Category:Mouse E14: Difference between revisions
mNo edit summary |
mNo edit summary |
||
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
==Events== | ==Events== | ||
* [[Salivary Gland Development]] - simple one-bud one-duct salivary gland has both grown and branched significantly, and the main duct begins to lumenize. The end buds undergo reorganization and begin to form acini – the main secretory units of the salivary gland. | * [[Salivary Gland Development]] - simple one-bud one-duct salivary gland has both grown and branched significantly, and the main duct begins to lumenize. The end buds undergo reorganization and begin to form acini – the main secretory units of the salivary gland.{{#pmid:20890964|PMID20890964}} | ||
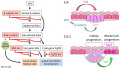
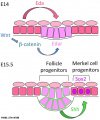
* | * {{Integumentary}} - Ectodysplasin receptor (EDAR) expressed in the epidermis basal cells and hair placodes.{{#pmid:11039935|PMID11039935}} | ||
** {{Hair}} - a primary wave of hair follicle placode induction takes place, these primary hairs only form 2% of the adult hair population and are associated with touch domes. Secondary ([[:Category:Mouse E16|E16]]) and tertiary ({{ME18}}) waves of hair follicle induction are responsible for forming the three remaining types of hair follicles.{{#pmid:19750518|PMID19750518}} | |||
** | ** {{Nail}} - primordial nails (claws) begin to appear on the dorsal surface of the developing distal digits of mouse limbs between {{ME14}} to {{ME15}},{{#pmid:23439395|PMID23439395}} | ||
* | * {{Pancreas}} - day 13 to 14 ({{ME13}}, {{ME13.5}}, {{ME14}}) stomach rotation brings the smaller ventral pancreatic bud dorsally to fuse with the larger dorsal pancreatic bud. | ||
* {{Palate}} - palatal shelves become elevated horizontally above the tongue. | |||
===References=== | ===References=== | ||
Latest revision as of 12:51, 16 November 2019
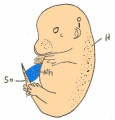
This Embryology category shows pages and media related to embryonic day 14 E14.0 of mouse development.
This staging by "days" relate to in the female presence of a vaginal plug indicating that the mating occurred, see timed pregnancy.
- Mouse Stages: E1 | E2.5 | E3.0 | E3.5 | E4.5 | E5.0 | E5.5 | E6.0 | E7.0 | E7.5 | E8.0 | E8.5 | E9.0 | E9.5 | E10 | E10.5 | E11 | E11.5 | E12 | E12.5 | E13 | E13.5 | E14 | E14.5 | E15 | E15.5 | E16 | E16.5 | E17 | E17.5 | E18 | E18.5 | E19 | E20 | Timeline | About timed pregnancy
| Carnegie | Stage | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Human | Days | 1 | 2-3 | 4-5 | 5-6 | 7-12 | 13-15 | 15-17 | 17-19 | 20 | 22 | 24 | 28 | 30 | 33 | 36 | 40 | 42 | 44 | 48 | 52 | 54 | 55 | 58 |
| Mouse | Days | 1 | 2 | 3 | E4.5 | E5.0 | E6.0 | E7.0 | E8.0 | E9.0 | E9.5 | E10 | E10.5 | E11 | E11.5 | E12 | E12.5 | E13 | E13.5 | E14 | E14.5 | E15 | E15.5 | E16 |
| Rat | Days | 1 | 3.5 | 4-5 | 5 | 6 | 7.5 | 8.5 | 9 | 10.5 | 11 | 11.5 | 12 | 12.5 | 13 | 13.5 | 14 | 14.5 | 15 | 15.5 | 16 | 16.5 | 17 | 17.5 |
| Note these Carnegie stages are only approximate day timings for average of embryos. Links: Carnegie Stage Comparison | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Timeline Links: human timeline | mouse timeline | mouse detailed timeline | chicken timeline | rat timeline | Medaka | Category:Timeline |
Events
- Salivary Gland Development - simple one-bud one-duct salivary gland has both grown and branched significantly, and the main duct begins to lumenize. The end buds undergo reorganization and begin to form acini – the main secretory units of the salivary gland.[1]
- integumentary - Ectodysplasin receptor (EDAR) expressed in the epidermis basal cells and hair placodes.[2]
- hair - a primary wave of hair follicle placode induction takes place, these primary hairs only form 2% of the adult hair population and are associated with touch domes. Secondary (E16) and tertiary (E18) waves of hair follicle induction are responsible for forming the three remaining types of hair follicles.[3]
- nail - primordial nails (claws) begin to appear on the dorsal surface of the developing distal digits of mouse limbs between E14 to E15,[4]
- pancreas - day 13 to 14 (E13, E13.5, E14) stomach rotation brings the smaller ventral pancreatic bud dorsally to fuse with the larger dorsal pancreatic bud.
- palate - palatal shelves become elevated horizontally above the tongue.
References
- ↑ Larsen M, Yamada KM & Musselmann K. (2010). Systems analysis of salivary gland development and disease. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Syst Biol Med , 2, 670-82. PMID: 20890964 DOI.
- ↑ Yan M, Wang LC, Hymowitz SG, Schilbach S, Lee J, Goddard A, de Vos AM, Gao WQ & Dixit VM. (2000). Two-amino acid molecular switch in an epithelial morphogen that regulates binding to two distinct receptors. Science , 290, 523-7. PMID: 11039935 DOI.
- ↑ Duverger O & Morasso MI. (2009). Epidermal patterning and induction of different hair types during mouse embryonic development. Birth Defects Res. C Embryo Today , 87, 263-72. PMID: 19750518 DOI.
- ↑ Cui CY, Klar J, Georgii-Heming P, Fröjmark AS, Baig SM, Schlessinger D & Dahl N. (2013). Frizzled6 deficiency disrupts the differentiation process of nail development. J. Invest. Dermatol. , 133, 1990-7. PMID: 23439395 DOI.
Search Pubmed: Mouse E14
Pages in category 'Mouse E14'
The following 3 pages are in this category, out of 3 total.
Media in category 'Mouse E14'
The following 9 files are in this category, out of 9 total.
- Day 14 Fingers Separate.JPG 517 × 541; 28 KB
- Integumentary touch dome model 01.jpg 1,280 × 724; 144 KB
- Integumentary touch dome model 03.jpg 603 × 724; 73 KB
- Mouse cloacal septation 01.jpg 917 × 318; 47 KB
- Mouse embryo E14 microCT icon.jpg 858 × 720; 33 KB
- Mouse embryo E14 sectioned microCT icon.jpg 322 × 519; 31 KB
- Mouse respiratory 36 to 60 somites.gif 394 × 432; 154 KB
- Mouse respiratory 60 somites.jpg 394 × 432; 34 KB