Developmental Signals - Sox: Difference between revisions
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
The SRY (480000) and SOX proteins share a DNA-binding domain known as the HMG box, defined by a 79-amino acid region. All SOX proteins have a single HMG box and bind linear DNA in a sequence-specific manner, resulting in the bending of DNA through large angles. Bending causes the DNA helix to open for some distance, which may affect binding and interactions of other transcription factors. SOX1, SOX2 (184429), and SOX3 (313430) show the closest homology to SRY. They share maximum homology within the HMG domain and are expressed mainly in the developing nervous system of the mouse (Collignon et al., 1996). These genes share significant homology outside the HMG box also and are highly conserved throughout their evolution. | The SRY (480000) and SOX proteins share a DNA-binding domain known as the HMG box, defined by a 79-amino acid region. All SOX proteins have a single HMG box and bind linear DNA in a sequence-specific manner, resulting in the bending of DNA through large angles. Bending causes the DNA helix to open for some distance, which may affect binding and interactions of other transcription factors. SOX1, SOX2 (184429), and SOX3 (313430) show the closest homology to SRY. They share maximum homology within the HMG domain and are expressed mainly in the developing nervous system of the mouse (Collignon et al., 1996). These genes share significant homology outside the HMG box also and are highly conserved throughout their evolution. | ||
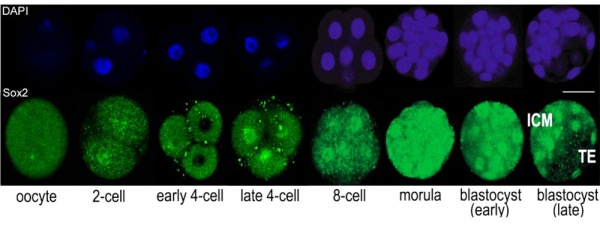
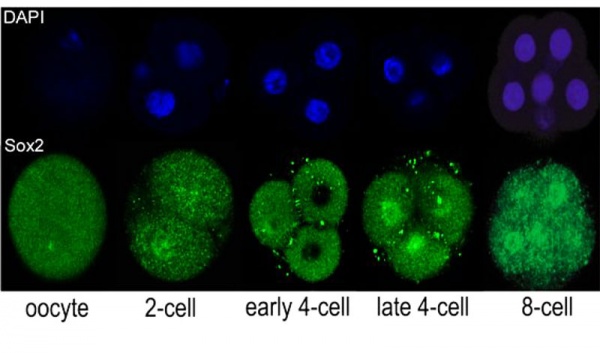
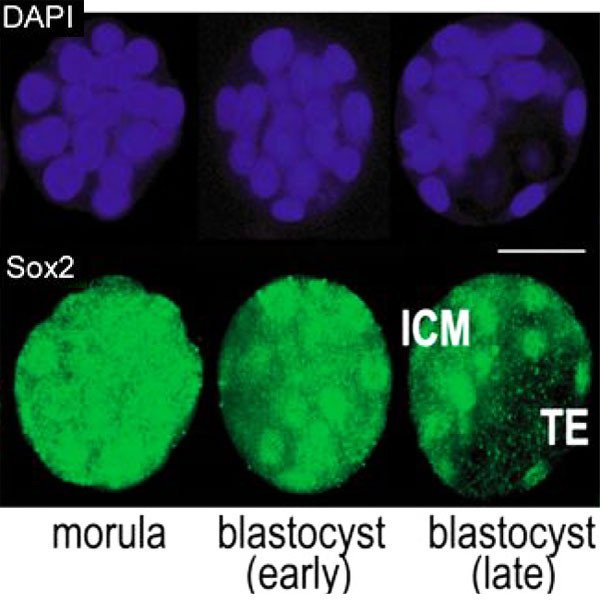
Sox2 is first expressed in very early (morula, blastocyst) development, and has also been identified as one of the 4 "Yamanaka Factors" required to generate an induced pluripotential stem cell (iPS cell). | Sox2 is first expressed in very early (morula, blastocyst) development, and has also been identified as one of the 4 "Yamanaka Factors" required to generate an induced pluripotential stem cell (iPS cell). It also forms a trimeric complex with OCT4, yet another "Yamanaka Factor". | ||
Revision as of 11:50, 10 October 2012
Introduction
The SRY (480000) and SOX proteins share a DNA-binding domain known as the HMG box, defined by a 79-amino acid region. All SOX proteins have a single HMG box and bind linear DNA in a sequence-specific manner, resulting in the bending of DNA through large angles. Bending causes the DNA helix to open for some distance, which may affect binding and interactions of other transcription factors. SOX1, SOX2 (184429), and SOX3 (313430) show the closest homology to SRY. They share maximum homology within the HMG domain and are expressed mainly in the developing nervous system of the mouse (Collignon et al., 1996). These genes share significant homology outside the HMG box also and are highly conserved throughout their evolution.
Sox2 is first expressed in very early (morula, blastocyst) development, and has also been identified as one of the 4 "Yamanaka Factors" required to generate an induced pluripotential stem cell (iPS cell). It also forms a trimeric complex with OCT4, yet another "Yamanaka Factor".
- Sox Links: Sox transcription factors cartoon | Image 1 - Preimplantation Mouse | Image 2 - Preimplantation Mouse | Image 3 - Preimplantation Mouse | Sox | Induced Stem Cells | Yamanaka Factors
| Factor Links: AMH | hCG | BMP | sonic hedgehog | bHLH | HOX | FGF | FOX | Hippo | LIM | Nanog | NGF | Nodal | Notch | PAX | retinoic acid | SIX | Slit2/Robo1 | SOX | TBX | TGF-beta | VEGF | WNT | Category:Molecular |
Some Recent Findings
|
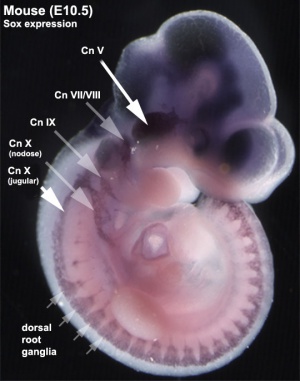
Early Mouse Expression
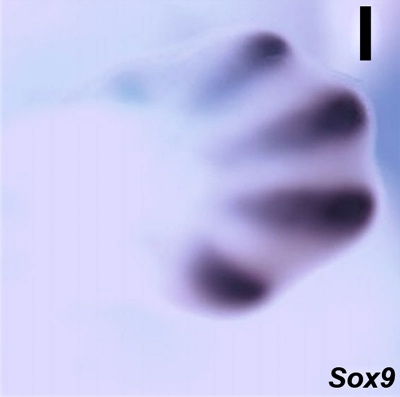
Limb Expression
Sox9 expression in E12.5 wild-type mouse embryonic forelimb.[3]
Function
Respiratory Development
Sox2
- regulates patterning of the anterior foregut into ventral (trachea) and dorsal (esophagus) fates
- endoderm expression during formation of foregut derivatives
- declines in regions undergoing lung bud morphogenesis
- declines in ventral region generating the trachea
- Links: Respiratory System Development | StemBook - Specification and patterning of the respiratory system
Signaling Pathway
(data from Expasy)
OMIM
About OMIM "Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man OMIM is a comprehensive, authoritative, and timely compendium of human genes and genetic phenotypes. The full-text, referenced overviews in OMIM contain information on all known mendelian disorders and over 12,000 genes. OMIM focuses on the relationship between phenotype and genotype. It is updated daily, and the entries contain copious links to other genetics resources." OMIM
References
- ↑ <pubmed>20704721</pubmed>| BMC Dev Biol.
- ↑ <pubmed>21103067</pubmed>| PMC2980489 | PLoS One.
- ↑ <pubmed>17194222</pubmed>| PMC1713256 | PLoS Genet.
Reviews
<pubmed></pubmed> <pubmed>21309066</pubmed> <pubmed>17584862</pubmed>
Search PubMed: Sox
External Links
The nature of the internet is that some links may change over time. If the link no longer functions, search the internet using the link term.
Glossary Links
- Glossary: A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | Numbers | Symbols | Term Link
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, April 19) Embryology Developmental Signals - Sox. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/Developmental_Signals_-_Sox
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G