File:Epithelial Mesenchymal Transition.jpg
Original file (1,280 × 1,608 pixels, file size: 323 KB, MIME type: image/jpeg)
Summary
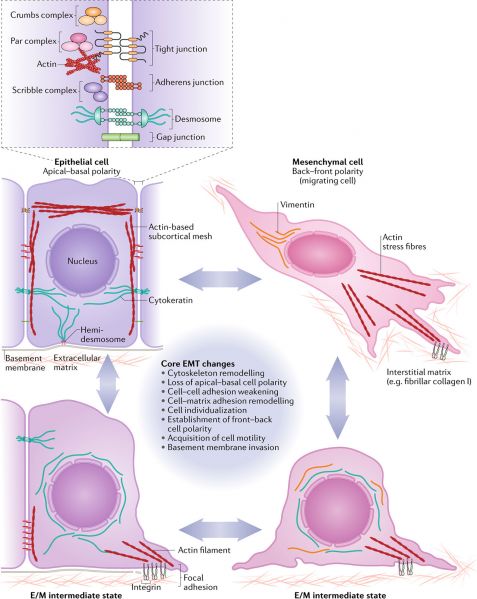
Epithelial Mesenchymal Transition
Various cellular features associated with an epithelial or a mesenchymal cell state are found in a range of combinations and to different degrees in cells in different developmental contexts. Epithelial cells are connected with each other via a variety of epithelial cell junctions, including adherens junctions, desmosomes, gap junctions and tight junctions. Adherens junctions are connected to cortical actin bundles, while desmosomes are linked with cytokeratin intermediate filaments. Tight junctions are localized at the apical-lateral contact points in order to help maintain epithelial polarity. Apical–basal polarity guides proper organization of the tight junctions, adherens junctions and desmosomes in epithelial cells. Polarity complexes, including the Par, Crumbs and Scribble complexes, define the apical versus basolateral domains of an epithelial cell. Epithelial cells are attached to the underlying basement membrane via hemidesmosomes, which contain integrin to allow binding to the basement membrane and are also linked to cytokeratins inside the cell. By contrast, mesenchymal cells do not contain functional epithelial junctions and present a back–front polarity in their actin stress fibres. Mesenchymal cells contain vimentin-based intermediate filaments and utilize integrin-containing focal adhesions to attach to the extracellular matrix. The accumulated loss or gain of epithelial/mesenchymal (E/M) characteristics pushes a cell towards various intermediate states (bottom left and right) in a fluid and reversible manner, between a complete epithelial (middle left) and a complete mesenchymal (middle right) state. EMT, epithelial–mesenchymal transition.
Reference
Yang J, Antin P, Berx G, Blanpain C, Brabletz T, Bronner M, Campbell K, Cano A, Casanova J, Christofori G, Dedhar S, Derynck R, Ford HL, Fuxe J, García de Herreros A, Goodall GJ, Hadjantonakis AK, Huang RJY, Kalcheim C, Kalluri R, Kang Y, Khew-Goodall Y, Levine H, Liu J, Longmore GD, Mani SA, Massagué J, Mayor R, McClay D, Mostov KE, Newgreen DF, Nieto MA, Puisieux A, Runyan R, Savagner P, Stanger B, Stemmler MP, Takahashi Y, Takeichi M, Theveneau E, Thiery JP, Thompson EW, Weinberg RA, Williams ED, Xing J, Zhou BP & Sheng G. (2020). Guidelines and definitions for research on epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. , , . PMID: 32300252 DOI.
Copyright
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 11:15, 23 April 2020 |  | 1,280 × 1,608 (323 KB) | Z8600021 (talk | contribs) | adjust image size |
| 11:12, 23 April 2020 |  | 1,713 × 2,152 (496 KB) | Z8600021 (talk | contribs) | ==Epithelial Mesenchymal Transition== Various cellular features associated with an epithelial or a mesenchymal cell state are found in a range of combinations and to different degrees in cells in different developmental contexts. Epithelial cells are connected with each other via a variety of epithelial cell junctions, including adherens junctions, desmosomes, gap junctions and tight junctions. Adherens junctions are connected to cortical actin bundles, while desmosomes are linked with cytok... |
You cannot overwrite this file.
File usage
The following page uses this file: