File:Epididymis histology 02.jpg: Difference between revisions
From Embryology
mNo edit summary |
mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Ductulus Efferentes== | |||
* Spermatozoa pass via the tubuli recti (low columnar epithelium) and the rete testis (flattened or cuboidal epithelium) into numerous ductuli efferentes, which are lined by a columnar epithelium, which consists of both absorptive and ciliated cells. The height of the two cells types which form the epithelium of the ductuli efferentes is variable which gives the lumen a characteristic wavy outline. | * Spermatozoa pass via the tubuli recti (low columnar epithelium) and the rete testis (flattened or cuboidal epithelium) into numerous ductuli efferentes, which are lined by a columnar epithelium, which consists of both absorptive and ciliated cells. The height of the two cells types which form the epithelium of the ductuli efferentes is variable which gives the lumen a characteristic wavy outline. | ||
The ductuli efferentes leave the testis and open into a common duct, the ductus epididymidis (about 6 m long!). It is lined by a very tall pseudostratified columnar epithelium. Most cells of the epithelium, also called principal cells, have long stereocilia. Stereocilia are non-motile structures, which in the EM resemble large microvilli. Towards the basal lamina we see a number of small nuclei, which belong to the basal cells of the ductus epididymidis. These cells regenerate the epithelium. | The ductuli efferentes leave the testis and open into a common duct, the ductus epididymidis (about 6 m long!). It is lined by a very tall pseudostratified columnar epithelium. Most cells of the epithelium, also called principal cells, have long stereocilia. Stereocilia are non-motile structures, which in the EM resemble large microvilli. Towards the basal lamina we see a number of small nuclei, which belong to the basal cells of the ductus epididymidis. These cells regenerate the epithelium. | ||
Revision as of 19:03, 27 May 2013
Ductulus Efferentes
- Spermatozoa pass via the tubuli recti (low columnar epithelium) and the rete testis (flattened or cuboidal epithelium) into numerous ductuli efferentes, which are lined by a columnar epithelium, which consists of both absorptive and ciliated cells. The height of the two cells types which form the epithelium of the ductuli efferentes is variable which gives the lumen a characteristic wavy outline.
The ductuli efferentes leave the testis and open into a common duct, the ductus epididymidis (about 6 m long!). It is lined by a very tall pseudostratified columnar epithelium. Most cells of the epithelium, also called principal cells, have long stereocilia. Stereocilia are non-motile structures, which in the EM resemble large microvilli. Towards the basal lamina we see a number of small nuclei, which belong to the basal cells of the ductus epididymidis. These cells regenerate the epithelium.
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 17:26, 27 May 2013 | 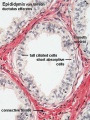 | 400 × 534 (71 KB) | Z8600021 (talk | contribs) |
You cannot overwrite this file.
File usage
The following 2 pages use this file: