HM Practical - Blood Vessel Histology
From Embryology
Introduction
HM/A Practical 3 for Monday July 23 and Wednesday July 25.
This page provides histology support information for blood vessel structure. It does not cover the pathology content.
- Links: Medicine | HMA | Histology | Histology Stains | Blood Vessel Development
Aims
- To understand the microscopic appearance of normal blood vessels of different dimensions and to recognize changes in the arterial wall as seen in atherosclerosis.
Key concepts
- Normal structure of large and medium blood vessels; tunica intima, tunica media & tunica adventitia and capillaries.
- Relation of blood vessel structure to function.
- Abnormalities of arteries in atherosclerosis.
Practical class activities
Note the features listed for the following virtual slides linked from: http://vslides.unsw.edu.au
- Aorta (elastic artery) - (2 virtual slides) Showing layers of the wall: tunica intima, tunica media and tunica adventitia. The media is extensive with multiple layers of smooth muscle mixed with elastic laminae, some of which are fenestrated. Vasa vasorum and nervi vasorum in the tunica adventitia; capillaries in adipose tissue surrounding the artery. (Note: capillaries are roughly 8 micrometers in diameter, enough to see 1 or 2 red blood cells inside the lumen).
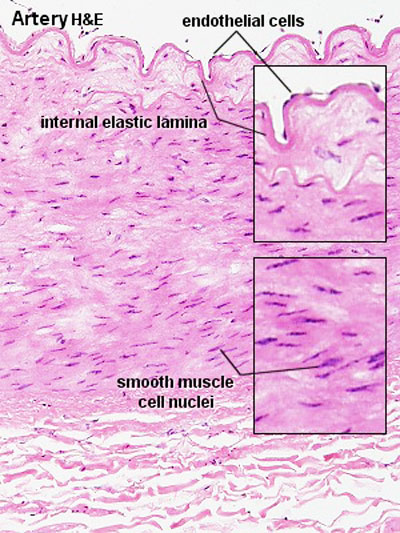
- Medium sized (muscular) artery and vein - (2 virtual slides) Distinct layers of wall of an artery: tunica intima, internal elastic lamina, tunica media (many layers of smooth muscle), external elastic lamina (multiple layers) extending into tunica adventitia; In the vein, the same 3 tunics can be seen but the tunica media is reduced, and the tunica adventitia is wider compared to the artery.
- Vena cava - Showing the 3 layers with an extensive tunica adventitia. Special features are the longitudinal smooth muscle bundles in the tunica adventitia.
- Atherosclerosis, artery - (Pathology is not covered on this histology support page) This section of a muscular artery from a 60-year-old male is very different from the normal vessels that you have just looked at. An adaptive tutorial is available to assist you to identify the features in this section.
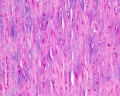
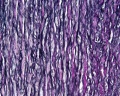
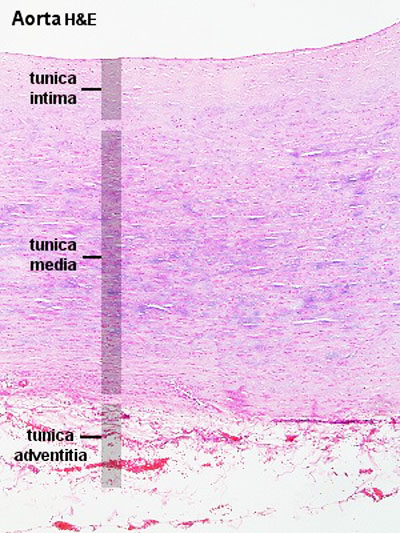
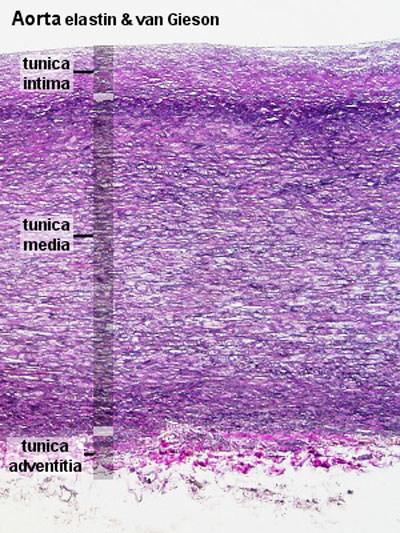
Aorta
- tunica intima - delimits the vessel wall towards the lumen of the vessel and comprises its endothelial lining (typically simple, squamous) and associated connective tissue.
- tunica media - layer of circumferential smooth muscle and variable amounts of connective tissue. A second layer of elastic fibers, the external elastic lamina, is located beneath the smooth muscle.
- tunica adventitia - mainly of connective tissue fibres. The tunica adventitia blends with the connective tissue surrounding the vessel, and the definition of the outer limit of the tunica adventitia is therefore somewhat arbitrary.
Labeled
|
|
| Aorta overview | Aorta elastin |
Unlabeled
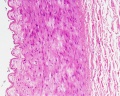
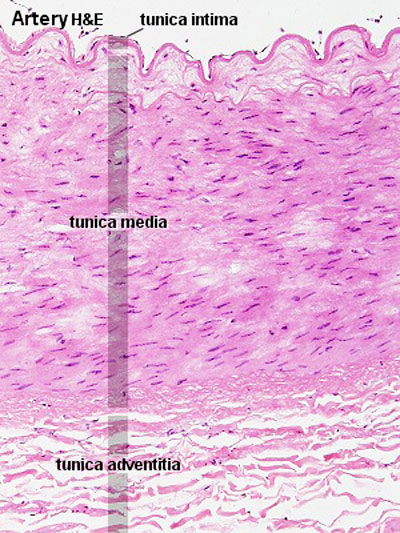
Arteries
- elastic arteries - the tunica intima of elastic arteries is thicker than in other arteries
|
|
| Artery overview | Artery detail |

|
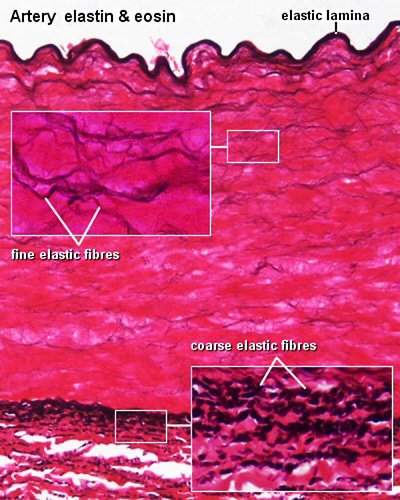
|
| Artery elastin | Artery elastin detail |
Unlabeled
Vein
Glossary Links
- Glossary: A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | Numbers | Symbols | Term Link
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, April 20) Embryology HM Practical - Blood Vessel Histology. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/HM_Practical_-_Blood_Vessel_Histology
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G