BGDB Face and Ear - Postnatal
| Practical 6: Trilaminar Embryo | Early Embryo | Late Embryo | Fetal | Postnatal | Abnormalities |
Postnatal Skull
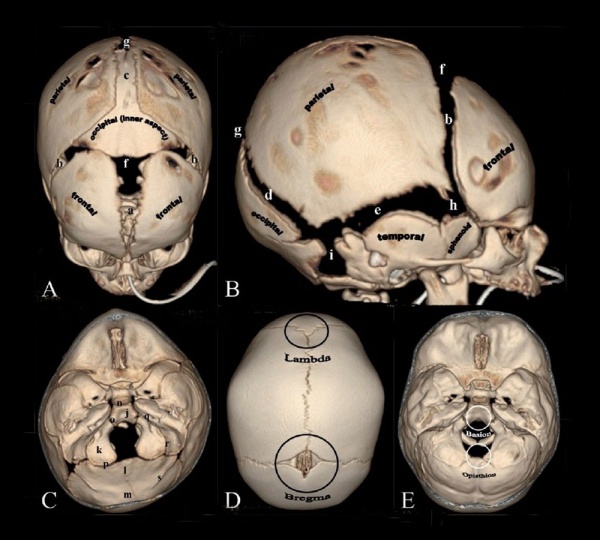
Skull CT Vertex, later and basal views.[1] |
Sutures and Fontanels
|
Head Growth
Head growth and corresponding charts differ slightly for girls and boys. Given as head circumference-for-age Birth to: 13 weeks, 2 years, 5 years.
| Girls | Boys |
|---|---|
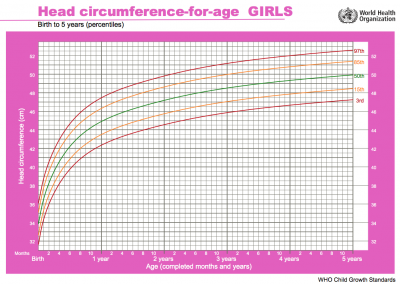
|
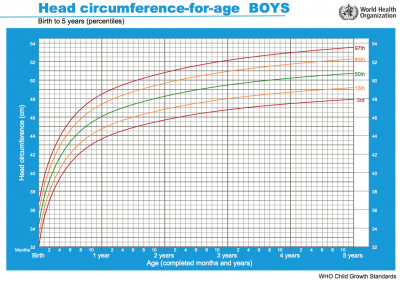
|
| Chart PDF | WHO - Girls | Chart PDF | WHO - Boys |
- Links: Growth Charts | Neural Exam Movies | - Standard Head circumference-for-age | WHO Growth Standards
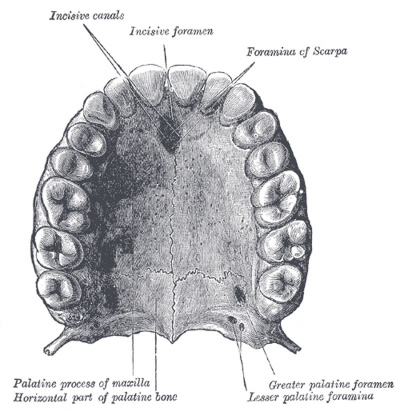
Adult Palate
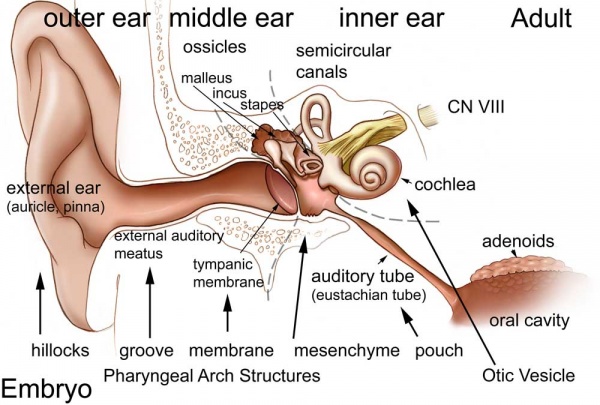
Postnatal Ear
First, look through the adult ear structures and identify their developmental origins.
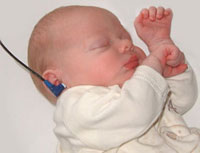
Hearing Testing
Abnormalities in neonatal hearing can impact upon development of the nervous system and developmental learning milestones, early detection is therefore key.
The incidence of significant permanent hearing loss is approximately 1-3/1000 newborns. Neonatal hearing screening is carried out in several countries including the USA, UK and in Australia. In NSW the Statewide Infant Screening Hearing (SWISH) Program was introduced in 2002.
There is also a general guide giving a timetable for a number of simple responses that a neonate should make if hearing has developed normally (More? Neonatal Hearing Check List).
The two major forms of hearing loss are conductive and sensorineural.
