BGDA Practical Placenta - Placental Functions: Difference between revisions
From Embryology
m (→Drugs) |
m (→Term Placenta) |
||
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
| | | | ||
|} | |} | ||
[[File:Placental mean weight graoph01.jpg|600px]] | |||
==Exchange== | ==Exchange== | ||
Revision as of 13:49, 6 June 2016
| Practical 14: Implantation and Early Placentation | Villi Development | Maternal Decidua | Cord Development | Placental Functions | Diagnostic Techniques | Abnormalities |
Term Placenta
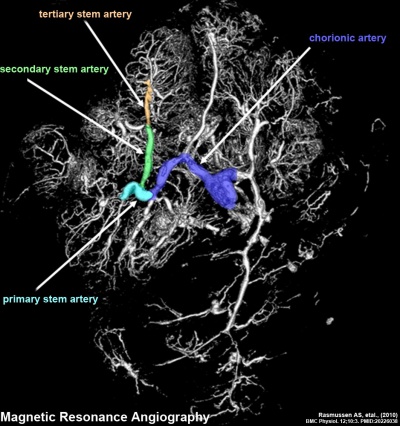
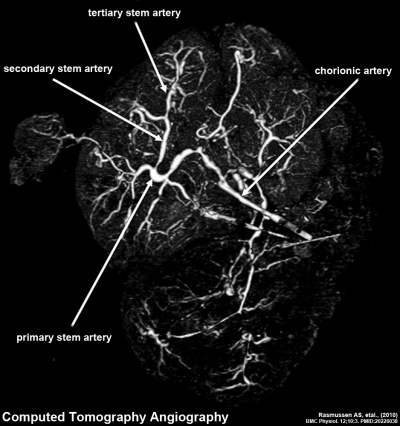
Placenta Vasculature - MRI and CT
Term placenta viewed from the fetal side.[1]
|
|
| Magnetic Resonance Angiography (MRA) | Computed Tomography Angiography (CTA) |
Legend
|
File:Placental mean weight graoph01.jpg
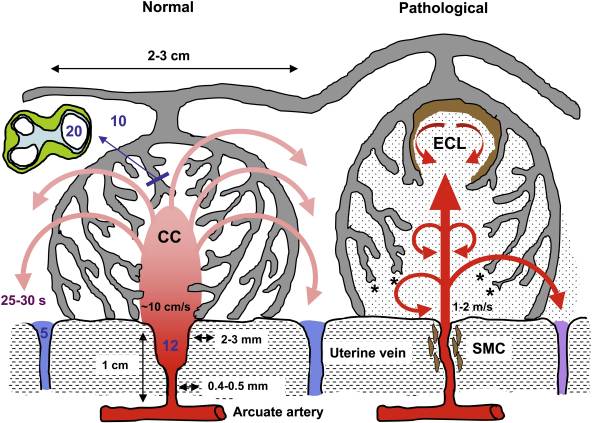
Exchange

|
|
- oxygen, carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide
- nutrients
- water, glucose, vitamins
- electrolytes
- waste products
- urea, uric acid, bilirubin.
- hormones
- mainly steroid, protein hormones poorly transported.
- maternal thyroid hormone can slowly cross.
- fetal insulin can impact on maternal diabetes.
- maternal antibodies
- maternal IgG antibodies are transferred from about week 13 (GA) across the placenta
- from the maternal lacunae syncytiotrophoblast cell endosomes bind IgG through neonatal Fc receptors.
- drugs and their metabolites
- pre-existing maternal conditions
- illegal drugs (fetal drug addiction)
- infectious agents
- cytomegalovirus, rubella, measles, malaria, listeria, microorganisms
Endocrine
Protein and steroid hormones.
- Human chorionic gonadotrophin (hCG) - like leutenizing hormone, supports corpus luteum in ovary, pregnant state rather than menstrual, maternal urine in some pregnancy testing
- Human chorionic somatommotropin (hCS) - or placental lactogen stimulate (maternal) mammary development
- rise through pregnancy, stimulates maternal metabolic processes, breast growth
- Human chorionic thyrotropin (hCT)
- Human chorionic corticotropin (hCACTH)
- Relaxin
- Steroid Hormones - progesterone (maintains pregnancy), estrogens (fetal adrenal/placenta)
Placental Metabolism
Synthesises - glycogen, cholesterol, fatty acids
- provides nutrient and energy
| Practical 14: Implantation and Early Placentation | Villi Development | Maternal Decidua | Cord Development | Placental Functions | Diagnostic Techniques | Abnormalities |
Additional Information
| Additional Information - Content shown under this heading is not part of the material covered in this class. It is provided for those students who would like to know about some concepts or current research in topics related to the current class page. |
- ↑ <pubmed>20226038</pubmed>| BMC Physiol.
Drugs
The placenta and fetal tissues may deal with drugs differently from adult target tissues. In particular, drugs are "cleared", metabolised and excreted, at a different rate in both the fetus and in newborn infants. In general there is a much lower rate of clearance.
<pubmed>21766440</pubmed> <pubmed>21789231</pubmed> <pubmed>19732616</pubmed>| PMC2767264
| Practical 14: Implantation and Early Placentation | Villi Development | Maternal Decidua | Cord Development | Placental Functions | Diagnostic Techniques | Abnormalities |
