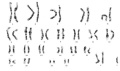File:Human idiogram-chromosome X.jpg: Difference between revisions
From Embryology
mNo edit summary |
|||
| (11 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
:'''Links:''' [[Molecular_Development_-_X_Inactivation|X Inactivation]] | [[Trisomy X]] | [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/mapview/maps.cgi?taxid=9606&chr=X Genome View - X chromosome] | [http://www.ensembl.org/Homo_sapiens/Location/Chromosome?r=X:81932856-82032856 Ensembl - X chromosome] | [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/omim/314670 OMIM - Xist] | [[2011_Group_Project_5|2011 Group Project - Fragile X Syndrome]] | |||
<br> | |||
<br> | |||
{{X Chromosome Links}} | |||
<br> | |||
<br> | |||
{{Human chromosomes}} | {{Human chromosomes}} | ||
[[Category:X Chromosome]][[Category:Genetics]] [[Category:Chromosome]] [[Category:Molecular]] [[Category:Cartoon]] | |||
[[Category:Genetics]] [[Category:Chromosome]] [[Category:Molecular]] [[Category:Cartoon]] | |||
Latest revision as of 09:04, 14 March 2018
Human Idiogram - Chromosome X
Idiogram- A drawing or photograph of the chromosomes of a particular cell.
- 155 million base pairs
- In contrast to the Y chromosome, the X chromosome contains about 5% of the haploid genome and encodes house-keeping and specialized functions.
- Genes such as Wnt-4 and DAX-1 necessary for initiation of female pathway ovary development
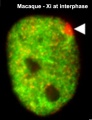
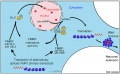
- An early discovery (1961) was that in order to have correct levels of X chromosome gene/protein expression (gene dosage), females must "inactivate" a single copy of the X chromosome in each and every cell. The initiator of the X inactivation process was discovered (1991) to be regulated by a region on the inactivating X chromosome encoding an X inactive specific transcript (XIST), that acts as RNA and does not encode a protein.
- The genetic content of the X chromosome has been strongly conserved between species because these genes have become adapted to working as a single dose - Ohno's law
- X inactivation occurs randomly throughout the embryo, generating a mosaic of maternal and paternally derived X chromosome activity in all tissues and organs. This can be seen in the fur colour of tortoiseshell cats.
- Links: X Inactivation | Trisomy X | Genome View - X chromosome | Ensembl - X chromosome | OMIM - Xist | 2011 Group Project - Fragile X Syndrome
| |
| Idiogram Chromosome Banding - The term refers to the light and dark pattern, seen after staining with a dye, of individual chromosomes identified in metaphase. It is only in meiosis and mitosis during metaphase that chromosomes can be easily identified, during the normal cell life (interphase) the chromosomes are unravelled and distributed within the nucleus in chromosome territories. A band is that part of a chromosome which is clearly distinguishable from nearby regions by appearing darker or brighter with one or more banding techniques. | |
| Genetic abnormality locations: 1-4 | 5-8 | 9-12 | 13-16 | 17-20 | 21-XY | sSMC | |
| |
| Links: Genetics | Abnormal Development - Genetic |
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, April 16) Embryology Human idiogram-chromosome X.jpg. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/File:Human_idiogram-chromosome_X.jpg
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 13:51, 23 April 2011 | 31 × 293 (3 KB) | S8600021 (talk | contribs) | ==Human Idiogram - Chromosome X== Idiogram- A drawing or photograph of the chromosomes of a particular cell. This drawing does not include the mitochondrial DNA. {{Human chromosomes}} Category:Genetics Category:Chromosome [[Category:Molecular |
You cannot overwrite this file.
File usage
The following 12 pages use this file:
- 2011 Lab 2 - Week 1
- 2011 Lab 8 - Sex Determination
- ANAT2341 Lab 1 - Sex Determination
- ANAT2341 Lab 8 - Sex Determination
- BGDA Practical 3 - Week 1 Summary
- Klinefelter syndrome
- Molecular Development - Genetics
- Molecular Development - X Inactivation
- Trisomy X
- X chromosome
- Talk:ANAT2341 Lab 1 - Fertilization
- Talk:ANAT2341 Lab 1 - Sex Determination