BGDA Practical Placenta - Cord Development
From Embryology
| Practical 14: Implantation and Early Placentation | Villi Development | Maternal Decidua | Cord Development | Placental Functions | Diagnostic Techniques | Abnormalities |
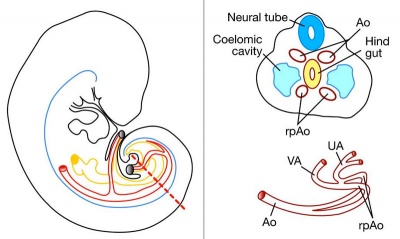
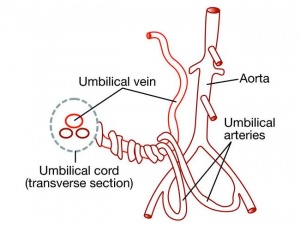
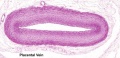
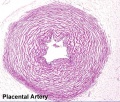
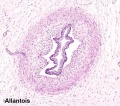
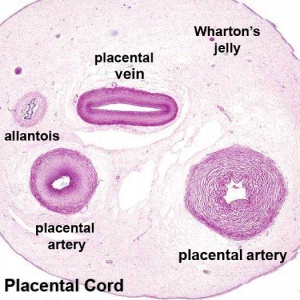
Placental Arteries and Vein
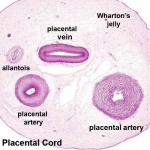
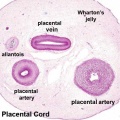
Placental Cord Histology
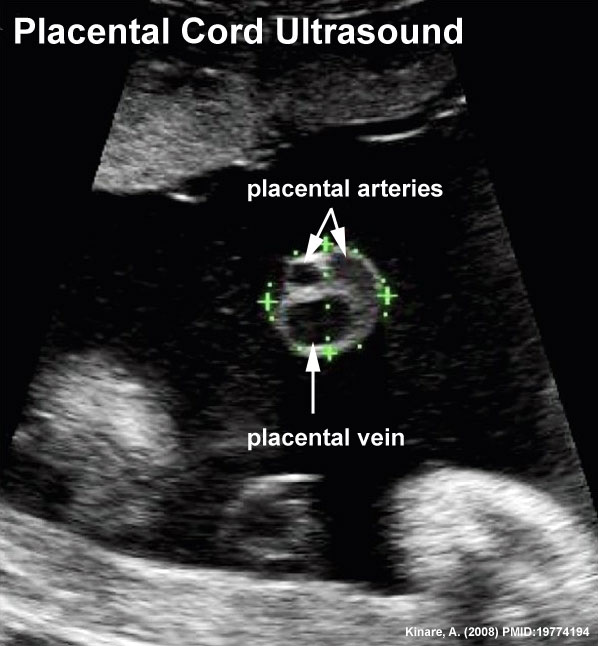
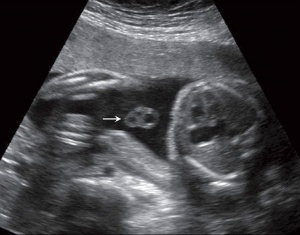
Placental Cord Ultrasound
Ultrasound image of transverse scan through the cord show the method of estimation of the cross-sectional area.
Wharton's Jelly
- placental cord connective tissue (substantia gelatinea funiculi umbilicalis)
- amorphous substance containing glycosaminoglycans, proteoglycans and hyaluronic acid.
- cells similar to smooth muscle that allows a contractile function.
- network of collagen that form canaliculi and perivascular spaces.
- maintain blood flow to the fetus during placental cord compression during pregnancy or delivery.
First described and named after Thomas Wharton (1614–1673) an English physician and anatomist.
Hofbauer Cells
- located the core of placental villi
- macrophages with micropinocytotic activity and phagocytosis ability
- possible paracrine role for early stages of placental vasculogenesis
- express angiogenic growth factors (VEGF)
Terms
| Practical 14: Implantation and Early Placentation | Villi Development | Maternal Decidua | Cord Development | Placental Functions | Diagnostic Techniques | Abnormalities |