BGDB Face and Ear - Postnatal: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
Skull CT Vertex, later and basal views.<ref name="PMID21431034"><pubmed>21431034</pubmed>| [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3056371 PMC3056371] | [http://www.ijri.org/article.asp?issn=0971-3026;year=2011;volume=21;issue=1;spage=49;epage=56;aulast=Khanna Indian J Radiol Imaging.]</ref> | Skull CT Vertex, later and basal views.<ref name="PMID21431034"><pubmed>21431034</pubmed>| [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3056371 PMC3056371] | [http://www.ijri.org/article.asp?issn=0971-3026;year=2011;volume=21;issue=1;spage=49;epage=56;aulast=Khanna Indian J Radiol Imaging.]</ref> | ||
| valign=top| | | valign=top| | ||
* rapid brain growth in the early years of life (growth of the neurocranium stopping at about 7 years of age). | |||
* fontanels usually close by the second year of life | |||
** posterior fontanel by about 3 months. | |||
** anterior fontanel by about 20 months. | |||
* Complete sutural fusion occurs after the third decade of life. | |||
'''Sutures and Fontanels''' | '''Sutures and Fontanels''' | ||
| Line 19: | Line 25: | ||
* '''i''' - mastoid fontanel | * '''i''' - mastoid fontanel | ||
|} | |} | ||
==Postnatal Ear== | ==Postnatal Ear== | ||
Revision as of 15:46, 13 May 2012
| Practical 6: Trilaminar Embryo | Early Embryo | Late Embryo | Fetal | Postnatal | Abnormalities |
Postnatal Skull
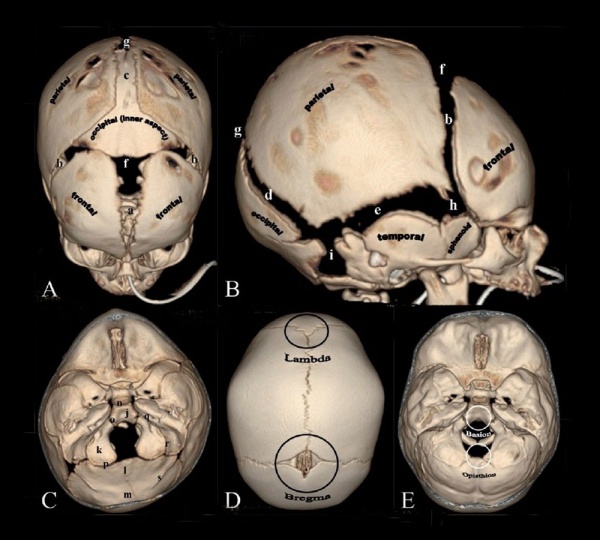
Skull CT Vertex, later and basal views.[1] |
Sutures and Fontanels
|
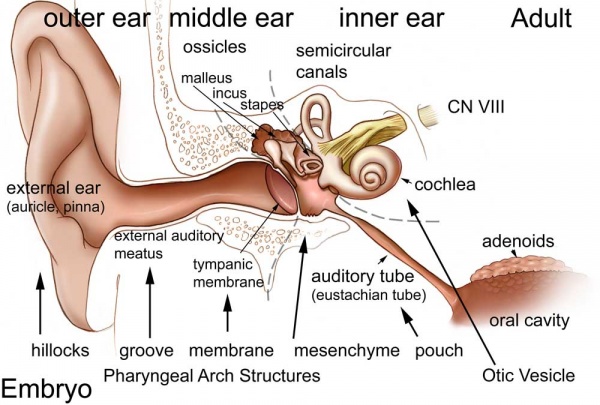
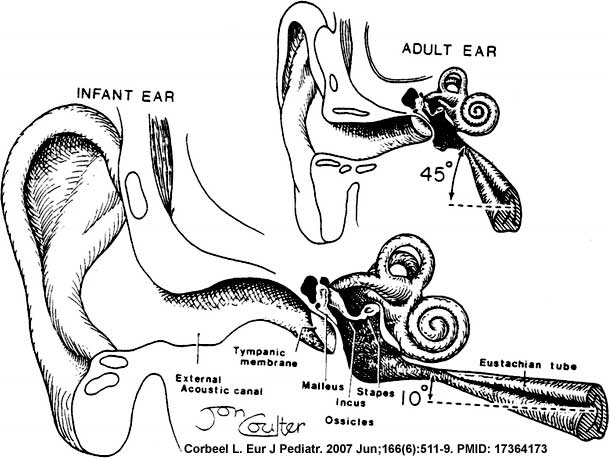
Postnatal Ear
First, look through the adult ear structures and identify their developmental origins.
Hearing Testing
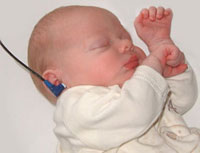
Abnormalities in neonatal hearing can impact upon development of the nervous system and developmental learning milestones, early detection is therefore key.
The incidence of significant permanent hearing loss is approximately 1-3/1000 newborns. Neonatal hearing screening is carried out in several countries including the USA, UK and in Australia. In NSW the Statewide Infant Screening Hearing Program (SWISH) was introduced in 2002.
There is also a general guide giving a timetable for a number of simple responses that a neonate should make if hearing has developed normally (More? Neonatal Hearing Check List).
The two major forms of hearing loss are conductive and sensorineural.
State Wide Infant Screening Hearing Program (SWISH) a newborn hearing testing program using an automated auditory response technology (AABR). Program was introduced in NSW Australia in 2002 across 17 area health service coordinators. It is thought that in NSW 86,000 births/year = 86-172 babies potentially born with significant permanent hearing loss.
Automated Auditory Brainstem Response (AABR) uses a stimulus which is delivered through earphones and detected by scalp electrodes. The test takes between 8 to 20 minutes and has a sensitivity 96-99%.
| Practical 6: Trilaminar Embryo | Early Embryo | Late Embryo | Fetal | Postnatal | Abnormalities |
BGDB: Lecture - Gastrointestinal System | Practical - Gastrointestinal System | Lecture - Face and Ear | Practical - Face and Ear | Lecture - Endocrine | Lecture - Sexual Differentiation | Practical - Sexual Differentiation | Tutorial
Glossary Links
- Glossary: A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | Numbers | Symbols | Term Link
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, April 18) Embryology BGDB Face and Ear - Postnatal. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/BGDB_Face_and_Ear_-_Postnatal
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G
- ↑ <pubmed>21431034</pubmed>| PMC3056371 | Indian J Radiol Imaging.