File:Blood-brain barrier cartoon.jpg: Difference between revisions

Original file (765 × 1,000 pixels, file size: 75 KB, MIME type: image/jpeg)
mNo edit summary |
m (→Reference) |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
Astrocytes extend its end-feet and establish a close interaction with endothelial cells through transmembrane proteins, such as aquaporins. Astrocytes also connect with pericytes and neurons and together regulate BBB maintenance and function. The interaction of the cell components of the NVU with neurons and microglia can influence barrier function. | Astrocytes extend its end-feet and establish a close interaction with endothelial cells through transmembrane proteins, such as aquaporins. Astrocytes also connect with pericytes and neurons and together regulate BBB maintenance and function. The interaction of the cell components of the NVU with neurons and microglia can influence barrier function. | ||
:'''Links:''' [[Neural_-_Vascular_Development#Blood-Brain_Barrier|Blood-Brain Barrier]] | [[Neural - Vascular Development]] | [[:File:Blood-brain barrier EM01.jpg|Blood-brain barrier EM]] | |||
===Terms=== | ===Terms=== | ||
| Line 21: | Line 22: | ||
===Reference=== | ===Reference=== | ||
{{#pmid:28484368}} | |||
Development and Function of the Blood-Brain Barrier in the Context of Metabolic Control. Haddad-Tóvolli R, Dragano NRV, Ramalho AFS, Velloso LA. Front Neurosci. 2017 Apr 21;11:224. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2017.00224. eCollection 2017. Review. [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28484368 PMID: 28484368] http://journal.frontiersin.org/article/10.3389/fnins.2017.00224/full | Development and Function of the Blood-Brain Barrier in the Context of Metabolic Control. Haddad-Tóvolli R, Dragano NRV, Ramalho AFS, Velloso LA. Front Neurosci. 2017 Apr 21;11:224. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2017.00224. eCollection 2017. Review. [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28484368 PMID: 28484368] http://journal.frontiersin.org/article/10.3389/fnins.2017.00224/full | ||
====Copyright==== | ====Copyright==== | ||
© 2017 Haddad-Tóvolli, Dragano, Ramalho and Velloso. This is an open- access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) or licensor are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms. | © 2017 Haddad-Tóvolli, Dragano, Ramalho and Velloso. This is an open- access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) or licensor are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms. | ||
Latest revision as of 19:57, 27 March 2018
Neurovascular unit (NVU)
A layer of brain endothelial cells connected by tight junctions forms the blood-brain barrier (BBB). The intimate contact of these specialized endothelial cells with different cell types constitutes the NVU.
A basement membrane embeds the brain endothelial cells, the pericytes, and astrocytes.
In areas where the basement membrane is absent, brain endothelial cells and pericytes connect through peg-socket junctions.
Astrocytes extend its end-feet and establish a close interaction with endothelial cells through transmembrane proteins, such as aquaporins. Astrocytes also connect with pericytes and neurons and together regulate BBB maintenance and function. The interaction of the cell components of the NVU with neurons and microglia can influence barrier function.
Terms
- aquaporins - transmembrane proteins that form channels for water and small solutes transfer across the membrane.
- astrocytes - glial cells named by their "star-like" branching appearance, are the most abundant cells in the brain.
- basement membrane - specialised extracellular matrix that underlies all epithelia.
- end-feet - specialised cellular club-shaped endings, often associated with neural synapses, but also found in other cell junctions.
- endothelial cells - squamous epithelial cells that line all blood vessels.
- pericytes - (Rouget cells) cells located at the abluminal surface of microvessels close to endothelial cells, mainly found associated with CNS vessels and involved in vessel formation, remodeling and stabilization.
Reference
Haddad-Tóvolli R, Dragano NRV, Ramalho AFS & Velloso LA. (2017). Development and Function of the Blood-Brain Barrier in the Context of Metabolic Control. Front Neurosci , 11, 224. PMID: 28484368 DOI.
Development and Function of the Blood-Brain Barrier in the Context of Metabolic Control. Haddad-Tóvolli R, Dragano NRV, Ramalho AFS, Velloso LA. Front Neurosci. 2017 Apr 21;11:224. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2017.00224. eCollection 2017. Review. PMID: 28484368 http://journal.frontiersin.org/article/10.3389/fnins.2017.00224/full
Copyright
© 2017 Haddad-Tóvolli, Dragano, Ramalho and Velloso. This is an open- access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) or licensor are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, April 24) Embryology Blood-brain barrier cartoon.jpg. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/File:Blood-brain_barrier_cartoon.jpg
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 10:05, 27 May 2017 |  | 765 × 1,000 (75 KB) | Z8600021 (talk | contribs) | |
| 10:04, 27 May 2017 | 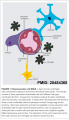 | 1,013 × 1,765 (238 KB) | Z8600021 (talk | contribs) | ==Neurovascular unit (NVU)== A layer of brain endothelial cells connected by tight junctions forms the blood-brain barrier. The intimate contact of these specialized endothelial cells with different cell types constitutes the NVU. A basement membrane... |
You cannot overwrite this file.
File usage
The following 2 pages use this file: