Developmental Signals - Pax
| Embryology - 16 Apr 2024 |
|---|
| Google Translate - select your language from the list shown below (this will open a new external page) |
|
العربية | català | 中文 | 中國傳統的 | français | Deutsche | עִברִית | हिंदी | bahasa Indonesia | italiano | 日本語 | 한국어 | မြန်မာ | Pilipino | Polskie | português | ਪੰਜਾਬੀ ਦੇ | Română | русский | Español | Swahili | Svensk | ไทย | Türkçe | اردو | ייִדיש | Tiếng Việt These external translations are automated and may not be accurate. (More? About Translations) |
Introduction
The name derived from Drosophila gene "paired" (prd) with a box (homeodomain) domain. A transcription factor of the helix-turn-helix structural family, DNA binding, and activating gene expression. In human, there are nine member proteins from Pax1 to Pax9.
Pax6 has been identified as regulating development of the central nervous system, eyes, nose, pancreas and pituitary gland.
Developmental Functions: Mesoderm | Neural | Vision | Pancreas | Pituitary | Thymus
| Factor Links: AMH | hCG | BMP | sonic hedgehog | bHLH | HOX | FGF | FOX | Hippo | LIM | Nanog | NGF | Nodal | Notch | PAX | retinoic acid | SIX | Slit2/Robo1 | SOX | TBX | TGF-beta | VEGF | WNT | Category:Molecular |
Some Recent Findings
|
| More recent papers |
|---|
|
This table allows an automated computer search of the external PubMed database using the listed "Search term" text link.
More? References | Discussion Page | Journal Searches | 2019 References | 2020 References Search term: Development Pax <pubmed limit=5>Development Pax</pubmed> |
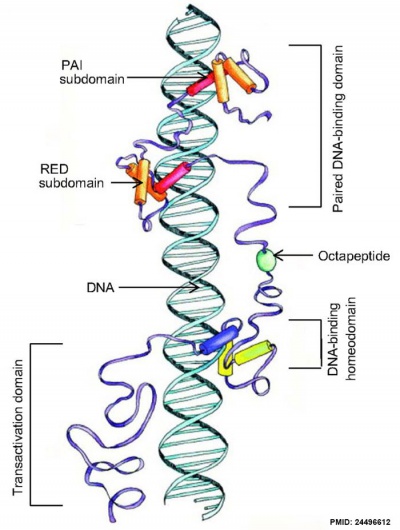
Transcription Factor
Pax and DNA molecular interaction[2]
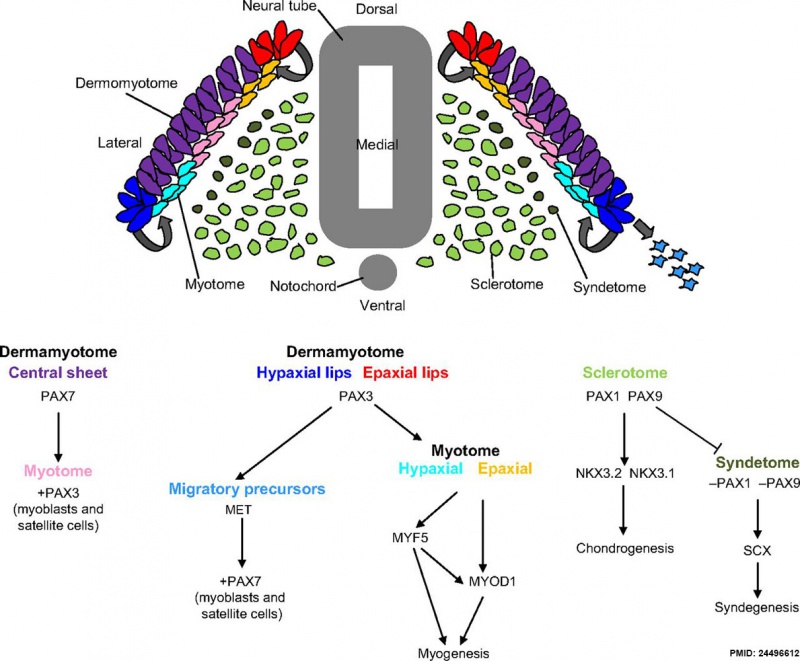
Mesoderm Development
Mesoderm Development and Pax[2]
Neural Development
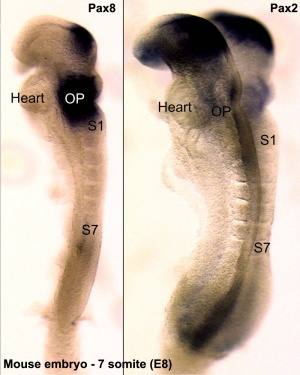
- Hoxd4 gene a direct target of Pax6[5]
- mouse embryo - Hoxd4 expression in rhombomere 7 and the spinal cord is reduced to some extent in the Pax6 mutant
- zebrafish embryo - double knockdown of pax6a and pax6b with MOs resulted in malformed rhombomere boundaries and an anteriorized hoxd4a expression border
- Pax3 is expressed in the somite, neural tube, and neural crest.
