Carnegie stage 1: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
Human early zygote showing pronuclei | Human early zygote showing pronuclei | ||
| | | | ||
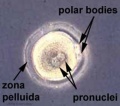
The early human zygote where the male and female pronuclei (centre of image) have not yet combined to form the single zygote nucleus. These pronuclei | The early human zygote where the male and female pronuclei (centre of image) have not yet combined to form the single zygote nucleus. These pronuclei are the nuclei from the spermatozoa (sperm) and oocyte (egg) and contain all the nuclear genetic material (chromosomes, DNA, genes). | ||
Two of the egg's polar bodies (right, 3 o'clock position of image) are shown at the edge of the egg cytoplasm. These polar bodies contain the excess DNA from the meiotic divisions of the egg. | Two of the egg's polar bodies (right, 3 o'clock position of image) are shown at the edge of the egg cytoplasm. These polar bodies contain the excess DNA from the meiotic divisions of the egg. | ||
The zona pellucida (edge of image) forms a specialised thick extracellular matrix layer around both the egg and the developing conceptus for the first week. | The zona pellucida (edge of image) forms a specialised thick extracellular matrix layer around both the egg and the developing conceptus for the first week. | ||
Mitochondria in the cytoplasm contain additional genes and in humans these mitochondrial genes are entirely derived from the oocyte. | |||
'''Facts:''' Week 1, size 0.1-0.15 mm | '''Facts:''' Week 1, size 0.1-0.15 mm | ||
Revision as of 06:58, 25 October 2011
Introduction

Human early zygote showing pronuclei |
The early human zygote where the male and female pronuclei (centre of image) have not yet combined to form the single zygote nucleus. These pronuclei are the nuclei from the spermatozoa (sperm) and oocyte (egg) and contain all the nuclear genetic material (chromosomes, DNA, genes). Two of the egg's polar bodies (right, 3 o'clock position of image) are shown at the edge of the egg cytoplasm. These polar bodies contain the excess DNA from the meiotic divisions of the egg. The zona pellucida (edge of image) forms a specialised thick extracellular matrix layer around both the egg and the developing conceptus for the first week. Mitochondria in the cytoplasm contain additional genes and in humans these mitochondrial genes are entirely derived from the oocyte. Facts: Week 1, size 0.1-0.15 mm Features: zygote, fertilized oocyte, pronuclei, polar bodies, zona pellucida
|
- Carnegie Stages: 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | About Stages | Timeline
Carnegie stage 1
Human zygote two pronuclei[1]
Human zygote two pronuclei[1]
Human zygote two pronuclei[1]
Human zygote two pronuclei (labelled)[1]
Human oocyte to blastocyst[2]
References
- Carnegie Stages: 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | About Stages | Timeline
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, April 16) Embryology Carnegie stage 1. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/Carnegie_stage_1
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G

![Human zygote two pronuclei[1]](/embryology/images/thumb/5/5b/Human_zygote_two_pronuclei_01.jpg/120px-Human_zygote_two_pronuclei_01.jpg)
![Human zygote two pronuclei[1]](/embryology/images/thumb/5/5c/Human_zygote_two_pronuclei_03.jpg/120px-Human_zygote_two_pronuclei_03.jpg)
![Human zygote two pronuclei[1]](/embryology/images/thumb/f/f8/Human_zygote_two_pronuclei_02.jpg/120px-Human_zygote_two_pronuclei_02.jpg)
![Human zygote two pronuclei (labelled)[1]](/embryology/images/thumb/2/27/Human_zygote_two_pronuclei_22.jpg/120px-Human_zygote_two_pronuclei_22.jpg)
![Human oocyte to blastocyst[2]](/embryology/images/thumb/9/94/Human-oocyte_to_blastocyst.jpg/120px-Human-oocyte_to_blastocyst.jpg)