Developmental Signals - TGF-beta: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Introduction== | ==Introduction== | ||
Transforming Growth Factor-beta (TGF-β) | |||
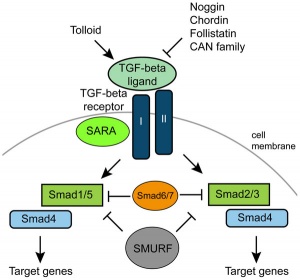
[[File:TGF-beta signaling pathway.jpg|thumb|TGF-beta signaling pathway<ref>Pang K, Ryan JF, Baxevanis AD, Martindale MQ (2011) '''Evolution of the TGF-β Signaling Pathway and Its Potential Role in the Ctenophore, Mnemiopsis leidyi.''' PLoS ONE 6(9): e24152 [http://www.plosone.org/article/info%3Adoi%2F10.1371%2Fjournal.pone.0024152 PLoS ONE]</ref> | [[File:TGF-beta signaling pathway.jpg|thumb|TGF-beta signaling pathway<ref>Pang K, Ryan JF, Baxevanis AD, Martindale MQ (2011) '''Evolution of the TGF-β Signaling Pathway and Its Potential Role in the Ctenophore, Mnemiopsis leidyi.''' PLoS ONE 6(9): e24152 [http://www.plosone.org/article/info%3Adoi%2F10.1371%2Fjournal.pone.0024152 PLoS ONE]</ref> | ||
| Line 11: | Line 12: | ||
* <ref name="PMID20227380"><pubmed>20227380</pubmed></ref> | * <ref name="PMID20227380"><pubmed>20227380</pubmed></ref> | ||
|} | |} | ||
==Structure== | |||
The precursor protein has three distinct regions: | |||
# '''signal peptide''' - targets it to the endoplasmic reticulum and secretion | |||
# '''propeptide''' - or the latency associated peptide | |||
# '''mature peptide''' - cleaved from the precursor protein and is actively involved in signalling | |||
==Function== | ==Function== | ||
Revision as of 16:06, 10 September 2011
Introduction
Transforming Growth Factor-beta (TGF-β)
| Factor Links: AMH | hCG | BMP | sonic hedgehog | bHLH | HOX | FGF | FOX | Hippo | LIM | Nanog | NGF | Nodal | Notch | PAX | retinoic acid | SIX | Slit2/Robo1 | SOX | TBX | TGF-beta | VEGF | WNT | Category:Molecular |
Some Recent Findings
Structure
The precursor protein has three distinct regions:
- signal peptide - targets it to the endoplasmic reticulum and secretion
- propeptide - or the latency associated peptide
- mature peptide - cleaved from the precursor protein and is actively involved in signalling
Function
Signaling Pathway
(data from Expasy)
OMIM
About OMIM "Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man OMIM is a comprehensive, authoritative, and timely compendium of human genes and genetic phenotypes. The full-text, referenced overviews in OMIM contain information on all known mendelian disorders and over 12,000 genes. OMIM focuses on the relationship between phenotype and genotype. It is updated daily, and the entries contain copious links to other genetics resources." OMIM
References
Reviews
Articles
<pubmed>17077151</pubmed>
Search PubMed: TGF-beta
External Links
External Links Notice - The dynamic nature of the internet may mean that some of these listed links may no longer function. If the link no longer works search the web with the link text or name. Links to any external commercial sites are provided for information purposes only and should never be considered an endorsement. UNSW Embryology is provided as an educational resource with no clinical information or commercial affiliation.
The nature of the internet is that some links may change over time. If the link no longer functions, search the internet using the link term.
Glossary Links
- Glossary: A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | Numbers | Symbols | Term Link
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, April 18) Embryology Developmental Signals - TGF-beta. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/Developmental_Signals_-_TGF-beta
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G