- Pax3 is required for enteric ganglia formation.[6]
- Pax2 and Pax5 in midbrain and cerebellum development.[7]
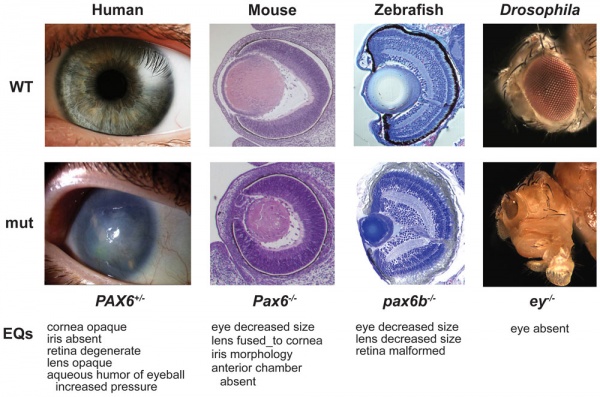
Vision Development
Pax6 mutation eye phenotypes[8]
Pancreas Development
- Pax6 acts in endocrine development in the pancreas as a glucagon gene transactivator role in alpha (α) cell development.
- Pax2 is also expressed in the pancreas.
- Pax4 is a regulator of pancreatic beta cell development.[9]
| Developmental Factors | |
|---|---|
|
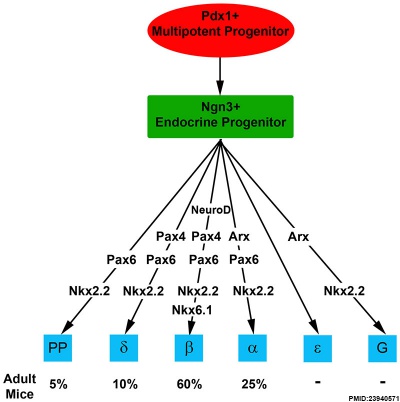
Molecular Development of Endocrine Pancreas Cells[10] |
- Links: Endocrine Pancreas
Thymus Development
Pax1 mouse KO thymus size reduction and impaired thymocyte maturation.
- Links: Thymus Pancreas
Structure
- tissue-specific transcriptional regulators
- contain a highly conserved DNA-binding domain with six alpha-helices (paired domain)
- a complete or residual homeodomain.
