Endocrine - Gonad Development
From Embryology
Gonad
Lecture - Genital Development | UNSW Embryology - Gonads see also previous Sexual Differentiation Lecture/Practical
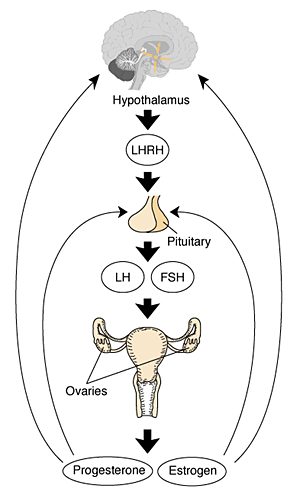
HPG Axis - Endocrinology - Simplified diagram of the actions of gonadotrophins
Gonad Development
- mesoderm - mesothelium and underlying mesenchyme, primordial germ cells
- Gonadal ridge - mesothelium thickening, medial mesonephros
- Primordial Germ cells - yolk sac, to mesentery of hindgut, to genital ridge of developing kidney
Differentiation
- testis-determining factor (TDF) from Y chromosome: presence (testes), absence (ovaries)
Testis
- 8 Weeks, mesenchyme, interstitial cells (of Leydig) secrete testosterone, androstenedione
- 8 to 12 Weeks - hCG stimulates testosterone production
- Sustentacular cells - produce anti-mullerian hormone to puberty
Ovary
- X chromosome genes regulate ovary development