BGDA Practical Placenta - Placental Functions: Difference between revisions
From Embryology
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 69: | Line 69: | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
==Endocrine== | |||
Protein and steroid hormones. | |||
* Human chorionic gonadotrophin (hCG) - like leutenizing hormone, supports corpus luteum in ovary, pregnant state rather than menstrual, maternal urine in some pregnancy testing | |||
* Human chorionic somatommotropin (hCS) - or placental lactogen stimulate (maternal) mammary development | |||
** rise through pregnancy, stimulates maternal metabolic processes, breast growth | |||
* Human chorionic thyrotropin (hCT) | |||
* Human chorionic corticotropin (hCACTH) | |||
* Relaxin | |||
* Steroid Hormones - progesterone (maintains pregnancy), estrogens (fetal adrenal/placenta) | |||
==Terms== | ==Terms== | ||
Revision as of 19:20, 29 May 2012
| Practical 14: Implantation and Early Placentation | Villi Development | Maternal Decidua | Cord Development | Placental Functions | Diagnostic Techniques | Abnormalities |
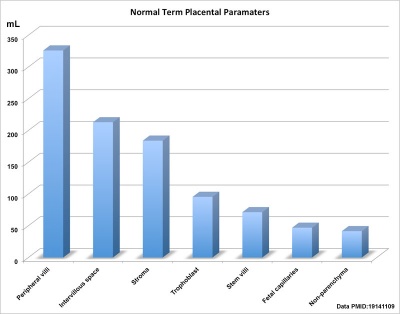
Term Placenta Parameters
Term of placental composition, villous capillarization and the mean cross-sectional areas of peripheral villi and capillaries, data from a study sample of 15 normal placenta (mean placental volume, 652 ml). [1]
| Variable | Unit | Placenta (mean, n = 15) |
| Intervillous space | mL | 213 |
| Stem villi | mL | 71.4 |
| Peripheral villi | mL | 326 |
| Trophoblast | mL | 95.5 |
| Stroma | mL | 184 |
| Fetal capillaries | mL | 46.9 |
| Non-parenchyma | mL | 41.5 |
| Peripheral villi | km | 89.2 |
| Fetal capillaries | km | 310 |
| TS area villi | µm2 | 3700 |
| TS area capillary | µm2 | 150 |
| Capillaries | mL mL-1 | 0.147 |
| Length ratio | km km-1 | 3.6 |
- ↑ <pubmed>19141109</pubmed>
Endocrine
Protein and steroid hormones.
- Human chorionic gonadotrophin (hCG) - like leutenizing hormone, supports corpus luteum in ovary, pregnant state rather than menstrual, maternal urine in some pregnancy testing
- Human chorionic somatommotropin (hCS) - or placental lactogen stimulate (maternal) mammary development
- rise through pregnancy, stimulates maternal metabolic processes, breast growth
- Human chorionic thyrotropin (hCT)
- Human chorionic corticotropin (hCACTH)
- Relaxin
- Steroid Hormones - progesterone (maintains pregnancy), estrogens (fetal adrenal/placenta)
Terms
BGDA: Lecture 1 | Lecture 2 | Practical 3 | Practical 6 | Practical 12 | Lecture Neural | Practical 14 | Histology Support - Female | Male | Tutorial
Glossary Links
- Glossary: A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | Numbers | Symbols | Term Link
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, April 25) Embryology BGDA Practical Placenta - Placental Functions. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/BGDA_Practical_Placenta_-_Placental_Functions
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G