File:Bovine morula 01.jpg: Difference between revisions
mNo edit summary |
|||
| (3 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
A Arrest and death of early blastomeres during the first four cleavage cycles. Maximum intensity z-projections of optical serial sections of embryos examined at day 4. Many embryos show large early blastomeres that are arrested at interphase (asterisks) or prophase (arrow heads) or already show clear signs of cell death: DAPI staining reveals variably sized and irregularly shaped clumps of highly condensed chromatin (large arrows). Notably, frequent findings are remnants of mitotic chromosome structures (small arrows). | A Arrest and death of early blastomeres during the first four cleavage cycles. Maximum intensity z-projections of optical serial sections of embryos examined at day 4. Many embryos show large early blastomeres that are arrested at interphase (asterisks) or prophase (arrow heads) or already show clear signs of cell death: DAPI staining reveals variably sized and irregularly shaped clumps of highly condensed chromatin (large arrows). Notably, frequent findings are remnants of mitotic chromosome structures (small arrows). | ||
The embryos were fixed and mounted on coverslips in such a way that the three-dimensional structure was maintained. DNA staining with DAPI is shown in white, f-actin filaments (phalloidin-TRITC) in orange. Scale bars represent 100 µm (overviews) or 10 µm (details). | The embryos were fixed and mounted on coverslips in such a way that the three-dimensional structure was maintained. DNA staining with DAPI is shown in white, f-actin filaments (phalloidin-TRITC) in orange. Scale bars represent 100 µm (overviews) or 10 µm (details). | ||
:{{Bovine Blastocyst Links}} | |||
===Reference=== | ===Reference=== | ||
{{#pmid:21811561}} | |||
====Copyright==== | |||
© 2011 Leidenfrost et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited. | |||
Figure 2. CLSM analysis (Panel cropped and resized from full figure) | |||
{{Footer}} | |||
[[Category:Bovine]] [[Category:Morula]] | [[Category:Bovine]] [[Category:Morula]] | ||
Latest revision as of 14:06, 14 November 2018
Bovine Morula
A Arrest and death of early blastomeres during the first four cleavage cycles. Maximum intensity z-projections of optical serial sections of embryos examined at day 4. Many embryos show large early blastomeres that are arrested at interphase (asterisks) or prophase (arrow heads) or already show clear signs of cell death: DAPI staining reveals variably sized and irregularly shaped clumps of highly condensed chromatin (large arrows). Notably, frequent findings are remnants of mitotic chromosome structures (small arrows).
The embryos were fixed and mounted on coverslips in such a way that the three-dimensional structure was maintained. DNA staining with DAPI is shown in white, f-actin filaments (phalloidin-TRITC) in orange. Scale bars represent 100 µm (overviews) or 10 µm (details).
- Links: Image - Morula and Blastocyst | Morula A | Blastocyst F | Blastocyst G | Bovine Development | Morula | Blastocyst
Reference
Leidenfrost S, Boelhauve M, Reichenbach M, Güngör T, Reichenbach HD, Sinowatz F, Wolf E & Habermann FA. (2011). Cell arrest and cell death in mammalian preimplantation development: lessons from the bovine model. PLoS ONE , 6, e22121. PMID: 21811561 DOI.
Copyright
© 2011 Leidenfrost et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Figure 2. CLSM analysis (Panel cropped and resized from full figure)
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, April 19) Embryology Bovine morula 01.jpg. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/File:Bovine_morula_01.jpg
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 13:33, 4 November 2011 | 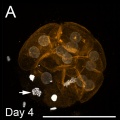 | 800 × 802 (84 KB) | S8600021 (talk | contribs) | ==Bovine Morula== A–F: Arrest and death of early blastomeres during the first four cleavage cycles. A–D: Maximum intensity z-projections of optical serial sections of embryos examined at day 4 (A, B) or day 5 (C, D). Many embryos show large early b |
You cannot overwrite this file.
File usage
The following 2 pages use this file: