File:Chicken- neural Wnt expression.jpg: Difference between revisions
(==Chicken dorsalmost expression - Wnt1 and Wnt6== (A-G) Expression of Wnt1 (A-F) and Wnt6 (G-L) in HH13 (G,J), HH14 (A,D), HH15 (H,K), HH16 (B,E), HH19 (I,L) and HH20 (C,F) chick embryo brains. Lateral (A-C,G-I) and dorsal (D-F,J-L) views are shown; an) |
mNo edit summary |
||
| (One intermediate revision by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
Abbreviations: di, diencephalon; hb, hindbrain; hy, hypothalamus; mb, midbrain; tel, telencephalon. | Abbreviations: di, diencephalon; hb, hindbrain; hy, hypothalamus; mb, midbrain; tel, telencephalon. | ||
:"The forebrain is exposed to a multitude of Wnts and Wnt inhibitors that are expressed in a highly dynamic and complex fashion, precluding simple correlative conclusions about their respective functions or signalling mechanisms. In various biological systems, Wnts are antagonised by Shh signalling. By demonstrating that Wnt4 expression in the thalamus is repressed by Shh from the ZLI we reveal an additional level of interaction between these two pathways and provide an example for the cross-regulation between patterning centres during forebrain regionalisation." | :"The forebrain is exposed to a multitude of Wnts and Wnt inhibitors that are expressed in a highly dynamic and complex fashion, precluding simple correlative conclusions about their respective functions or signalling mechanisms. In various biological systems, Wnts are antagonised by Shh signalling. By demonstrating that Wnt4 expression in the {{thalamus}} is repressed by Shh from the ZLI we reveal an additional level of interaction between these two pathways and provide an example for the cross-regulation between patterning centres during forebrain regionalisation." | ||
==Reference== | ==Reference== | ||
{{#pmid:19732418}} | |||
Quinlan et al. Neural Development 2009 4:35 doi:10.1186/1749-8104-4-35 | |||
====Copyright==== | |||
© 2009 Quinlan et al; licensee BioMed Central Ltd. | © 2009 Quinlan et al; licensee BioMed Central Ltd. | ||
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. | This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. | ||
Original file name: Figure 1. 1749-8104-4-35-1.jpg http://www.neuraldevelopment.com/content/4/1/35/figure/F1 | |||
{{Footer}} | |||
[[Category:Chicken]] [[Category:Wnt]] [[Category:Neural]] | [[Category:Chicken]] [[Category:Wnt]] [[Category:Neural]] | ||
Latest revision as of 07:17, 14 October 2018
Chicken dorsalmost expression - Wnt1 and Wnt6
(A-G) Expression of Wnt1 (A-F) and Wnt6 (G-L) in HH13 (G,J), HH14 (A,D), HH15 (H,K), HH16 (B,E), HH19 (I,L) and HH20 (C,F) chick embryo brains.
Lateral (A-C,G-I) and dorsal (D-F,J-L) views are shown; anterior points to the right.
Note the broadening of Wnt1 expression at its anterior limit between HH14 and HH16 (arrowheads, A,B,D,E).
Note expression of Wnt1 anterior to the epiphysis (arrow) and along the dorsal border of the pallium (arrowhead) at HH19 (C,F). Note the expression of Wnt6 in the evaginating pineal gland at HH19 (arrow and inset, I).
Punctate expression of Wnt6 in (G-K) is likely to be in cranial ectoderm that was not completely removed from the neural tube [63]. Scale bars represent 0.2 mm.
Abbreviations: di, diencephalon; hb, hindbrain; hy, hypothalamus; mb, midbrain; tel, telencephalon.
- "The forebrain is exposed to a multitude of Wnts and Wnt inhibitors that are expressed in a highly dynamic and complex fashion, precluding simple correlative conclusions about their respective functions or signalling mechanisms. In various biological systems, Wnts are antagonised by Shh signalling. By demonstrating that Wnt4 expression in the thalamus is repressed by Shh from the ZLI we reveal an additional level of interaction between these two pathways and provide an example for the cross-regulation between patterning centres during forebrain regionalisation."
Reference
Quinlan R, Graf M, Mason I, Lumsden A & Kiecker C. (2009). Complex and dynamic patterns of Wnt pathway gene expression in the developing chick forebrain. Neural Dev , 4, 35. PMID: 19732418 DOI.
Quinlan et al. Neural Development 2009 4:35 doi:10.1186/1749-8104-4-35
Copyright
© 2009 Quinlan et al; licensee BioMed Central Ltd. This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Original file name: Figure 1. 1749-8104-4-35-1.jpg http://www.neuraldevelopment.com/content/4/1/35/figure/F1
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, April 16) Embryology Chicken- neural Wnt expression.jpg. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/File:Chicken-_neural_Wnt_expression.jpg
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 14:44, 29 September 2010 | 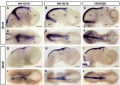 | 600 × 424 (55 KB) | S8600021 (talk | contribs) | ==Chicken dorsalmost expression - Wnt1 and Wnt6== (A-G) Expression of Wnt1 (A-F) and Wnt6 (G-L) in HH13 (G,J), HH14 (A,D), HH15 (H,K), HH16 (B,E), HH19 (I,L) and HH20 (C,F) chick embryo brains. Lateral (A-C,G-I) and dorsal (D-F,J-L) views are shown; an |
You cannot overwrite this file.
File usage
The following 2 pages use this file: