Developmental Mechanism - Cell Junctions
| Embryology - 23 Apr 2024 |
|---|
| Google Translate - select your language from the list shown below (this will open a new external page) |
|
العربية | català | 中文 | 中國傳統的 | français | Deutsche | עִברִית | हिंदी | bahasa Indonesia | italiano | 日本語 | 한국어 | မြန်မာ | Pilipino | Polskie | português | ਪੰਜਾਬੀ ਦੇ | Română | русский | Español | Swahili | Svensk | ไทย | Türkçe | اردو | ייִדיש | Tiếng Việt These external translations are automated and may not be accurate. (More? About Translations) |
Introduction
Many developmental mechanisms require dynamic changes in cell adhesion that acts through different types of cell junctions.
Adhesion Cartoons
Adhesion EM Images
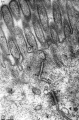
- Adhesion EM Images: GIT epithelia EM1 | GIT epithelia EM2 | GIT epithelia EM3 | Desmosome EM
- Adhesion Cartoons: Tight junction | Adherens Junction | Desmosome | Gap Junction
Some Recent Findings
| More recent papers |
|---|
|
This table allows an automated computer search of the external PubMed database using the listed "Search term" text link.
More? References | Discussion Page | Journal Searches | 2019 References | 2020 References Search term: Developmental Tight Junction | Developmental Desmosome | Developmental Gap Junction | Developmental Adherens Junction |
| Older papers |
|---|
| These papers originally appeared in the Some Recent Findings table, but as that list grew in length have now been shuffled down to this collapsible table.
See also the Discussion Page for other references listed by year and References on this current page. |
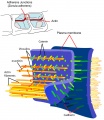
Tight Junction

Tight Junction |
Search PubMed: Tight Junction
Adherens Junction
Cadherin isoform naming was based upon the site of original identification: P-cadherin (placenta cadherin, cadherin 3), E-cadherin (epithelial cadherin cadherin 1), N-cadherin (neural cadherin, cadherin 2). |
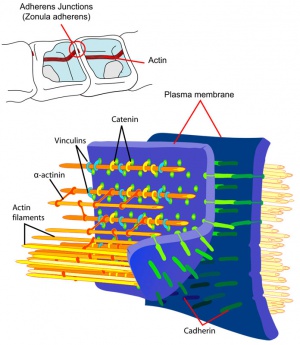
Adherens Junction |
Search PubMed: Adherens Junction
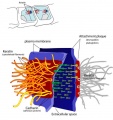
Desmosome
|
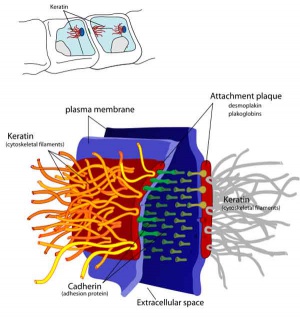
Desmosome |
Search PubMed: Desmosome
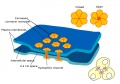
Gap Junction
|
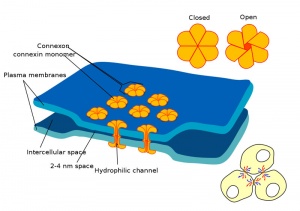
Gap Junction |
Search PubMed: gap junction
References
Reviews
Articles
External Links
External Links Notice - The dynamic nature of the internet may mean that some of these listed links may no longer function. If the link no longer works search the web with the link text or name. Links to any external commercial sites are provided for information purposes only and should never be considered an endorsement. UNSW Embryology is provided as an educational resource with no clinical information or commercial affiliation.
Glossary Links
- Glossary: A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | Numbers | Symbols | Term Link
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, April 23) Embryology Developmental Mechanism - Cell Junctions. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/Developmental_Mechanism_-_Cell_Junctions
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G