File:NOTCH-endothelial-cartoon.jpg
Original file (1,280 × 888 pixels, file size: 92 KB, MIME type: image/jpeg)
NOTCH Signaling in the Endothelium
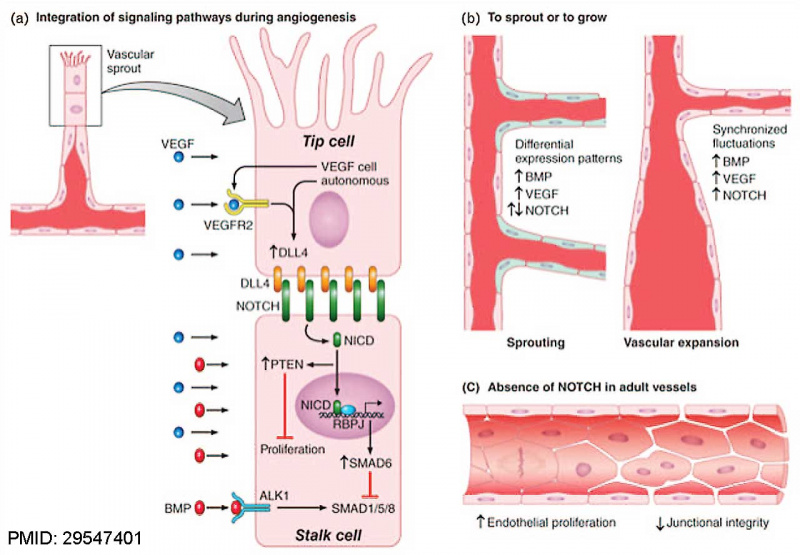
(a) A vascular sprout is characterized by a leading ‘tip’ cell followed by ‘stalk’ cells. Tip cells express high levels of DLL4 that activate NOTCH1 in the stalk cells to promote NOTCH signaling and impose differential gene expression. Increase of DLL4 in tip cells is achieved by both endothelial and non-endothelial derived VEGF to activate VEGFR2. In stalk cells, activation of the receptor results in generation of NICD that translocates to the nucleus where it binds to RBPJ and regulates gene expression. A consequence of NOTCH activation is to increase PTEN levels that suppress proliferation and to upregulate SMAD6 that titrates the signaling mediated by BMPs.
(b) Regulation of new sprouting during vascular expansion depends on integration of BMP signaling, NOTCH signaling and VEGF signaling. Differential expression patterns (illustrated by the different colors in the schema) of the NOTCH, VEGF, and BMP pathways are required to enable sprouting of new vessels. In contrast, synchronized fluctuations of the pathways favor vessel enlargement and disfavor branching. (c) In adult vessels, NOTCH is responsible for maintaining endothelial quiescence and junctional integrity. BMPs, bone morphogenetic proteins; DLL4, delta-like 4; NICD, NOTCH ICD; PTEN, phosphatase and tensin homolog; RBPJ, recombination signal-binding protein for immunoglobulin kappa J; SMAD, mothers against decapentaplegic; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor; VEGFR2, vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2.
Reference
Mack JJ & Iruela-Arispe ML. (2018). NOTCH regulation of the endothelial cell phenotype. Curr. Opin. Hematol. , , . PMID: 29547401 DOI.
Copyright
This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 (CCBY), which permits unrestricted use, distri- bution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, April 25) Embryology NOTCH-endothelial-cartoon.jpg. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/File:NOTCH-endothelial-cartoon.jpg
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 20:42, 21 March 2018 |  | 1,280 × 888 (92 KB) | Z8600021 (talk | contribs) | |
| 20:41, 21 March 2018 |  | 2,136 × 1,983 (365 KB) | Z8600021 (talk | contribs) | ===Reference=== {{#pmid:29547401}} ====Copyright==== This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 (CCBY), which permits unrestricted use, distri- bution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the ori... |
You cannot overwrite this file.
File usage
The following page uses this file: