File:Kollmann766-769.jpg
Kollmann766-769.jpg (694 × 311 pixels, file size: 25 KB, MIME type: image/jpeg)
- This text is a Google translate computer generated translation and may contain many errors.
Images from - Atlas of the Development of Man (Volume 2)
(Handatlas der entwicklungsgeschichte des menschen)
- Kollmann Atlas 2: Gastrointestinal | Respiratory | Urogenital | Cardiovascular | Neural | Integumentary | Smell | Vision | Hearing | Kollmann Atlas 1 | Kollmann Atlas 2 | Julius Kollmann
- Links: Julius Kollman | Atlas Vol.1 | Atlas Vol.2 | Embryology History
| Historic Disclaimer - information about historic embryology pages |
|---|
| Pages where the terms "Historic" (textbooks, papers, people, recommendations) appear on this site, and sections within pages where this disclaimer appears, indicate that the content and scientific understanding are specific to the time of publication. This means that while some scientific descriptions are still accurate, the terminology and interpretation of the developmental mechanisms reflect the understanding at the time of original publication and those of the preceding periods, these terms, interpretations and recommendations may not reflect our current scientific understanding. (More? Embryology History | Historic Embryology Papers) |
Reference
Kollmann JKE. Atlas of the Development of Man (Handatlas der entwicklungsgeschichte des menschen). (1907) Vol.1 and Vol. 2. Jena, Gustav Fischer. (1898).
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, April 19) Embryology Kollmann766-769.jpg. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/File:Kollmann766-769.jpg
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G
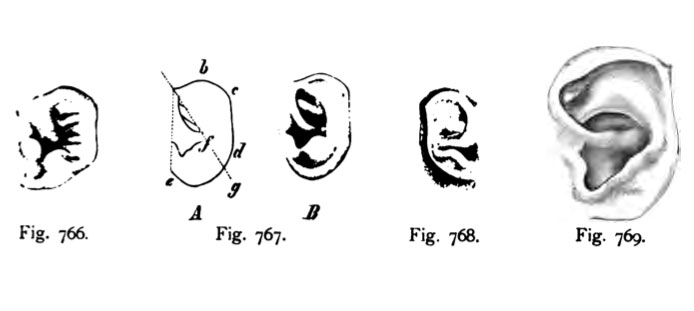
Fig. 766. Variante in der Bildung der Ohrmuschel.
Linkes Ohr eines menschlichen Embryo aus dem 4. Monat. 2 mal vergrö&ert.
(Nach Schwalbe aus Bardeleben.) Mit drei Höckerchen am Tragus.
Fig. 767. Linkes Ohr eines 6 Monate alten menschlichen Fetus.
(Nach Schwalbe.)
Die einzelnen Punkte ftir die Vergleichung der Ohrmuschel mit derjenigen der Anthro- poiden, Oberhaupt der Primaten sind folgende : ae = Ohrbasis, b = Scheitelspitze, c = Ohrspitze, d = unterer, hinterer Winkel.
Der Helix dieses Ohres ist noch nicht umgeklappt. Der Helix zeigt bei c eine kleine Ecke, die Ohrspitze oder Darwinsche Spitze genannt und bei b eine etwas schwächere Er- hebung, die Scheitelspitze. Beide Bildungen sind theromorph (tierähniich). Ihre stärkere Ent- wicklung führt bei den Tieren zur Ohrspitze.
Fig. 768. Ohrmuschel eines menschlichen Fetus vom 6. Monat.
Nat. Größe. (Nach Schwalbe.)
Diese Form des Ohres mit der Darwinschen Spitze repräsentiert den Typus des Makaken- Ohres. Die Scheitelspitze ist durch den umgebogenen Helix bereits zurück gebildet.
Fig. 769. Ohrmuschel eines neugeborenen Knaben mit konvergierenden Härchen
an der stark ausgebildeten Darwinschen Spitze.
(Nach Schwalbe.)
Als Darwinsche Spitze bezeichnet man die Zuspitzung des Helix bei c (siehe Fig. 767 A). Diese Ohrform gleicht derjenigen eines Cercopithecus erythraeus.
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 12:42, 21 October 2011 |  | 694 × 311 (25 KB) | S8600021 (talk | contribs) | {{Kollmann1907}} Category:Hearing Fig. 766. Variante in der Bildung der Ohrmuschel. Linkes Ohr eines menschlichen Embryo aus dem 4. Monat. 2 mal vergrö&ert. (Nach Schwalbe aus Bardeleben.) Mit drei Höckerchen am Tragus. Fig. 767. Linkes O |
You cannot overwrite this file.
File usage
The following page uses this file: