|
|
| Line 6: |
Line 6: |
| ===Copyright=== | | ===Copyright=== |
| © 2014 American Academy of Neurology | | © 2014 American Academy of Neurology |
|
| |
| "Sensory ganglionitis, variably called ganglionopathy, is a disease of sensory neurons in dorsal root ganglia. Major forms of these diseases are associated with neoplasm, Sjögren syndrome, and paraproteinemia or polyclonal gammopathy with or without known autoantibodies. Most cases follow subacute courses, but there are forms that develop chronically and acutely as well. Clinical signs seen include sensory ataxia exhibited by gait unsteadiness, a positive Romberg sign, reduced deep tendon reflexes, poor coordination, and pseudo-athetoid movements in the hands. Axonal degeneration warrants the treatment as early as possible. Early cases of immunologic origin that are immune-mediated may respond to plasmapheresis and immunosuppression. Differential diagnoses include environmental and industrial intoxication and adverse effects of antineoplastic and antibiotic drugs. The term “sensory neuronopathy” or “ganglionitis” refers to disorders of small neurons, larger neurons, and/or neurons of both sizes in the sensory ganglia."
| |
|
| |
|
| {{Student image 2018}} | | {{Student image 2018}} |
Latest revision as of 15:06, 15 October 2018
Legend
Reference
Szmulewicz DJ, McLean CA, Rodriguez ML, Chancellor AM, Mossman S, Lamont D, Roberts L, Storey E & Halmagyi GM. (2014). Dorsal root ganglionopathy is responsible for the sensory impairment in CANVAS. Neurology , 82, 1410-5. PMID: 24682971 DOI.
Copyright
© 2014 American Academy of Neurology
Template:Student image 2018
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment |
|---|
| current | 07:02, 28 August 2018 | 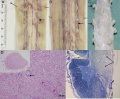 | 660 × 544 (152 KB) | Z5229399 (talk | contribs) | |
You cannot overwrite this file.
File usage
The following page uses this file:
This file contains additional information, probably added from the digital camera or scanner used to create or digitise it.
If the file has been modified from its original state, some details may not fully reflect the modified file.
