File:Macaque Xi at interphase 02.jpg: Difference between revisions
(==Distribution of euchromatic chromatin marks relative to the macaque Xi at interphase== Typical examples of male and female rhesus macaque (R. Macaque) interphase nuclei showing the distribution of H3K27me3 (red), H3K4me3 (green), H3K36me2 (green) and a) |
|||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
Original image name: Figure 6. Gb-2011-12-4-r37-6-l-new.jpg http://genomebiology.com/2011/12/4/R37/figure/F6 (image cropped upper right panel, resized and labeled from [[:File:Macaque Xi at interphase 01.jpg|full figure]]) | Original image name: Figure 6. Gb-2011-12-4-r37-6-l-new.jpg http://genomebiology.com/2011/12/4/R37/figure/F6 (image cropped upper right panel, resized and labeled from [[:File:Macaque Xi at interphase 01.jpg|full figure]]) | ||
==Reference== | ===Reference=== | ||
McLaughlin CR, Chadwick BP. Characterization of DXZ4 conservation in primates implies important functional roles for CTCF binding, array expression and tandem repeat organization on the X chromosome. Genome Biol. 2011 Apr 13;12(4):R37. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21489251 PMID: 21489251] | [http://genomebiology.com/2011/12/4/R37 Genome Biol.] | McLaughlin CR, Chadwick BP. Characterization of DXZ4 conservation in primates implies important functional roles for CTCF binding, array expression and tandem repeat organization on the X chromosome. Genome Biol. 2011 Apr 13;12(4):R37. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21489251 PMID: 21489251] | [http://genomebiology.com/2011/12/4/R37 Genome Biol.] | ||
© 2011 McLaughlin and Chadwick; licensee BioMed Central Ltd. | © 2011 McLaughlin and Chadwick; licensee BioMed Central Ltd. | ||
This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. | This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. | ||
Revision as of 13:52, 12 February 2012
Distribution of euchromatic chromatin marks relative to the macaque Xi at interphase
Typical examples of male and female rhesus macaque (R. Macaque) interphase nuclei showing the distribution of H3K27me3 (red), H3K4me3 (green), H3K36me2 (green) and acetylated lysine (Pan-Ac-K, green) as determined by indirect immunofluorescence.
Nuclei are counterstained with DAPI (blue). White arrowheads in the female images indicate the location of the Xi.
Original image name: Figure 6. Gb-2011-12-4-r37-6-l-new.jpg http://genomebiology.com/2011/12/4/R37/figure/F6 (image cropped upper right panel, resized and labeled from full figure)
Reference
McLaughlin CR, Chadwick BP. Characterization of DXZ4 conservation in primates implies important functional roles for CTCF binding, array expression and tandem repeat organization on the X chromosome. Genome Biol. 2011 Apr 13;12(4):R37. PMID: 21489251 | Genome Biol.
© 2011 McLaughlin and Chadwick; licensee BioMed Central Ltd. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 10:00, 29 May 2011 | 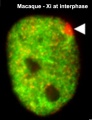 | 273 × 355 (18 KB) | S8600021 (talk | contribs) | ==Distribution of euchromatic chromatin marks relative to the macaque Xi at interphase== Typical examples of male and female rhesus macaque (R. Macaque) interphase nuclei showing the distribution of H3K27me3 (red), H3K4me3 (green), H3K36me2 (green) and a |
You cannot overwrite this file.
File usage
The following 26 pages use this file:
- 2011 Lab 8 - Sex Determination
- ANAT2341 Lab 1 - Sex Determination
- ANAT2341 Lab 2 - Week 2
- ANAT2341 Lab 8 - Sex Determination
- Abnormal Development - Twinning
- BGDA Practical 3 - Week 1 Summary
- BGDA Practical 3 - Week 2 Summary
- BGDB Sexual Differentiation - Sex Determination
- BGD Tutorial - Applied Embryology and Teratology
- Embryology History - Mary Lyon
- Molecular Development - Epigenetics
- Molecular Development - X Inactivation
- Placenta - Membranes
- Week 2
- X Chromosome
- X chromosome
- Talk:ANAT2341 Lab 1 - Sex Determination
- File:Fragile X protein cartoon.jpg
- File:Human X chromosome.jpg
- File:Human idiogram-chromosome X.jpg
- File:Macaque Xi at interphase 02.jpg
- Template:Monoygotic Twinning Table
- Template:Week 2 Embryo Stages and Events table
- Template:X Chromosome Links
- Template talk:Week 4 Embryo Stages and Events table
- Category:X Chromosome