Foundations Practical - Neonatal
Foundations Practical: Introduction | Week 1 and 2 | Week 3 and 4 | Week 1 to 8 | Week 9 to 36 | Neonatal | Critical Periods | Additional Resources | Quiz
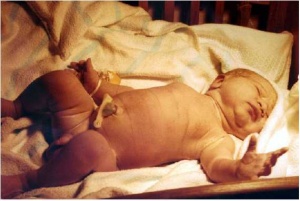
Newborn Infant
- Some essential systems come online, others continue to develop.
The neonatal period is about the transition from an interuterine placenta and maternally supported life to life to relatively independent life in the external environment.
In developing a broad understanding of the neonatal period you need to think about the two different environments and the effects of loss of placental support. Remember that substantial postnatal development still has to occur in many systems. Identify these systems and the associated changes that occur.
Birth
|
<html5media height="500" width="400">File:Birth MRI.mp4</html5media> |
The median duration of gestation for first births from assumed ovulation to delivery was 274 days (just over 39 weeks). For multiple births, the median duration of pregnancy was 269 days (38.4 weeks).
Birth Weight
The primary causes of VLBW are premature birth (born <37 weeks gestation, and often <30 weeks) and intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR), usually due to problems with placenta, maternal health, or to birth defects. Many VLBW babies with IUGR are preterm and thus are both physically small and physiologically immature.
| Birth weight (grams) | less 500 | 500 – 999 | 1,000 – 1,499 | 1,500 – 1,999 | 2,000 – 2,499 | 2,500 – 2,999 | 3,000 – 3,499 | 3,500 – 3,999 | 4,000 – 4,499 | 4,500 – 4,999 | 5,000 or more |
| Classification | Extremely Low Birth Weight | Very Low Birth Weight | Low Birth Weight | Normal Birth Weight | High Birth Weight | ||||||
Newborn Homoeostasis
|
The newborn has to establish:
|
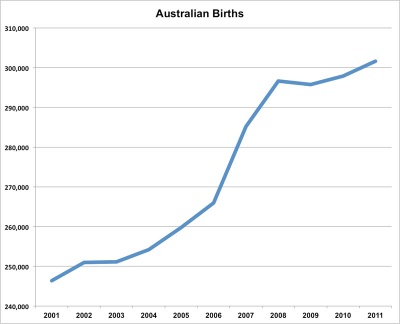
Australian Birth
Now briefly consider the current Australian trends in birth and the new reproductive technologies available.
Australian births (2011)
Assisted reproductive technology in Australia and New Zealand
Assisted Reproduction Technology (ART) is also sometimes also used to identify In vitro fertilization (IVF) but now includes many new techniques.
See the 2014 report[1]
- 70,082 assisted reproductive technology (ART) treatment cycles performed in Australia (64,905 ) and New Zealand (5,177),
- 3,590 babies born (including 13,312 liveborn babies) following ART treatment in 2012.
- an increase of 5.8% for Australia and a decrease of 0.2% for New Zealand on 2011.
- 13.7 cycles per 1,000 women of reproductive age (15–44 years) in Australia
- Women used their own oocytes or embryos (autologous) in 95.2% of treatments, and 34.8% of all cycles used frozen/thawed embryos.
- 36,171 women who undertook 66,710 autologous fresh and/or thaw cycles in Australia and New Zealand in 2012.
- average, 1.8 cycles per woman were undertaken in 2012, with more cycles per woman in Australia (1.9 cycles per woman) than in New Zealand (1.5 cycles per woman).
- increase in cycles where preimplantation genetic diagnosis was performed, from 2.0% of cycles in 2011 to 3.7% of cycles in 2012.
- Maternal Age
- women aged under 30, the live delivery rate was 26.0% for both autologous fresh and thaw cycles.
- women aged over 44, the live delivery rate was 0.9% and 4.6% for autologous fresh and thaw cycles respectively.
(More? Assisted Reproductive Technology)
Maternal Changes
- Puerperium - six weeks following birth, maternal reproductive organs and physiology return to pre-pregnancy state.
- Involution - process of tissue catabolism of uterus.
- Lochia - uterine (placental) discharge, blood plus mucous, continues for about 4 weeks.
- Mammary - glandular development and function.
Development does not finish at Birth
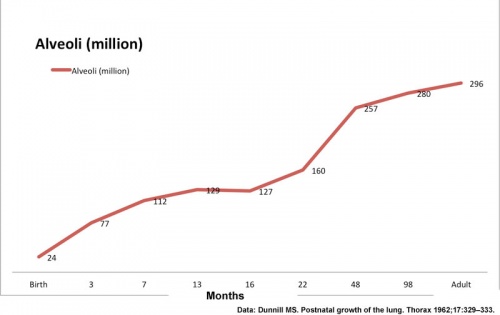
Many systems continue to grow and differentiate after birth, in particular neural, sensory, respiratory, renal, endocrine and genital.
Terms
Note - linked terms in the list below are external resources to the current class content.
| Birth Terms | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
|
Foundations Practical: Introduction | Week 1 and 2 | Week 3 and 4 | Week 1 to 8 | Week 9 to 36 | Neonatal | Critical Periods | Additional Resources | Quiz
Glossary: A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | Numbers
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, April 19) Embryology Foundations Practical - Neonatal. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/Foundations_Practical_-_Neonatal
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G