File:Autosomal recessive inheritance.jpg: Difference between revisions
mNo edit summary |
|||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
* '''Tay-Sachs disease''' (More? {{neural}}} | * '''Tay-Sachs disease''' (More? {{neural}}} | ||
Preconception carrier tests are available for some autosomal recessive (AR) diseases. These tests were initially developed for autosomal recessive diseases that were frequent in specific ethnic groups: | |||
* Tay–Sachs disease - Ashkenazi Jews | |||
* hemoglobinopathies - Mediterranean and African populations | |||
* cystic fibrosis - European-derived populations | |||
| Line 15: | Line 21: | ||
:'''Links:''' [[ | :'''Links:''' [[Abnormal Development - Genetic|Genetic Abnormalities]] | {{Spermatozoa}} | {{Oocyte}} | [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez?db=pubmed&cmd=search&term=autosomal_inheritance Search Pubmed - autosomal inheritance] | ||
===Reference=== | ===Reference=== | ||
Latest revision as of 11:19, 23 October 2018
Autosomal Recessive Inheritance
In this example, two unaffected parents each carry one copy of a gene mutation for an autosomal recessive disorder. They have one affected child and three unaffected children, two of which carry one copy of the gene mutation.
Examples of Autosomal Recessive Disease
- Cystic fibrosis (CF) (More? respiratory}
- Sickle cell anaemia (More? blood)
- Tay-Sachs disease (More? neural}
Preconception carrier tests are available for some autosomal recessive (AR) diseases. These tests were initially developed for autosomal recessive diseases that were frequent in specific ethnic groups:
- Tay–Sachs disease - Ashkenazi Jews
- hemoglobinopathies - Mediterranean and African populations
- cystic fibrosis - European-derived populations
- Inheritance Pattern images: Genetic Abnormalities | autosomal dominant | autosomal recessive | X-linked dominant (affected father) | X-Linked dominant (affected mother) | X-Linked recessive (affected father) | X-Linked recessive (carrier mother) | mitochondrial inheritance | Codominant inheritance | Genogram symbols | Genetics
Reference
Image Source: Genetics Home Reference. http://ghr.nlm.nih.gov/handbook/illustrations/autorecessive
Copyright
Government information at NLM Web sites is in the public domain. Public domain information may be freely distributed and copied, but it is requested that in any subsequent use the National Library of Medicine (NLM) be given appropriate acknowledgement. http://www.nlm.nih.gov/copyright.html
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, April 16) Embryology Autosomal recessive inheritance.jpg. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/File:Autosomal_recessive_inheritance.jpg
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 09:43, 12 May 2010 | 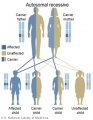 | 307 × 396 (65 KB) | S8600021 (talk | contribs) | Autosomal Recessive Inheritance In this example, two unaffected parents each carry one copy of a gene mutation for an autosomal recessive disorder. They have one affected child and three unaffected children, two of which carry one copy of the gene mutati |
You cannot overwrite this file.
File usage
The following 15 pages use this file:
- 2010 BGD Practical 3 - Gametogenesis
- 2011 Lab 1 - Gametogenesis
- A
- ANAT2341 Lab 1 - Gametogenesis
- ANAT2341 Lab 3 2013
- Abnormal Development - Genetic
- B
- BGDA Practical 3 - Gametogenesis
- Fetal Cells in Maternal Blood
- Genome Sequencing
- Molecular Development - Genetics
- Neonatal Diagnosis
- Non-Invasive Prenatal Testing
- Preimplantation Genetic Diagnosis
- Prenatal Diagnosis