BGDB Face and Ear - Late Embryo
| Practical 6: Trilaminar Embryo | Early Embryo | Late Embryo | Fetal | Postnatal | Abnormalities |
Week 6
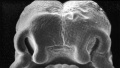
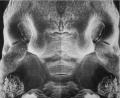
Primary Palate
- Beginning week 6 there is fusion of the upper lip.
- Formed by the maxillary prominences of of the first pharyngeal arch and the frontonasal prominence.
- Failure of this embryonic process leads to cleft lip.
Above images show face development through week 6 to week 7 (1mm scale markings).
The animation shows the early fusion of the primary palate in the human embryo between stage 17 and 18, going from an epithelial seam to the mesenchymal bridge.
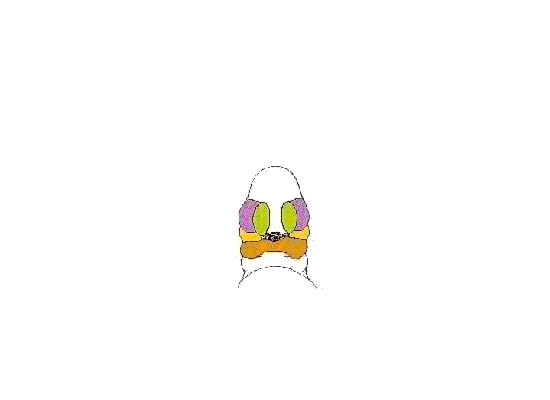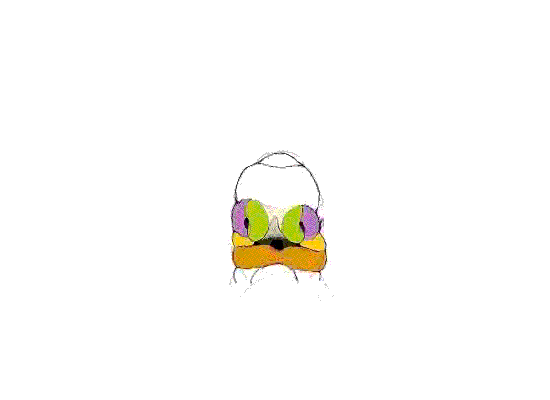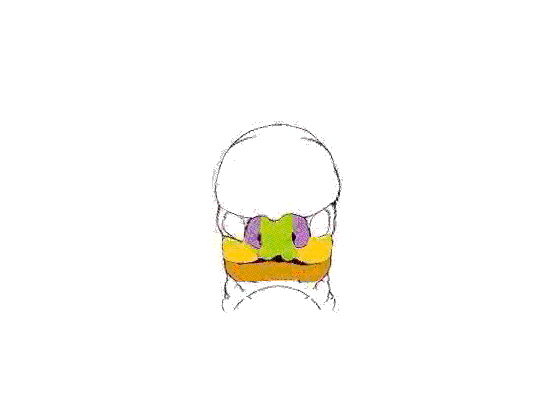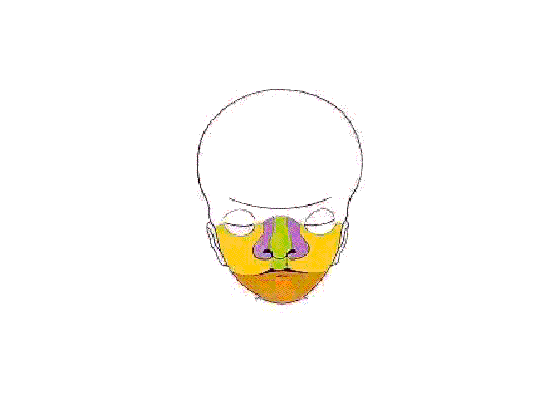 Face Development Movie | MP4 movie
Face Development Movie | MP4 movie|
This animation shows a ventral view of development of the human face from approximately week 5 through to neonate.
