BGDA Practical Placenta - Cord Development: Difference between revisions
From Embryology
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
==Placental/Umbilical Cord== | ==Placental/Umbilical Cord== | ||
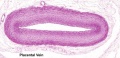
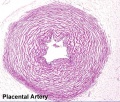
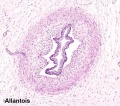
The placental cord (umbilical cord) is the connecting region between the functional placenta and the embryo/fetal umbilical region. The human cord varies | The placental cord (umbilical cord) is the connecting region between the functional placenta and the embryo/fetal umbilical region. The human cord varies physically in overall length, increasing to about 60 to 70 cm at term, degree of coiling, number of vessels and insertion site on the placenta. This extraembryonic structure contains the placental blood vessels and allantois. | ||
==Placental Arteries and Vein== | ==Placental Arteries and Vein== | ||
Revision as of 13:33, 4 June 2012
| Practical 14: Implantation and Early Placentation | Villi Development | Maternal Decidua | Cord Development | Placental Functions | Diagnostic Techniques | Abnormalities |
Placental/Umbilical Cord
The placental cord (umbilical cord) is the connecting region between the functional placenta and the embryo/fetal umbilical region. The human cord varies physically in overall length, increasing to about 60 to 70 cm at term, degree of coiling, number of vessels and insertion site on the placenta. This extraembryonic structure contains the placental blood vessels and allantois.
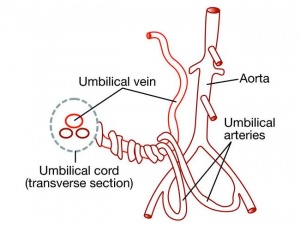
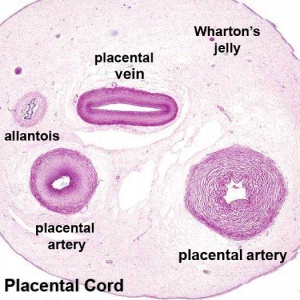
Placental Arteries and Vein
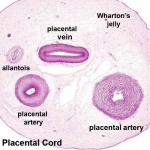
Placental Cord Histology
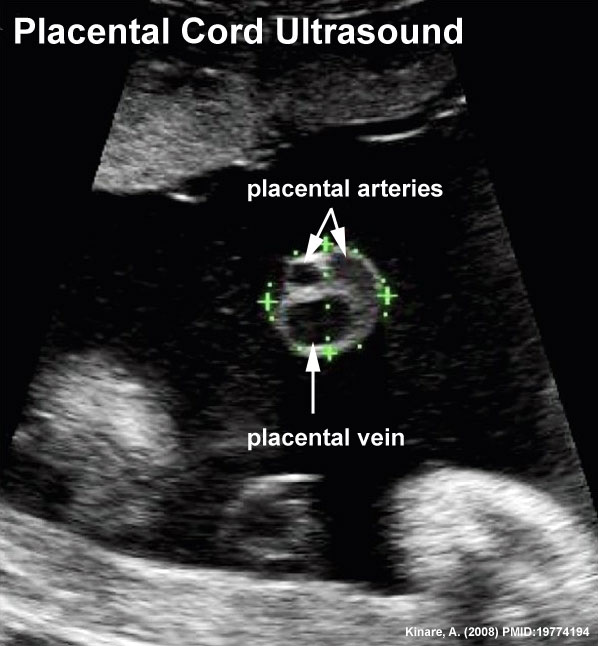
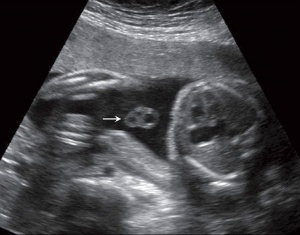
Placental Cord Ultrasound
Ultrasound image of transverse scan through the cord show the method of estimation of the cross-sectional area.
Wharton's Jelly
- placental cord connective tissue (substantia gelatinea funiculi umbilicalis)
- amorphous substance containing glycosaminoglycans, proteoglycans and hyaluronic acid.
- cells similar to smooth muscle that allows a contractile function.
- network of collagen that form canaliculi and perivascular spaces.
- maintain blood flow to the fetus during placental cord compression during pregnancy or delivery.
First described and named after Thomas Wharton (1614–1673) an English physician and anatomist.
Hofbauer Cells
- located the core of placental villi
- macrophages with micropinocytotic activity and phagocytosis ability
- possible paracrine role for early stages of placental vasculogenesis
- express angiogenic growth factors (VEGF)
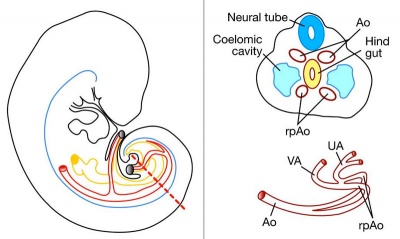
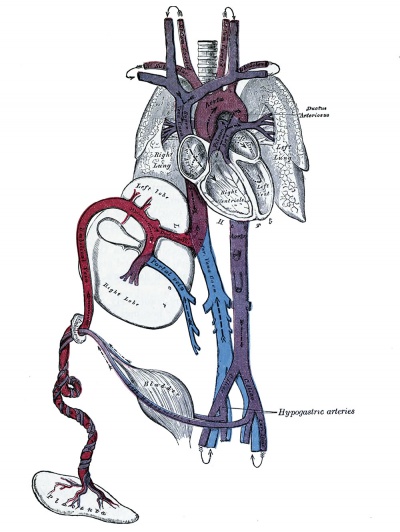
Fetal Circulation
Terms
| Practical 14: Implantation and Early Placentation | Villi Development | Maternal Decidua | Cord Development | Placental Functions | Diagnostic Techniques | Abnormalities |