File:Fawcett 1910 fig12.jpg: Difference between revisions
({{Fawcett1910_sphenoid_figures}}) |
mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Fig. 12 Coronal section of the head of a 37 mm embryo Harvard Collection== | |||
[[Harvard Collection]] It shows us that the external pterygoidplate (E.P.) is composed of connective tissue. E.P.M.is the external pterygoid muscle; I.P.P. is the bony (ectochondral) internal pterygoid plate; T.P. the tensor palati; M. mandible; M.C. Meckel's cartilage; M.G. Meckel's ganglion; N.S. nasal septum; N. nasal cavity; 0. the mouth; I.P. internal pterygoid muscle; P. the ununited palate. | |||
{{Fawcett1910_sphenoid_figures}} | {{Fawcett1910_sphenoid_figures}} | ||
[[Category:Harvard Collection]] | |||
Latest revision as of 08:57, 29 December 2014
Fig. 12 Coronal section of the head of a 37 mm embryo Harvard Collection
Harvard Collection It shows us that the external pterygoidplate (E.P.) is composed of connective tissue. E.P.M.is the external pterygoid muscle; I.P.P. is the bony (ectochondral) internal pterygoid plate; T.P. the tensor palati; M. mandible; M.C. Meckel's cartilage; M.G. Meckel's ganglion; N.S. nasal septum; N. nasal cavity; 0. the mouth; I.P. internal pterygoid muscle; P. the ununited palate.
| Historic Disclaimer - information about historic embryology pages |
|---|
| Pages where the terms "Historic" (textbooks, papers, people, recommendations) appear on this site, and sections within pages where this disclaimer appears, indicate that the content and scientific understanding are specific to the time of publication. This means that while some scientific descriptions are still accurate, the terminology and interpretation of the developmental mechanisms reflect the understanding at the time of original publication and those of the preceding periods, these terms, interpretations and recommendations may not reflect our current scientific understanding. (More? Embryology History | Historic Embryology Papers) |
|
|
Reference
Fawcett E. Notes on the development of the human sphenoid. (1910) J Anat. Physiol. 44(3): 207-22. PMID 17232842
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, April 16) Embryology Fawcett 1910 fig12.jpg. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/File:Fawcett_1910_fig12.jpg
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 08:33, 29 December 2014 | 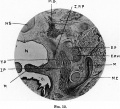 | 1,068 × 970 (282 KB) | Z8600021 (talk | contribs) | {{Fawcett1910_sphenoid_figures}} |
You cannot overwrite this file.
File usage
The following page uses this file:
