BGDB Face and Ear - Late Embryo: Difference between revisions
mNo edit summary |
mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 69: | Line 69: | ||
{| | {| | ||
| [[File:Streeter1906 | | [[File:Streeter1906 plate01.jpg|400px]] | ||
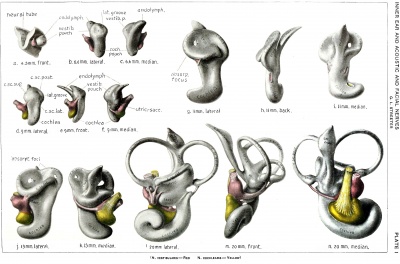
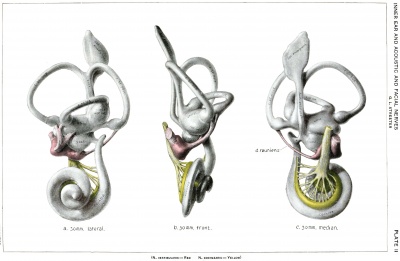
Embryonic development of the human membranous labyrinth. | |||
| [[File:Streeter1906 plate02.jpg|400px]] | | [[File:Streeter1906 plate02.jpg|400px]] | ||
| Line 89: | Line 89: | ||
{{Med Prac additional Information}} | {{Med Prac additional Information}} | ||
[[File:Streeter1906 fig04.jpg400px]] | |||
Growth and stages of differentiation of the human membranous labyrinth. | |||
{{BGDBFooter}} | {{BGDBFooter}} | ||
Revision as of 11:59, 16 May 2016
| Practical 6: Trilaminar Embryo | Early Embryo | Late Embryo | Fetal | Postnatal | Abnormalities |
Week 6
Primary Palate
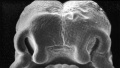
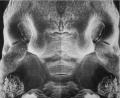
- Beginning week 6 there is fusion of the upper lip.
- Formed by the maxillary prominences of of the first pharyngeal arch and the frontonasal prominence.
- Failure of this embryonic process leads to cleft lip.
Above images show face development through week 6 to week 7 (1mm scale markings).
The animation shows the early fusion of the primary palate in the human embryo between stage 17 and 18, going from an epithelial seam to the mesenchymal bridge.
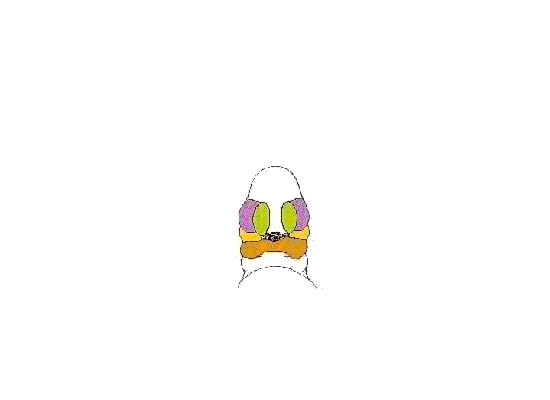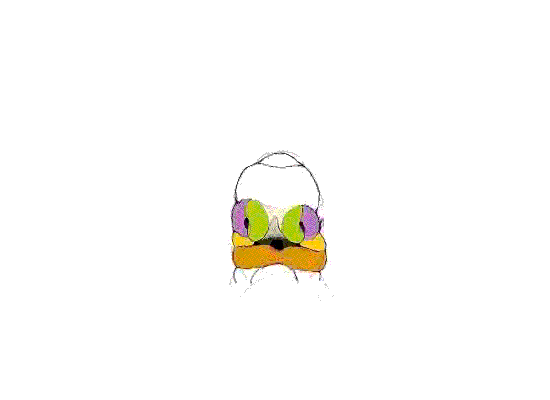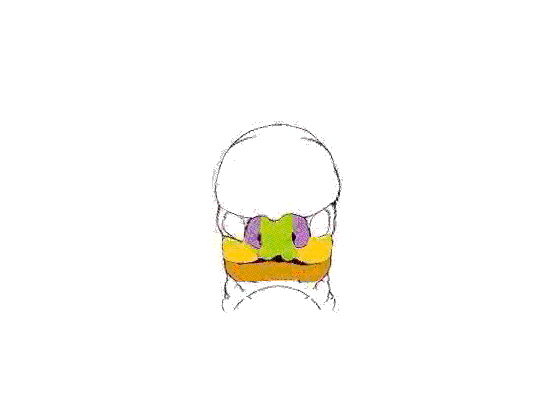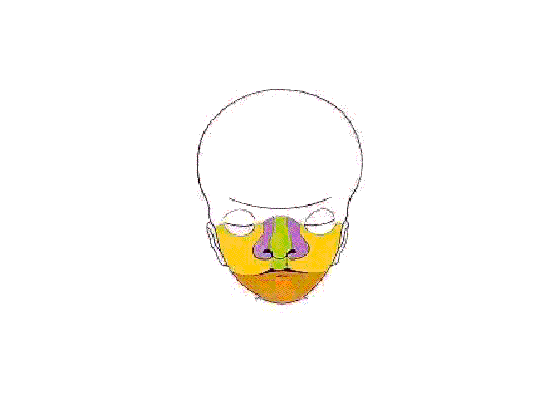 Face Development Movie | MP4 movie
Face Development Movie | MP4 movie|
This animation shows a ventral view of development of the human face from approximately week 5 through to neonate.
