Intermediate - Outflow Tract: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[Image:Intermediateicon.jpg|left|70px|link=Intermediate_Cardiac_Embryology]] | [[Image:Intermediateicon.jpg|left|70px|link=Intermediate_Cardiac_Embryology]] | ||
{{Template:Intermediate Cardiac menu}} | {{Template:Intermediate Cardiac menu}} | ||
{{Template:Cardiac_modules}} | {{Template:Cardiac_modules}} | ||
| Line 17: | Line 18: | ||
<Flowplayer height="540" width="720" autoplay="true">Heart outflow tract 002.flv</Flowplayer> | <Flowplayer height="540" width="720" autoplay="true">Heart outflow tract 002.flv</Flowplayer> | ||
{| width="100%" | |||
|- | |||
|width="30%" bgcolor="gold"|<big>'''[[Intermediate_-_Atrial_Ventricular_Septation|Back to Septation]]'''</big> | |||
| | |||
|width="30%" bgcolor="gold" align="right"|<big>'''[[Intermediate_-_Heart_Valves|Next: Development of Heart Valves]]'''</big> | |||
|- | |||
|bgcolor="limegreen"|<big>'''[[Basic_-_Embryonic_Heart_Divisions|Go to this section in the basic level]]'''</big> | |||
| | |||
|bgcolor="firebrick" align="right"|<big>'''[[Advanced_-_Outflow_Tract|Go to this section in the advanced level]]'''</big> | |||
|} | |||
Revision as of 09:33, 14 October 2009
| Begin Intermediate: | Primordial Heart Tube | Heart Tube Looping | Atrial Ventricular Septation | Outflow Tract | Heart Valves | Cardiac Abnormalities | Vascular Overview |
| Cardiac Embryology | Begin Basic | Begin Intermediate | Begin Advanced |
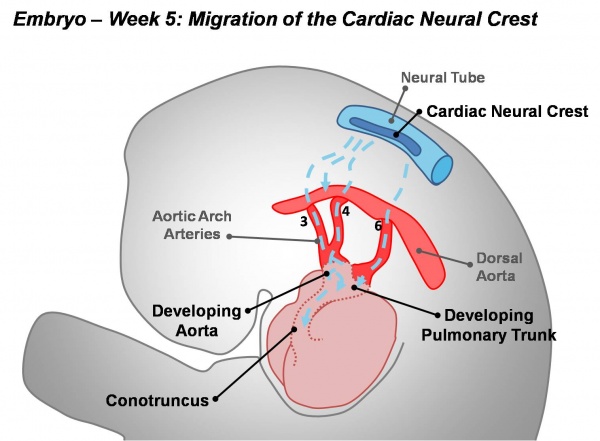
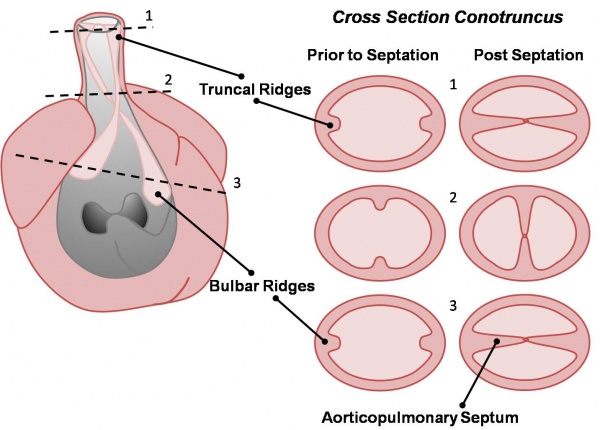
Active proliferation of neural crest mesenchymal cells in the bulbus cordis during the fifth week creates bulbar ridges which are continuous in the truncus arteriosus. The neural crest cells migrate through the primordial pharynx and over the aortic arches to reach the outflow tract (pictured below). The bulbar ridges undergo a 180° spiral to create the helical aorticopulmonary septum. As the ridges grow and develop myocardium they fuse. Fusion occurs in a distal to proximal direction during the sixth week allowing for cleavage of the aorta and pulmonary trunk. The spiralling nature of the ridges causes the pulmonary trunk to twist around the aorta. Note that the bulbus cordis accounts for the smooth conus arteriosus (or infundibulum) in the right ventricle and the aortic vestibule in the left ventricle.
The following animation shows the process occuring in a right oblique view of the heart with the anterolateral wall of the right ventricle having been removed.
<Flowplayer height="540" width="720" autoplay="true">Heart outflow tract 002.flv</Flowplayer>
| Back to Septation | Next: Development of Heart Valves | |
| Go to this section in the basic level | Go to this section in the advanced level |