File:Molecular & Genetic Cardiac Development Factors.jpg
From Embryology
Size of this preview: 574 × 600 pixels. Other resolution: 1,475 × 1,541 pixels.
Original file (1,475 × 1,541 pixels, file size: 269 KB, MIME type: image/jpeg)
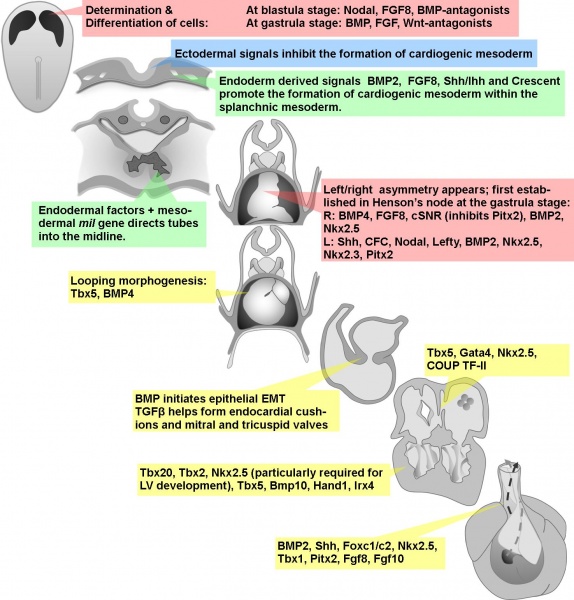
Molecular Factors in Cardiac Development
Identification of the predominant molecular and genetic factors involved in cardiac development.
Transcription Factors
- Nk family transcription factors are expressed in all animals with contractile vascular cells and hence are crucial for myocardial development; Nkx2.5 is specifically required for left ventricular chamber development.
- Gata family transcription factors interact with Nk factors to promote differentiation of cardiomyocytes, smooth muscle cells and endoderm; Gata4 regulates myocardial expression and is required for fusion of the heart tubes in the ventral midline; Gata5 is required for endocardial differentiation.
- T-box - (Tbx) genes play an important role in cardiac morphogenesis; Tbx1 may play a role in neural crest proliferation/function; Tbx2 plays a significant role in chamber specification; Tbx5 is required for atrial septation.
- Pitx2 is a left-sided transcription factor that controls normal cardiac morphogenesis by regulating cell proliferation.
Signalling Molecules
- Bone morphogenetic protein - (BMP) (particularly Bmp2) is expressed in cardiogenic mesoderm and is important for specification and myocardial differentiation.
- Wnt - signalling inhibition promotes cardiogenesis in the cardiogenic mesoderm.
- Fibroblast growth factor - (Fgf) acts alongside Bmp to allow for myocardial differentiation. Fgf8 is expressed in cardiogenic mesoderm and hence allows for cardiac specification.
- Notch - signalling establishes sub-populations within the cardiogenic mesoderm by regulating asymmetric cell division. Notch also has an inhibitory effect on myocardial differentiation.
- Cripto mediates Nodal signalling to allow for myocardial differentiation.
| Factor Links: AMH | hCG | BMP | sonic hedgehog | bHLH | HOX | FGF | FOX | Hippo | LIM | Nanog | NGF | Nodal | Notch | PAX | retinoic acid | SIX | Slit2/Robo1 | SOX | TBX | TGF-beta | VEGF | WNT | Category:Molecular |
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, April 19) Embryology Molecular & Genetic Cardiac Development Factors.jpg. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/File:Molecular_%26_Genetic_Cardiac_Development_Factors.jpg
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 12:09, 14 March 2010 |  | 1,475 × 1,541 (269 KB) | Z3212774 (talk | contribs) | category:Heart ILP Identification of the predominant molecular and genetic factors involved in cardiac development. |
You cannot overwrite this file.