- 4 Groups: group I (Pax-1, 9), II (Pax-2, 5, 8), III (Pax-3, 7), and IV (Pax-4, 6)[11]
Mouse Expression
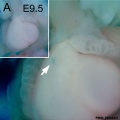
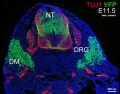
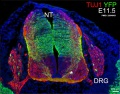
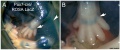
The following gallery is from a recent paper using a Pax7-cre/reporter mouse.[12]
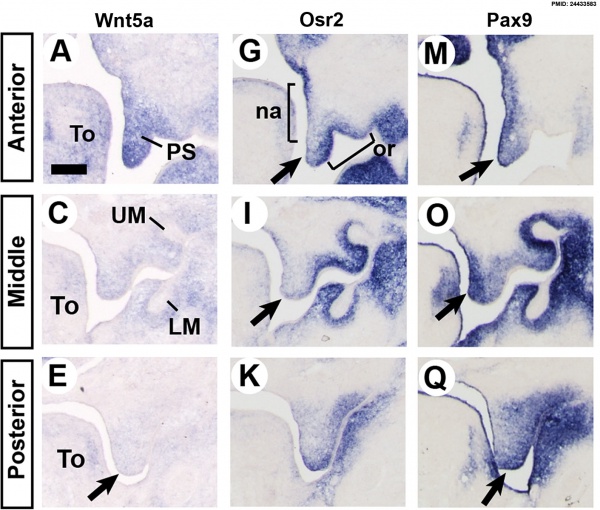
Mouse Palatal Shelf Wnt5a, Osr2 and Pax9 Expression.[13]
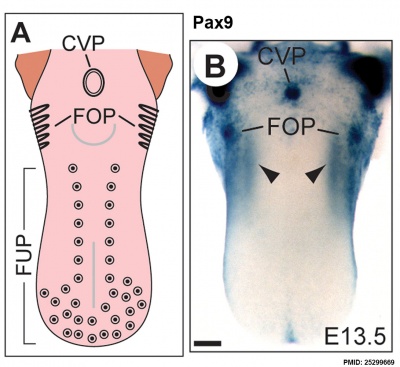
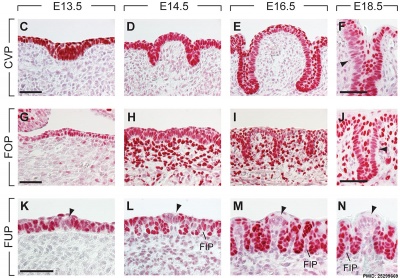
The following data is from a recent paper using a Pax9 reporter.[14]
Abnormalities
Associated with defects in each Pax protein or their signaling pathway.
Pax2
- renal-coloboma syndrome (RCS)
Pax3
- Waardenburg syndrome type 1 (WS1)
- Waardenburg syndrome type 3 (WS3)
- craniofacial-deafness-hand syndrome (CDHS)
- rhabdomyosarcoma type 2 (RMS2)
Pax5
- acute lymphoblastic leukemia
Pax6
A series of vision associated defects.
- aniridia (AN)
- Peters anomaly
- ectopia pupillae
- foveal hypoplasia
- autosomal dominant keratitis
- ocular coloboma
- coloboma of optic nerve
- bilateral optic nerve hypoplasia
- aniridia cerebellar ataxia and mental deficiency (ACAMD)
- Links: Vision Abnormalities
Pax7
- rhabdomyosarcoma type 2 (RMS2)
Pax8
- congenital hypothyroidism non-goitrous type 2 (CHNG2)
- Links:Thyroid Abnormalities
References
- ↑ <pubmed>9144207</pubmed>
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 <pubmed>24496612</pubmed>| Development
- ↑ <pubmed>20082710</pubmed>| BMC Dev. Biol.
- ↑ <pubmed>20727173</pubmed>| PMC2939565 | BMC Dev Biol.
- ↑ <pubmed>17010333</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>11032856</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>9405645</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>19956802</pubmed>| PLoS Biol.
- ↑ <pubmed>15650323</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>23940571</pubmed>| PLoS One.
- ↑ <pubmed>9254921</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>22848431</pubmed>| PMC2634972 | PLoS One.
- ↑ <pubmed>24433583</pubmed>| BMC Dev Biol.
- ↑ <pubmed>25299669</pubmed>| PLoS Genet.
Search Bookshelf Pax
Reviews
<pubmed>17506689</pubmed> <pubmed>10197584</pubmed>
Search Pubmed
Search Pubmed Now: Pax
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/omim
External Links
External Links Notice - The dynamic nature of the internet may mean that some of these listed links may no longer function. If the link no longer works search the web with the link text or name. Links to any external commercial sites are provided for information purposes only and should never be considered an endorsement. UNSW Embryology is provided as an educational resource with no clinical information or commercial affiliation.
- OMIM - Pax6
Glossary Links
- Glossary: A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | Numbers | Symbols | Term Link
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, April 16) Embryology Developmental Signals - Pax. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/Developmental_Signals_-_Pax
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G