental processes and research material. Two different formats are currently available. Human System Development
Human Neonatal
Human Abnormal Development
Please note that abnormal development pages may contain clinical images not suitable for children. Class Notes
Animal Development
Textbooks/Journals
Contributed Pages
|
Glossary Links
- Glossary: A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | Numbers | Symbols | Term Link
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, April 19) Embryology Main Page. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/Main_Page
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G