File:CRISPR Cas9 interaction with target DNA.jpg: Difference between revisions
mNo edit summary |
mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==CRISPR Cas9 interaction with target DNA== | ==CRISPR Cas9 interaction with target DNA== | ||
The CRISPR/Cas9 complex of Streptococcus pyogenes consists of the Cas9 protein (in gray) and a guide RNA that is a chimera of natural crRNA and tracRNA (in orange). | The CRISPR/Cas9 complex of Streptococcus pyogenes consists of the '''Cas9 protein''' (in gray) and a '''guide RNA''' that is a chimera of natural crRNA and tracRNA (in orange). | ||
The targeting sequence at the 5′end of the guide RNA base-pairs with complementary sequences on the target DNA (in blue); the targeting sequence is 20 nucleotides long, but may be shortened to increase specificity (the addition of 1 to 2 unpaired nucleotides at the 5′ end is also tolerated). | The targeting sequence at the 5′end of the guide RNA base-pairs with complementary sequences on the target DNA (in blue); the targeting sequence is 20 nucleotides long, but may be shortened to increase specificity (the addition of 1 to 2 unpaired nucleotides at the 5′ end is also tolerated). | ||
Revision as of 09:25, 26 March 2015
CRISPR Cas9 interaction with target DNA
The CRISPR/Cas9 complex of Streptococcus pyogenes consists of the Cas9 protein (in gray) and a guide RNA that is a chimera of natural crRNA and tracRNA (in orange).
The targeting sequence at the 5′end of the guide RNA base-pairs with complementary sequences on the target DNA (in blue); the targeting sequence is 20 nucleotides long, but may be shortened to increase specificity (the addition of 1 to 2 unpaired nucleotides at the 5′ end is also tolerated).
The presence of a PAM (protospacer adjacent motif, NGG for Streptococcus pyogenes), located immediately downstream of the 20-nucleotide sequence targeted by the guide RNA, is also essential for target recognition and cleavage.
The PAM sequence does not have a counterpart on the guide RNA. Following recognition of the PAM and base-pairing between the guide RNA and the target,
Cas9 cleaves each of the target DNA strands a few nucleotides upstream of the PAM (red arrowheads). Each strand is cleaved by a different nuclease domain present in Cas9 (HNH and RuvC domains). These domains have been mutated independently to generate Cas9 nickases.
Reference
<pubmed>25699168</pubmed>| Evodevo.
Copright
© 2014 Gilles and Averof; licensee BioMed Central Ltd. This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly credited. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
Gilles and Averof EvoDevo 2014 5:43 doi:10.1186/2041-9139-5-43 Text above from original figure legend.
2041-9139-5-43-2.jpg
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 09:13, 26 March 2015 | 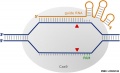 | 600 × 366 (28 KB) | Z8600021 (talk | contribs) | ==CRISPR Cas9 interaction with target DNA== 2041-9139-5-43-2.jpg |
You cannot overwrite this file.
File usage
The following 3 pages use this file: