File:Gray0903.jpg
Gray0903.jpg (600 × 389 pixels, file size: 42 KB, MIME type: image/jpeg)
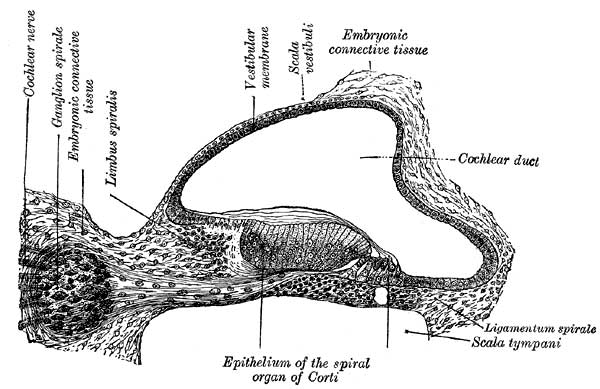
Fig. 903. Cochlear Duct and Ganglia
Transverse section of the cochlear duct of a fetal cat. (After Boettcher and Ayres.)
The mesodermal tissue surrounding the various parts of the epithelial labyrinth is converted into a cartilaginous ear-capsule, and this is finally ossified to form the bony labyrinth. Between the cartilaginous capsule and the epithelial structures is a stratum of mesodermal tissue which is differentiated into three layers, viz., an outer, forming the periosteal lining of the bony labyrinth; an inner, in direct contact with the epithelial structures; and an intermediate, consisting of gelatinous tissue: by the absorption of this latter tissue the perilymphatic spaces are developed. The modiolus and osseous spiral lamina of the cochlea are not preformed in cartilage but are ossified directly from connective tissue.
- Links: Inner Ear Development | Cat Development
- Gray's Images: Development | Lymphatic | Neural | Vision | Hearing | Somatosensory | Integumentary | Respiratory | Gastrointestinal | Urogenital | Endocrine | Surface Anatomy | iBook | Historic Disclaimer
| Historic Disclaimer - information about historic embryology pages |
|---|
| Pages where the terms "Historic" (textbooks, papers, people, recommendations) appear on this site, and sections within pages where this disclaimer appears, indicate that the content and scientific understanding are specific to the time of publication. This means that while some scientific descriptions are still accurate, the terminology and interpretation of the developmental mechanisms reflect the understanding at the time of original publication and those of the preceding periods, these terms, interpretations and recommendations may not reflect our current scientific understanding. (More? Embryology History | Historic Embryology Papers) |
| iBook - Gray's Embryology | |
|---|---|
|
|
Reference
Gray H. Anatomy of the human body. (1918) Philadelphia: Lea & Febiger.
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, April 18) Embryology Gray0903.jpg. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/File:Gray0903.jpg
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 00:15, 28 September 2009 |  | 600 × 389 (42 KB) | S8600021 (talk | contribs) |
You cannot overwrite this file.