File:Image of taste being evoked by visualising ATP release.jpeg: Difference between revisions
(This image shows the that ATP release is greater in the WT mouse (A) than the DKO mouse (B). z3332337 [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3188419/] Expression of key elements for taste-evoked ATP release and degradation is similar between wild) |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3188419/] | [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3188419/] | ||
'''Original Figure explanation''' | |||
Expression of key elements for taste-evoked ATP release and degradation is similar between wild type and DKO mice | Expression of key elements for taste-evoked ATP release and degradation is similar between wild type and DKO mice | ||
A,B, Immunostaining for pannexin 1, a gap junction hemichannel through which ATP is believed to be secreted from taste Receptor (Type II) cells. A, Vallate taste buds from wild-type (WT) mouse. B, Vallate taste buds from DKO mouse. C, Photomicrographs of TrpM5 immunoreactivity in vallate papillae of a wild type and a DKO mouse (WT, DKO). D, PCR for TRPM5 and Px1 from wildtype (WT) and DKO mice, from taste (foliate, vallate) and nontaste (NT) epithelium and no template control (−). E, Histochemical staining for ecto-ATPase in vallate papilla from a DKO mouse. The pattern and degree of staining in taste buds and underlying nerve fibers is typical of wildtype mice as has been shown previously (Bartel et al, 2006). None of the markers shown in this figure differ significantly between taste tissue from wild type and DKO mice. | A,B, Immunostaining for pannexin 1, a gap junction hemichannel through which ATP is believed to be secreted from taste Receptor (Type II) cells. A, Vallate taste buds from wild-type (WT) mouse. B, Vallate taste buds from DKO mouse. C, Photomicrographs of TrpM5 immunoreactivity in vallate papillae of a wild type and a DKO mouse (WT, DKO). D, PCR for TRPM5 and Px1 from wildtype (WT) and DKO mice, from taste (foliate, vallate) and nontaste (NT) epithelium and no template control (−). E, Histochemical staining for ecto-ATPase in vallate papilla from a DKO mouse. The pattern and degree of staining in taste buds and underlying nerve fibers is typical of wildtype mice as has been shown previously (Bartel et al, 2006). None of the markers shown in this figure differ significantly between taste tissue from wild type and DKO mice. | ||
Copyright Huang et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited. | Copyright Huang et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited. | ||
{{2012 Student image}} | |||
Latest revision as of 00:47, 5 October 2012
This image shows the that ATP release is greater in the WT mouse (A) than the DKO mouse (B).
z3332337 [1]
Original Figure explanation Expression of key elements for taste-evoked ATP release and degradation is similar between wild type and DKO mice A,B, Immunostaining for pannexin 1, a gap junction hemichannel through which ATP is believed to be secreted from taste Receptor (Type II) cells. A, Vallate taste buds from wild-type (WT) mouse. B, Vallate taste buds from DKO mouse. C, Photomicrographs of TrpM5 immunoreactivity in vallate papillae of a wild type and a DKO mouse (WT, DKO). D, PCR for TRPM5 and Px1 from wildtype (WT) and DKO mice, from taste (foliate, vallate) and nontaste (NT) epithelium and no template control (−). E, Histochemical staining for ecto-ATPase in vallate papilla from a DKO mouse. The pattern and degree of staining in taste buds and underlying nerve fibers is typical of wildtype mice as has been shown previously (Bartel et al, 2006). None of the markers shown in this figure differ significantly between taste tissue from wild type and DKO mice.
Copyright Huang et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 10:57, 19 September 2012 | 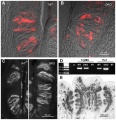 | 800 × 830 (129 KB) | Z3332337 (talk | contribs) | This image shows the that ATP release is greater in the WT mouse (A) than the DKO mouse (B). z3332337 [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3188419/] Expression of key elements for taste-evoked ATP release and degradation is similar between wild |
You cannot overwrite this file.
File usage
The following 2 pages use this file: