File:Bone marrow histology 02.jpg: Difference between revisions
From Embryology
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (5 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Bone Marrow Histology== | ==Bone Marrow Histology== | ||
See matching field image showing [[:File:Bone marrow histology 01.jpg|adipocytes and blood sinusoids]]. | |||
===Megakaryoblast=== | ===Megakaryoblast=== | ||
* precursor of megakaryocyte. | |||
* earliest identifiable precursor in the thrombocytic series. | |||
* matures to form the promegakaryocyte. | |||
===Megakaryocyte=== | ===Megakaryocyte=== | ||
* largest cells observed in the bone marrow. | * largest cells observed in the bone marrow. | ||
| Line 8: | Line 11: | ||
* develop through a process called endoreduplication, which forms cells with 16N and 32N chromosomal content. | * develop through a process called endoreduplication, which forms cells with 16N and 32N chromosomal content. | ||
* large amount of DNA increases protein production and cytoplasm volume. | * large amount of DNA increases protein production and cytoplasm volume. | ||
* platelets form by pinching off from the cell surface. | * platelets begin to form by pinching off from the cell surface. | ||
===Thrombocyte=== | |||
* platelets form by pinching off from the cell surface of a megakaryocytic. | |||
** not easily seen in bone marrow, visible in blood. | |||
* cell fragment ( 2-3 microns in diameter) with 5-9 day lifespan. | |||
* normal range in blood 150,000-450,000/mm<sup>3</sup> (ml) | |||
* abnormal levels in bone marrow or blood disorders. | |||
{{Bone Marrow Histology}} | {{Bone Marrow Histology}} | ||
{{Blue Histology}} | {{Blue Histology}} | ||
Latest revision as of 08:41, 25 February 2012
Bone Marrow Histology
See matching field image showing adipocytes and blood sinusoids.
Megakaryoblast
- precursor of megakaryocyte.
- earliest identifiable precursor in the thrombocytic series.
- matures to form the promegakaryocyte.
Megakaryocyte
- largest cells observed in the bone marrow.
- responsible for platelet production.
- develop through a process called endoreduplication, which forms cells with 16N and 32N chromosomal content.
- large amount of DNA increases protein production and cytoplasm volume.
- platelets begin to form by pinching off from the cell surface.
Thrombocyte
- platelets form by pinching off from the cell surface of a megakaryocytic.
- not easily seen in bone marrow, visible in blood.
- cell fragment ( 2-3 microns in diameter) with 5-9 day lifespan.
- normal range in blood 150,000-450,000/mm3 (ml)
- abnormal levels in bone marrow or blood disorders.
- Bone Marrow Histology: Blood Development | Marrow overview | Megakaryocyte | Megakaryocyte detail | Myelocyte | Normoblast | Reticulocyte | Blood Histology | Bone Development | Category:Blood
Links: Histology | Histology Stains | Blue Histology images copyright Lutz Slomianka 1998-2009. The literary and artistic works on the original Blue Histology website may be reproduced, adapted, published and distributed for non-commercial purposes. See also the page Histology Stains.
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, April 16) Embryology Bone marrow histology 02.jpg. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/File:Bone_marrow_histology_02.jpg
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 07:28, 25 February 2012 | 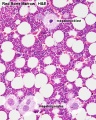 | 480 × 600 (109 KB) | Z8600021 (talk | contribs) | ==Bone Marrow Histology== Bone marrow histology 01.jpg {{Bone Marrow Histology}} {{Blue Histology}} |
You cannot overwrite this file.