File:Lymph node cartoon 02.jpg: Difference between revisions
From Embryology
({{Lymph node cartoons}}) |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Cell Trafficking into and out of Lymph Nodes== | |||
Lymphocytes and dendritic cells (DCs) enter lymph nodes by different routes. | |||
===Lymphocytes=== | |||
* Most lymphocytes migrating to lymph nodes enter from the peripheral blood. | |||
* Although various types of leukocyte are found in the arteries of lymph nodes, only lymphocytes can interact with and extravasate through high endothelial venules (HEVs) to migrate into the lymph-node parenchyma. | |||
* T and B cells (lymphocytes) subsequently segregate into the T-cell zones and B-cell zones. | |||
===Dendritic cells=== | |||
* DCs, together with small numbers of lymphocytes, enter lymph nodes through the afferent lymphatics. | |||
* then accumulate in the vicinity of high endothelial venules. | |||
* high endothelial venules are surrounded by fibroblastic reticular cells (FRCs) | |||
===Fibroblastic reticular cells=== | |||
* (FRCs) form channels (FRC conduits) that project from the subcapsular sinus into the T-cell zone. | |||
* Some chemokines produced extranodally might reach HEVs through the FRC conduit. | |||
{{Lymph node cartoons}} | {{Lymph node cartoons}} | ||
===Reference=== | |||
<pubmed>15122201</pubmed>| [http://www.nature.com/nri/journal/v4/n5/full/nri1354.html Nat Rev Immunol.] | |||
Revision as of 09:48, 28 February 2012
Cell Trafficking into and out of Lymph Nodes
Lymphocytes and dendritic cells (DCs) enter lymph nodes by different routes.
Lymphocytes
- Most lymphocytes migrating to lymph nodes enter from the peripheral blood.
- Although various types of leukocyte are found in the arteries of lymph nodes, only lymphocytes can interact with and extravasate through high endothelial venules (HEVs) to migrate into the lymph-node parenchyma.
- T and B cells (lymphocytes) subsequently segregate into the T-cell zones and B-cell zones.
Dendritic cells
- DCs, together with small numbers of lymphocytes, enter lymph nodes through the afferent lymphatics.
- then accumulate in the vicinity of high endothelial venules.
- high endothelial venules are surrounded by fibroblastic reticular cells (FRCs)
Fibroblastic reticular cells
- (FRCs) form channels (FRC conduits) that project from the subcapsular sinus into the T-cell zone.
- Some chemokines produced extranodally might reach HEVs through the FRC conduit.
- Lymph Node Cartoons: Detailed structure | Cartoon with Histology | Lymphocyte traffic | Simple structure | Simple node anatomy | Wiki node image | Internal structure | Mesenteric lymph node | Histology | Gallery | Lymph Node Development
Reference
<pubmed>15122201</pubmed>| Nat Rev Immunol.
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 09:56, 28 February 2012 | 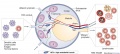 | 1,000 × 449 (97 KB) | Z8600021 (talk | contribs) | |
| 09:41, 28 February 2012 | 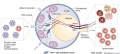 | 1,000 × 449 (95 KB) | Z8600021 (talk | contribs) | {{Lymph node cartoons}} |
You cannot overwrite this file.