Foundations Practical - Critical Periods
We have now had a very quick trip through more than 9 months of development in nearly 2 hours. Before we finish it is worth thinking about times in development when things may go wrong.
Environment Effects
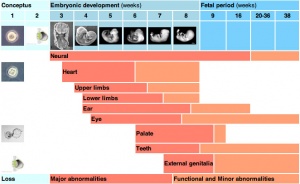
- These are developmental times (stages) sensitive to insult, be aware of these times, the causes and the potential effects.
Critical periods of development refer to times when genetic or materal effects can impact upon the developmental process. The timing of these effects will impact on different systems at different times.
Links: Embryonic Development | Timeline human development | Movie - Human Development annotated cartoon | Human - critical periods | Human Abnormal Development
Systems with long periods of development or complex developmental origins are more susceptible to developmental abnormalities.
- Which systems will take a long time to develop?
- Which systems are complex in origin?
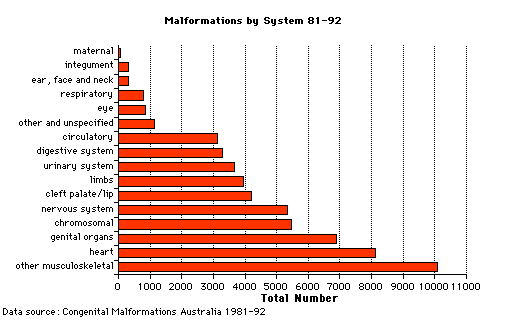
Australian Statistics
Australian Congenital Anomalies Monitoring System (ACAMS) contains data based on notifications of major congenital anomalies to birth defects registers in New South Wales, Victoria, Western Australia and South Australia and on data collected on congenital anomalies in Queensland, Tasmania and the Australian Capital Territory. Information is included on live births and stillbirths of 20 weeks gestational age or more or 400 grams birthweight or more (including induced abortions) with a congenital anomaly. Congenital anomalies are coded using the British Paediatric Association Classification of Diseases (ICD-9-BPA), which is based on the International Classification of Diseases, 9th Revision (ICD-9). ACAMS
| USA Statistics | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Genetic
- Links: Genetics
Fetal Origins Hypothesis
The Fetal period is also potentially sensitive to maternal effects that impact upon interuterine growth. Along these lines there is growing evidence that low birth weight, and therefore inhibited fetal growth, has postnatal effects on lifelong health outcomes.
Foundations Practical: Introduction | Week 1 and 2 | Week 3 and 4 | Week 1 to 8 | Week 9 to 36 | Neonatal | Critical Periods | Additional Resources | Quiz
Glossary: A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | Numbers
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, April 19) Embryology Foundations Practical - Critical Periods. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/Foundations_Practical_-_Critical_Periods
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G