State Wide Infant Screening Hearing Program (SWISH) a newborn hearing testing program using an automated auditory response technology (AABR). Program was introduced in NSW Australia in 2002 across 17 area health service coordinators. It is thought that in NSW 86,000 births/year = 86-172 babies potentially born with significant permanent hearing loss.
Automated Auditory Brainstem Response (AABR) uses a stimulus which is delivered through earphones and detected by scalp electrodes. The test takes between 8 to 20 minutes and has a sensitivity 96-99%.
- Links: Hearing test
Additional Information
| Additional Information - Content shown under this heading is not part of the material covered in this class. It is provided for those students who would like to know about some concepts or current research in topics related to the current class page. |
Head Measurements
| Normal Head | Abnormal Head | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| ||||||
|
|
- Links: Growth Charts | Neural Exam Movies | - Standard Head circumference-for-age | WHO Growth Standards
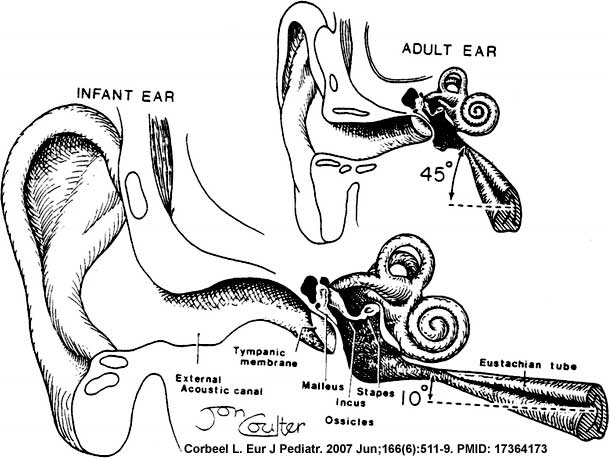
External Auditory Meatus Changes

|
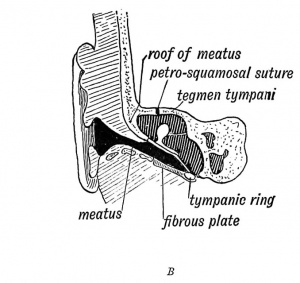
|
| Birth | Adult |
Neonatal Hearing Check List
The timing and types of responses listed below reflect only a rough guide for the general population. Abnormalities in neurological, visual or motor skill development can also affect responses.
- Birth to 3 months - Reacts to loud sounds, Quiets to familiar voices or sounds, Makes cooing noises, Responds to speech by looking at speaker’s face.
- 3 to 6 months - Turns eyes or head toward sounds, Starts to make speech-like sounds, Laughs and makes noises to indicate pleasure and displeasure.
- 6 to 9 months - Babbles, ‘dada’‘ma-ma’‘baba’, Shouts/vocalises to get attention, Will often respond to ‘no’ and own name, Responds to singing and music.
- 9 to 12 months - Imitates speech sounds of others, Understands simple words, eg ‘ball’,‘dog’, ‘daddy’, Turns head to soft sounds, First words emerge.
- 12 to 18 months _ Appears to understand some new words each week, Follows simple spoken instructions, eg ‘get the ball’, Points to people, body parts or toys when asked, Continually learns new words to say although may be unclear.
- 18 to 24 months - Listens to simple stories or songs, Combines two or more words in short phrases eg ‘more juice’.
Hearing check list text based upon NSW Health Pamphlet - Why does my baby need a hearing check?
Neural Exam
The following are examples of simple neural assessment of development in early hearing and understanding.
| 12 month Behaviour | 18 month Behaviour | 30 month Behaviour |
|---|---|---|
| <html5media height="290" width="320">File:12mo 02.mp4</html5media> | <html5media height="290" width="320">File:18mo 02.mp4</html5media> | <html5media height="290" width="320">File:30mo 02.mp4</html5media> |
| Movie Source - Paul D. Larsen |
|---|
| Movies from the PediNeuroLogic Exam website are used by permission of Paul D. Larsen, M.D., University of Nebraska Medical Center and Suzanne S. Stensaas, Ph.D., University of Utah School of Medicine. Additional materials were drawn from resources provided by Alejandro Stern, Stern Foundation, Buenos Aires, Argentina; Kathleen Digre, M.D., University of Utah; and Daniel Jacobson, M.D., Marshfield Clinic, Wisconsin. The movies are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommerical-ShareAlike 2.5 License. |
| Practical 6: Trilaminar Embryo | Early Embryo | Late Embryo | Fetal | Postnatal | Abnormalities |
BGDB: Lecture - Gastrointestinal System | Practical - Gastrointestinal System | Lecture - Face and Ear | Practical - Face and Ear | Lecture - Endocrine | Lecture - Sexual Differentiation | Practical - Sexual Differentiation | Tutorial
Glossary Links
- Glossary: A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | Numbers | Symbols | Term Link
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, April 19) Embryology BGDB Face and Ear - Postnatal. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/BGDB_Face_and_Ear_-_Postnatal
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G
- ↑ <pubmed>21431034</pubmed>| PMC3056371 | Indian J Radiol Imaging.