|
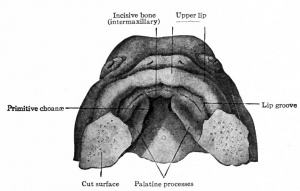
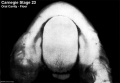
Week 8
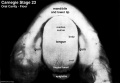
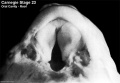
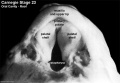
- Oral Cavity (stage 23)
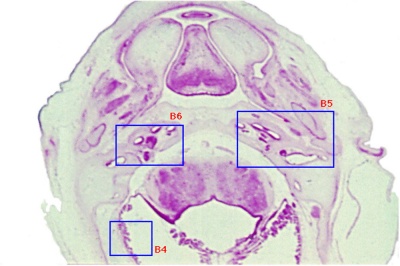
 Selected Head Images: B4 - Choroid Plexus | B5 - Cochlea | B6 - Cochlea
Selected Head Images: B4 - Choroid Plexus | B5 - Cochlea | B6 - Cochlea
Palate
Hearing
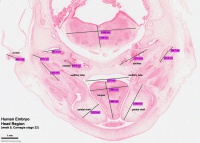
|
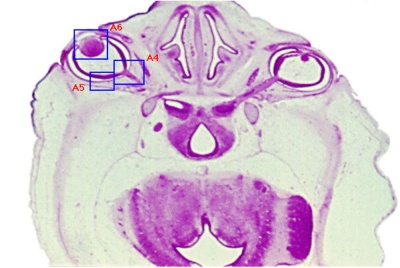
Behind that a pale cartilagenous region (that later ossifies) encloses the structuctures of the inner ear, beside which middle ear bones are forming. On the righthand side of the head the external ear is visible. The lower half of the image shows the developing brainstem with a large ventricular space occupied in part by an extensive choroid plexus (manufacturer of cerebrospinal fluid). |
|
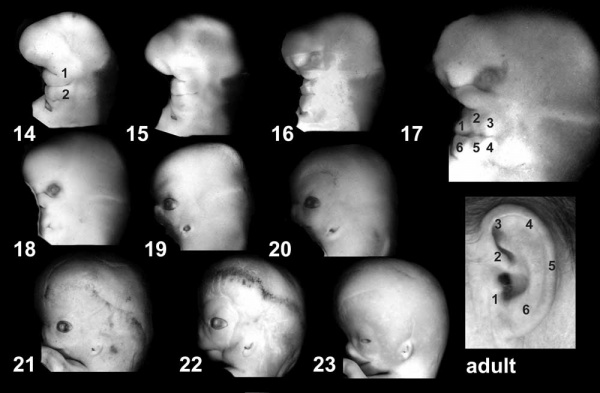
Embryonic External Ear
Shown below are the changes in external ear development between week 5 to week 8. Development changes from a series of 6 hillocks on arch 1 and arch 2 (week 5) to a structure resembling the adult ear (week 8).
| Practical 6: Trilaminar Embryo | Early Embryo | Late Embryo | Fetal | Postnatal | Abnormalities |
Additional Information
| Additional Information - Content shown under this heading is not part of the material covered in this class. It is provided for those students who would like to know about some concepts or current research in topics related to the current class page. |
File:Streeter1906 fig04.jpg400px
Growth and stages of differentiation of the human membranous labyrinth.
BGDB: Lecture - Gastrointestinal System | Practical - Gastrointestinal System | Lecture - Face and Ear | Practical - Face and Ear | Lecture - Endocrine | Lecture - Sexual Differentiation | Practical - Sexual Differentiation | Tutorial
Glossary Links
- Glossary: A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | Numbers | Symbols | Term Link
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, April 16) Embryology BGDB Face and Ear - Late Embryo. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/BGDB_Face_and_Ear_-_Late_Embryo
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G