Cell Division - Meiosis
From Embryology
Introduction
Some Recent Findings
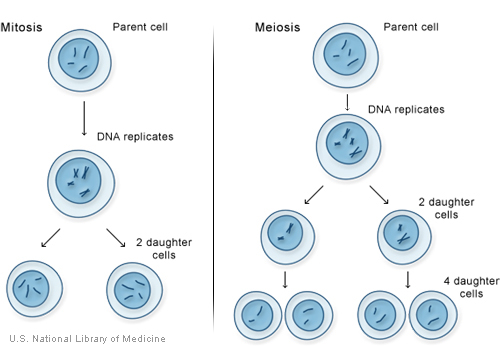
Mitosis and Meiosis
Mitosis 2 Daughter cells identical to parent (diploid)
Meiosis Germ cell division (haploid)
- Reductive division
- Generates haploid gametes (egg, sperm)
- Each genetically distinct from parent
- Genetic recombination (prophase 1)
- Exchanges portions of chromosomes maternal/paternal homologous pairs
- Independent assortment of paternal chromosomes (meiosis 1)
Cell Birth - Mitosis and Meiosis 1st cell division- Meiosis
Homologous chromosomes pairing unique to meiosis
- Each chromosome duplicated and exists as attached sister chromatids before pairing occurs
- Genetic Recombination shown by chromosomes part red and part black
- chromosome pairing in meiosis involves crossing-over between homologous chromosomes
(For clarity only 1 pair of homologous chromosomes shown)
Comparison of Meiosis/Mitosis
- After DNA replication 2 nuclear (and cell) divisions required to produce haploid gametes
- Each diploid cell in meiosis produces 4 haploid cells (sperm) 1 haploid cell (egg)
- Each diploid cell mitosis produces 2 diploid cells
Abnormalities
Meiotic Nondisjunction
- Occurs when homologues fail to separate during meiotic division I or II
- Down Syndrome
- Caused by an extra copy of chromosome 21
Chromosomal Translocations
- Philadelphia chromosome
- Chronic myelogenous leukemia
- Piece of Chr9 exchanged with Chr22 Generates truncated abl
Overstimulates cell production
Meiosis Sex Differences
Female (oogenesis)
- Meiosis initiated once in a finite population of cells
- 1 gamete produced / meiosis
- Completion of meiosis delayed for months or years
- Meiosis arrested at 1st meiotic prophase and reinitiated in a smaller population of cells
- Differentiation of gamete occurs while diploid in first meiotic prophase
- All chromosomes exhibit equivalent transcription and recombination during meiotic prophase
Male (spermatogenesis)
- Meiosis initiated continuously in a mitotically dividing stem cell population
- 4 gametes produced / meiosis
- Meiosis completed in days or weeks
- Meiosis and differentiation proceed continuously without cell cycle arrest
- Differentiation of gamete occurs while haploid after meiosis ends
Sex chromosomes excluded from recombination and transcription during first meiotic prophase
References
Reviews
Articles
Search Pubmed
Search Pubmed: meiosis
Additional Images
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, April 16) Embryology Cell Division - Meiosis. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/Cell_Division_-_Meiosis
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G