File:HPG female axis.jpg
Original file (600 × 700 pixels, file size: 41 KB, MIME type: image/jpeg)
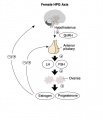
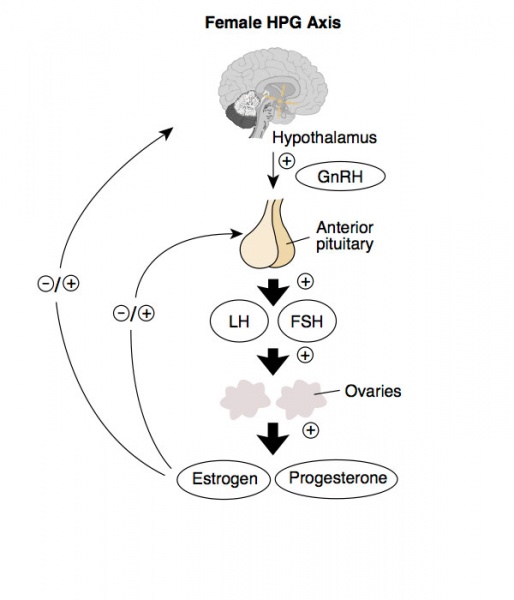
Hypothalamus - Pituitary - Gonad (female) Endocrine Axis
- Links: Menstrual Cycle | Ovary Development | Oocyte Development
- Links: Image - HPA | Hypothalamus | Pituitary | Adrenal | Image - HPT Axis | Thyroid | Image - HPG female | Image - HPG male | Gonad
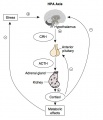
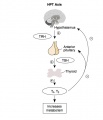
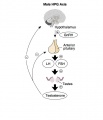
Hypothalamus
The hypothalamus is a small region located within the brain that controls many bodily functions, including eating and drinking, sexual functions and behaviors, blood pressure and heart rate, body temperature maintenance, the sleep-wake cycle, and emotional states (e.g., fear, pain, anger, and pleasure). Hypothalamic hormones play pivotal roles in the regulation of many of those functions. Because the hypothalamus is part of the central nervous system, the hypothalamic hormones actually are produced by nerve cells (i.e., neurons).
Pituitary
The anterior pituitary produces several important hormones that either stimulate target glands (e.g., the adrenal glands, gonads, or thyroid gland) to produce target gland hormones or directly affect target organs. The pituitary hormones include adreno-corticotropic hormone (ACTH); gonadotropins; thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), also called thyrotropin; growth hormone (GH); and prolactin.
The first three of those hormones (ACTH, gonadotropins, and TSH) act on other glands.
- ACTH stimulates the adrenal cortex to produce corticosteroid hormones (primarily cortisol) as well as small amounts of female and male sex hormones.
- Gonadotropins comprise two molecules, luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH). These two hormones regulate the production of female and male sex hormones in the ovaries and testes as well as the production of the germ cells (oocyte and spermatozoa).
- TSH stimulates the thyroid gland to produce and release thyroid hormone.
The remaining two pituitary hormones, GH and prolactin, directly affect their target organs.
Reference
<pubmed>15706790</pubmed>| PDF
Copyright
Unless otherwise noted in the text, all material appearing in this journal is in the public domain and may be reproduced without permission. Citation of the source is appreciated.
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 16:53, 15 May 2012 |  | 600 × 700 (41 KB) | Z8600021 (talk | contribs) | ==Hypothalamus - Pituitary - Gonad (female) Endocrine Axis== ===Reference=== <pubmed>15706790</pubmed> Unless otherwise noted in the text, all material appearing in this journal is in the public domain and may be reproduced without permission. Cita |
You cannot overwrite this file.
File usage
The following 15 pages use this file:
- ANAT2241 Endocrine System
- BGDB Sexual Differentiation - Postnatal
- BGD Lecture - Endocrine Development
- BGD Lecture - Endocrine Histology
- BGD Lecture - Sexual Differentiation
- Endocrine - Hypothalamus Development
- Endocrine - Pituitary Development
- Lecture - Endocrine Development
- Lecture - Genital Development
- File:HPA axis.jpg
- File:HPG female axis.jpg
- File:HPG male axis.jpg
- File:HPT axis.jpg
- File:Hypothalamus endocrine system.jpg
- Template:HPA axis