|
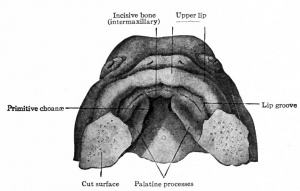
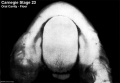
Week 8
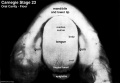
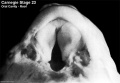
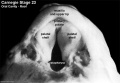
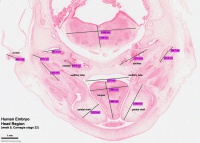
- Oral Cavity (stage 23)
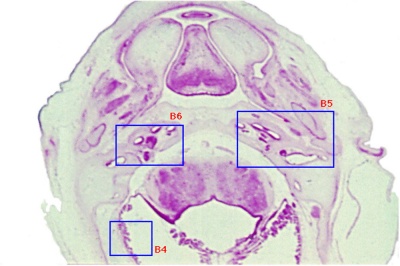
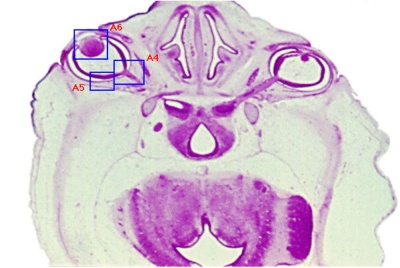
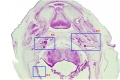 Selected Head Images: B4 - Choroid Plexus | B5 - Cochlea | B6 - Cochlea
Selected Head Images: B4 - Choroid Plexus | B5 - Cochlea | B6 - Cochlea
Palate
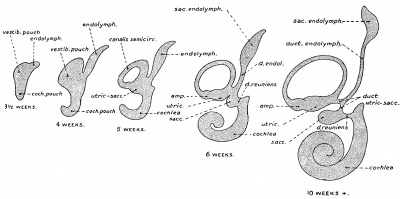
Hearing
Growth and stages of differentiation of the human membranous labyrinth.
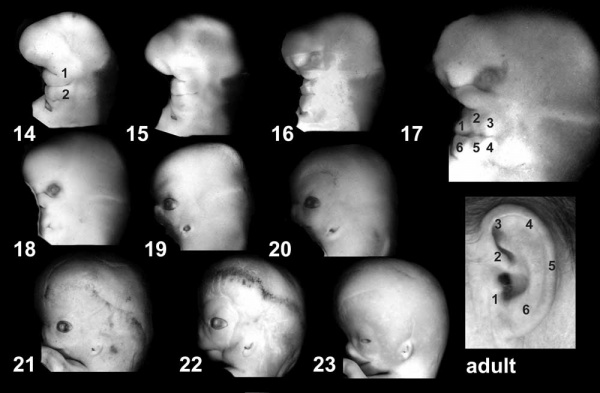
Embryonic External Ear
Shown below are the changes in external ear development between week 5 to week 8. Development changes from a series of 6 hillocks on arch 1 and arch 2 (week 5) to a structure resembling the adult ear (week 8).
| Practical 6: Trilaminar Embryo | Early Embryo | Late Embryo | Fetal | Postnatal | Abnormalities |
Additional Information
| Additional Information - Content shown under this heading is not part of the material covered in this class. It is provided for those students who would like to know about some concepts or current research in topics related to the current class page. |
External Auditory Meatus Timeline
| Time | EAM Appearance |
| Embryonic period | Ectodermal cells proliferate and fill the entire lumen forming a meatal plug |
| 10 weeks | Meatal plug extends in a disc-like fashion. In the horizontal plane the meatus is boot-shaped with a narrow neck and the sole of the meatal plug spreading widely to form the future tympanic membrane medially. Proximal portion of the neck starts to be resorbed. |
| 13 weeks | Disc-like plug innermost surface in contact with the primordial malleus, contributes to the formation of the tympanic membrane. |
| 16.5 week | Meatus is fully patent throughout its length, lumen is still narrow and curved. |
| 18 week | Meatus is already fully expanded to its complete form. |
Based on data from PMID 1441991
BGDB: Lecture - Gastrointestinal System | Practical - Gastrointestinal System | Lecture - Face and Ear | Practical - Face and Ear | Lecture - Endocrine | Lecture - Sexual Differentiation | Practical - Sexual Differentiation | Tutorial
Glossary Links
- Glossary: A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | Numbers | Symbols | Term Link
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, April 19) Embryology BGDB Face and Ear - Late Embryo. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/BGDB_Face_and_Ear_-_Late_Embryo
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G