File:Figure 1 Spry1-2.jpeg: Difference between revisions
(uploaded a new version of "File:Figure 1 Spry1-2.jpeg": Original Figure Explanation Deletion of Spry2 leads to a duplication of the CVP in the posterior tongue. (A) Cartoon showing location of gustatory papillae in the rodent tongue. (B,C) I) |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
Original Figure Explanation | Deletion of ''Spry'' genes leads to a doubling of CVP papillae. | ||
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21655085 | |||
'''Original Figure Explanation''' | |||
Deletion of Spry2 leads to a duplication of the CVP in the posterior tongue. | Deletion of Spry2 leads to a duplication of the CVP in the posterior tongue. | ||
(A) Cartoon showing location of gustatory papillae in the rodent tongue. (B,C) In situ hybridization staining of Shh. Wild-type mice possess a single CVP in the posterior tongue, whereas the CVP is duplicated in Spry2−/− mice (arrowheads). (D,E) SEM images of the tongue at E14.5. Scale bar, 500 µm. (F,G) DAPI fluorescence staining shows that the two CVPs (arrowheads) persist into adulthood in Spry2−/− mice. (D'-G') Higher magnification images of boxed areas. (D',E') Scale bar, 25 µm. | (A) Cartoon showing location of gustatory papillae in the rodent tongue. (B,C) In situ hybridization staining of Shh. Wild-type mice possess a single CVP in the posterior tongue, whereas the CVP is duplicated in Spry2−/− mice (arrowheads). (D,E) SEM images of the tongue at E14.5. Scale bar, 500 µm. (F,G) DAPI fluorescence staining shows that the two CVPs (arrowheads) persist into adulthood in Spry2−/− mice. (D'-G') Higher magnification images of boxed areas. (D',E') Scale bar, 25 µm. | ||
Revision as of 00:57, 5 October 2012
Deletion of Spry genes leads to a doubling of CVP papillae.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21655085
Original Figure Explanation Deletion of Spry2 leads to a duplication of the CVP in the posterior tongue. (A) Cartoon showing location of gustatory papillae in the rodent tongue. (B,C) In situ hybridization staining of Shh. Wild-type mice possess a single CVP in the posterior tongue, whereas the CVP is duplicated in Spry2−/− mice (arrowheads). (D,E) SEM images of the tongue at E14.5. Scale bar, 500 µm. (F,G) DAPI fluorescence staining shows that the two CVPs (arrowheads) persist into adulthood in Spry2−/− mice. (D'-G') Higher magnification images of boxed areas. (D',E') Scale bar, 25 µm.
Copyright Petersen et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 00:56, 5 October 2012 | 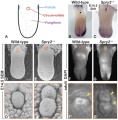 | 456 × 465 (148 KB) | Z3332337 (talk | contribs) | Original Figure Explanation Deletion of Spry2 leads to a duplication of the CVP in the posterior tongue. (A) Cartoon showing location of gustatory papillae in the rodent tongue. (B,C) In situ hybridization staining of Shh. Wild-type mice possess a single |
| 00:55, 5 October 2012 | 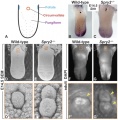 | 456 × 465 (148 KB) | Z3332337 (talk | contribs) | Original Figure Explanation Deletion of Spry2 leads to a duplication of the CVP in the posterior tongue. (A) Cartoon showing location of gustatory papillae in the rodent tongue. (B,C) In situ hybridization staining of Shh. Wild-type mice possess a single |
You cannot overwrite this file.
File usage
The following 2 pages use this file: