File:Adult hearing embryonic origins.jpg
From Embryology
Size of this preview: 800 × 540 pixels. Other resolution: 1,000 × 675 pixels.
Original file (1,000 × 675 pixels, file size: 80 KB, MIME type: image/jpeg)
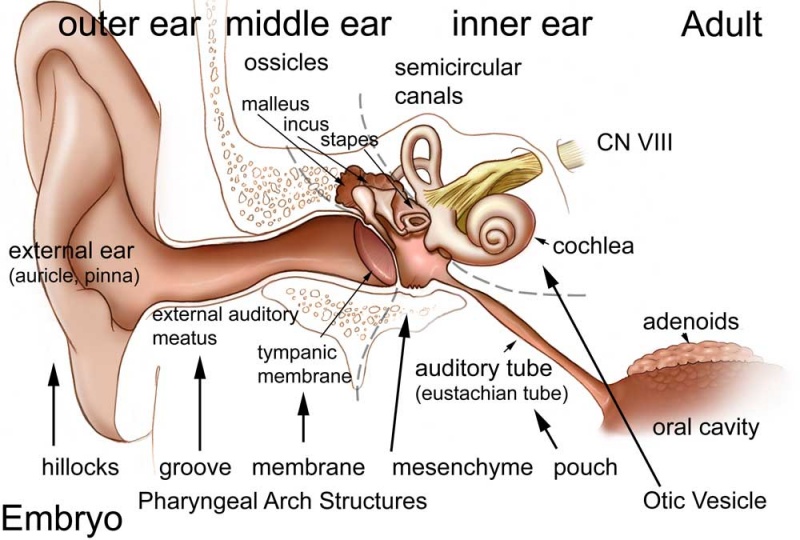
Adult Hearing Embryonic Origins
Many different embryonic components contribute to the sensory structures required for hearing. It is always considered/divided in terms of the 3 main divisions (external, middle and inner), each of which have their own separate components from different embryonic origins.
The complexity and time course of development leads to many associated abnormalities.
External Ear
- Auricle - Pharyngeal Arches 1 and 2 (ectoderm, mesoderm)
- form from 6 hillocks (week 5) 3 on each of arch 1 and 2
- External Auditory Meatus - Pharyngeal Arch 1 groove or cleft (ectoderm)
- Tympanic Membrane - Pharyngeal Arch 1 membrane (ectoderm, mesoderm, endoderm)
Middle Ear
- Middle Ear Ossicles
- Malleus and incus - Pharyngeal Arch 1 cartilage Neural crest (ectoderm)
- Stapes - Pharyngeal Arch 2 cartilage Neural crest (ectoderm)
- Middle Ear Muscles
- Tensor tympani - Pharyngeal Arch 1 (mesoderm)
- Stapedius - Pharyngeal Arch 2 (mesoderm)
- Middle ear cavity - Pharyngeal Arch 1 pouch (endoderm)
Inner Ear
- Inner Ear Labyrinth
- Cochlea - Otic vesicle - Otic placode (ectoderm)
- Semicircular canals - Otic vesicle - Otic placode (ectoderm)
- Saccule and utricle - Otic vesicle - Otic placode (ectoderm)
- Cranial Nerve VIII
- Auditory component - Otic vesicle and neural crest (ectoderm)
- Vestibular component - Otic vesicle and neural crest (ectoderm)
Related images: Image - Adult hearing embryonic origins | Image - without embryology
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 23:55, 27 September 2009 |  | 1,000 × 675 (80 KB) | S8600021 (talk | contribs) |
You cannot overwrite this file.
File usage
The following 15 pages use this file:
- 2009 Lecture 17
- 2010 Lecture 17
- 2011 Lab 10 - Postnatal
- AACP Meeting 2013 - Face Embryology
- ANAT2341 Lab 10 - Postnatal
- Abnormal Development - Thalidomide
- BGDB Face and Ear - Postnatal
- BGD Lecture - Face and Ear Development
- Hearing - Inner Ear Development
- Hearing - Middle Ear Development
- Hearing - Outer Ear Development
- Lecture - Head Development
- Lecture - Sensory Development
- Neural - Cranial Nerve Development
- Sensory - Hearing and Balance Development