File:Reticulocyte.jpg: Difference between revisions
From Embryology
(==Reticulocyte== {{Bone Marrow Histology}} {{Blue Histology}}) |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Reticulocyte== | ==Reticulocyte== | ||
* contain some cell organelles and are the initial form of erythrocytes (red blood cells, RBCs) that enter the blood (circulation). | |||
* remain for a few days in either bone marrow or spleen to mature to erythrocytes. | |||
* may be visible in blood smears by a very slight basophilic staining (homogeneous or stippling). | |||
===Erythropoiesis=== | |||
# proerythroblast - large, slightly basophilic cell, which contains a large, lightly stained nulceus. | |||
# basophilic erythroblast | |||
# polychromatophilic normoblast | |||
# orthochromic normoblast | |||
# reticulocyte | |||
# erythrocyte | |||
===Proerythroblasts=== | |||
* proliferate to generate a sequence of cells | |||
* each show a gradual decrease in size and condensation of their chromatin. | |||
* each named after changes in the staining (basophilic, polychromatophilic and orthochromic) of their cytoplasm. | |||
* nucleus is finally extruded from the normoblast. The cell enters circulation as a reticulocyte, which still contains some organelles. | |||
Latest revision as of 08:20, 25 February 2012
Reticulocyte
- contain some cell organelles and are the initial form of erythrocytes (red blood cells, RBCs) that enter the blood (circulation).
- remain for a few days in either bone marrow or spleen to mature to erythrocytes.
- may be visible in blood smears by a very slight basophilic staining (homogeneous or stippling).
Erythropoiesis
- proerythroblast - large, slightly basophilic cell, which contains a large, lightly stained nulceus.
- basophilic erythroblast
- polychromatophilic normoblast
- orthochromic normoblast
- reticulocyte
- erythrocyte
Proerythroblasts
- proliferate to generate a sequence of cells
- each show a gradual decrease in size and condensation of their chromatin.
- each named after changes in the staining (basophilic, polychromatophilic and orthochromic) of their cytoplasm.
- nucleus is finally extruded from the normoblast. The cell enters circulation as a reticulocyte, which still contains some organelles.
- Bone Marrow Histology: Blood Development | Marrow overview | Megakaryocyte | Megakaryocyte detail | Myelocyte | Normoblast | Reticulocyte | Blood Histology | Bone Development | Category:Blood
Links: Histology | Histology Stains | Blue Histology images copyright Lutz Slomianka 1998-2009. The literary and artistic works on the original Blue Histology website may be reproduced, adapted, published and distributed for non-commercial purposes. See also the page Histology Stains.
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, April 25) Embryology Reticulocyte.jpg. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/File:Reticulocyte.jpg
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 08:06, 25 February 2012 | 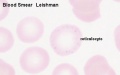 | 500 × 313 (14 KB) | Z8600021 (talk | contribs) | ==Reticulocyte== {{Bone Marrow Histology}} {{Blue Histology}} |
You cannot overwrite this file.
File usage
The following 3 pages use this file: