File:JNK1.png: Difference between revisions
(Figure: JNK is phosphorylated during mitosis of retinal progenitor cells. (A, B) Representative confocal photomicrographs of immunohistochemistry for phospho-JNK (red) and phospho-histone-H3 (green) in sections of retinal tissue maintained for 3 hours in) |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
Figure: JNK is phosphorylated during mitosis of retinal progenitor cells. | Figure: '''"JNK is phosphorylated during mitosis of retinal progenitor cells."''' | ||
(A, B) Representative confocal photomicrographs of immunohistochemistry for phospho-JNK (red) and phospho-histone-H3 (green) in sections of retinal tissue maintained for 3 hours in vitro either in absence (A - CTR) or presence of taxol (B - TAX) showing the NBL. The sections were counterstained with DAPI (blue). Arrows indicate examples of cells double stained for phospho-JNK and phospho-histone-H3. Scale bar: 20 µm. (C) Higher magnification of mitotic cell showing the subcellular localization of phospho-JNK (red), phospho-histone-H3 (green), and DAPI (blue). Scale bar: 10 µm. (D) Numbers of phospho-JNK or phospho-histone-H3 stained cells per 100 µm of linear extent parallel to the retinal surface, along the mitotic stratum of retinal explants maintained in vitro for 3 hours, either in the absence (CTR) or presence of taxol (TAX). (E) Percentage of cells stained for phospho-JNK among all cells immunolabeled for phospho-histone-H3 in the mitotic stratum. Data are means±S.E.M. from three independent experiments. CTR - control; TAX - taxol; NBL - neuroblastic layer; *** P<0.001 versus CTR. | |||
"(A, B) Representative confocal photomicrographs of immunohistochemistry for phospho-JNK (red) and phospho-histone-H3 (green) in sections of retinal tissue maintained for 3 hours in vitro either in absence (A - CTR) or presence of taxol (B - TAX) showing the NBL. The sections were counterstained with DAPI (blue). Arrows indicate examples of cells double stained for phospho-JNK and phospho-histone-H3. Scale bar: 20 µm. (C) Higher magnification of mitotic cell showing the subcellular localization of phospho-JNK (red), phospho-histone-H3 (green), and DAPI (blue). Scale bar: 10 µm. (D) Numbers of phospho-JNK or phospho-histone-H3 stained cells per 100 µm of linear extent parallel to the retinal surface, along the mitotic stratum of retinal explants maintained in vitro for 3 hours, either in the absence (CTR) or presence of taxol (TAX). (E) Percentage of cells stained for phospho-JNK among all cells immunolabeled for phospho-histone-H3 in the mitotic stratum. Data are means±S.E.M. from three independent experiments. CTR - control; TAX - taxol; NBL - neuroblastic layer; *** P<0.001 versus CTR. " | |||
doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0034483.g001 | doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0034483.g001 | ||
Citation: | Citation: <pubmed>22496813</pubmed> | ||
Copyright: © 2012 Ribas et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited. | Copyright: © 2012 Ribas et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited. | ||
{{Template:Student Image}} | |||
Latest revision as of 03:31, 3 October 2012
Figure: "JNK is phosphorylated during mitosis of retinal progenitor cells."
"(A, B) Representative confocal photomicrographs of immunohistochemistry for phospho-JNK (red) and phospho-histone-H3 (green) in sections of retinal tissue maintained for 3 hours in vitro either in absence (A - CTR) or presence of taxol (B - TAX) showing the NBL. The sections were counterstained with DAPI (blue). Arrows indicate examples of cells double stained for phospho-JNK and phospho-histone-H3. Scale bar: 20 µm. (C) Higher magnification of mitotic cell showing the subcellular localization of phospho-JNK (red), phospho-histone-H3 (green), and DAPI (blue). Scale bar: 10 µm. (D) Numbers of phospho-JNK or phospho-histone-H3 stained cells per 100 µm of linear extent parallel to the retinal surface, along the mitotic stratum of retinal explants maintained in vitro for 3 hours, either in the absence (CTR) or presence of taxol (TAX). (E) Percentage of cells stained for phospho-JNK among all cells immunolabeled for phospho-histone-H3 in the mitotic stratum. Data are means±S.E.M. from three independent experiments. CTR - control; TAX - taxol; NBL - neuroblastic layer; *** P<0.001 versus CTR. " doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0034483.g001
Citation: <pubmed>22496813</pubmed>
Copyright: © 2012 Ribas et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
- Note - This image was originally uploaded as part of an undergraduate science student project and may contain inaccuracies in either description or acknowledgements. Students have been advised in writing concerning the reuse of content and may accidentally have misunderstood the original terms of use. If image reuse on this non-commercial educational site infringes your existing copyright, please contact the site editor for immediate removal.
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 11:31, 19 September 2012 | 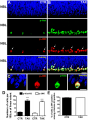 | 441 × 600 (174 KB) | Z3370664 (talk | contribs) | Figure: JNK is phosphorylated during mitosis of retinal progenitor cells. (A, B) Representative confocal photomicrographs of immunohistochemistry for phospho-JNK (red) and phospho-histone-H3 (green) in sections of retinal tissue maintained for 3 hours in |
You cannot overwrite this file.
File usage
The following page uses this file: