Endocrine - Placenta Development
From Embryology
Introduction
Lecture - Placenta Development | UNSW Embryology - Endocrine Placenta
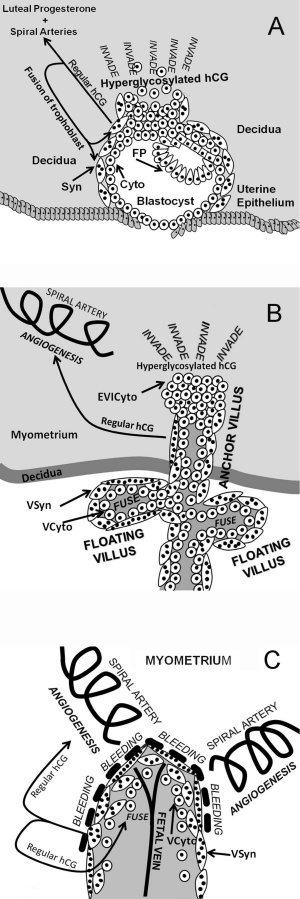
- Human chorionic gonadotrophin (hCG) - like leutenizing hormone, supports corpus luteum in ovary, pregnant state rather than menstrual, maternal urine in some pregnancy testing
- Human chorionic somatommotropin (hCS) - or placental lactogen stimulate (maternal) mammary development
- Human chorionic thyrotropin (hCT)
- Human chorionic corticotropin (hCACTH)
- progesterone and estrogens - support maternal endometrium
- Relaxin
- Placenta - Maternal (decidua) and Fetal (trophoblastic cells, extraembryonic mesoderm) components
- Endocrine function - maternal and fetal precursors, synthesis and secretion
- Protein Hormones - chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), chorionic somatomammotropin (hCS) or placental lactogen (hPL), chorionic thyrotropin (hCT), chorionic corticotropin (hCACTH)
- hCG - up to 20 weeks, fetal adrenal cortex growth and maintenance
- hCS – rise through pregnancy, stimulates maternal metabolic processes, breast growth
- Steroid Hormones - progesterone (maintains pregnancy), estrogens (fetal adrenal/placenta)
- Protein Hormones - chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), chorionic somatomammotropin (hCS) or placental lactogen (hPL), chorionic thyrotropin (hCT), chorionic corticotropin (hCACTH)