BGDA Practical 7 - Week 3: Difference between revisions
mNo edit summary |
|||
| (39 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{ | {{BGDALab7}} | ||
==Introduction== | ==Introduction== | ||
Key events of human development during the third week (week 3) following fertilization | Key events of human development during the third week (week 3) following fertilization clinical {{GA}} week 5. | ||
Note that during this time the conceptus cells not contributing to the embryo are contributing to placental membranes and the early placenta. This page describes the mechanical events and changes occurring in each of the 3 germ layers (some concepts will also be covered in later weeks). | |||
===Gastrulation=== | |||
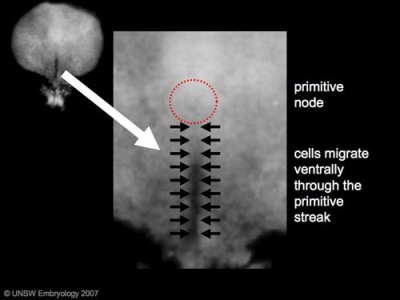
Through week 3 the process of {{gastrulation}} continues, as cells to migrate through the primitive streak contributing to {{mesoderm}}. | |||
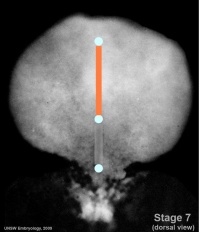
As the embryonic disc grows overall in size, the primitive streak appears to become more caudal as it does not increase in size. | |||
[[File:Stage7_primitive_streak_labelled.jpg|400px]] [[File:Trilaminar_embryo.jpg|400px]] | |||
===Folding=== | ===Folding=== | ||
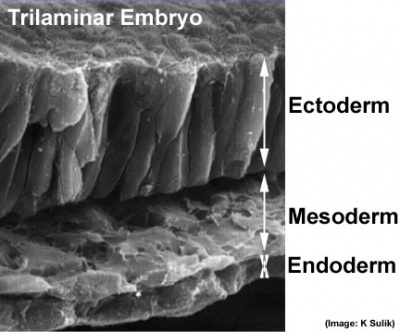
Endoderm, mesoderm and ectoderm layers. There are two major folding processes that take place during this time. | Endoderm, mesoderm and ectoderm layers. There are two major folding processes that take place during this time. | ||
# Folding of the whole embryonic disc ventrally, separates the endoderm to form the epithelial lining of the gut. Folding of the embryonic disc occurs ventrally around the notochord, which forms a rod-like region running rostro-caudally in the midline. | # Folding of the whole embryonic disc ventrally, separates the endoderm to form the epithelial lining of the gut. Folding of the [[E#embryonic disc|embryonic disc]] occurs ventrally around the {{notochord}}, which forms a rod-like region running rostro-caudally in the midline. | ||
# Folding of the ecoderm will form a neural groove, then closing to form a neural tube, separating the neural ectoderm from the embryo surface ectoderm. | # Folding of the ecoderm will form a [[N#neural groove|neural groove]], then closing to form a [[N#neural tube|neural tube]], separating the neural ectoderm from the embryo surface ectoderm. | ||
===Mesoderm Segmentation=== | ===Mesoderm Segmentation=== | ||
Different regions of mesoderm form early intermediate structures. | Different regions of mesoderm form early intermediate structures. | ||
# [[ | # [[Basic_-_Primitive_Heart_Tube|Cardiac development]] - forming the simple heart tube within splanchnic mesoderm. | ||
# | # {{Somitogenesis}} - when part of the mesoderm layer segments commences during week 3 to form balls of mesoderm called somites. The later migration of cells forms the mesoderm germ layer. An embryonic connective tissue ([[M#mesenchyme|mesenchyme]]) which forms nearly all the connective tissues of the body (the head is different). Somitogenesis is when part of this layer segments during week 3 to form balls of mesoderm called somites, note that the majority of somites form during week 4. | ||
# {{Intra-embryonic coelom}} - Within the embryonic disc lateral plate mesoderm a space (coelom) forms, it lies within the embryo and so is called the '''intraembryonic coelom'''. This single "horseshoe-shaped" space will form the 3 major body cavities: '''pericardial''' (around the heart), '''pleural''' (around the lungs) and '''peritoneal''' (around the GIT and visceral organs). | |||
==Ectoderm== | |||
The central portion of the embryonic disc forms the neural plate, the edge of this plate forms neural crest and | The central portion of the embryonic disc forms the '''neural plate''', the edge of this plate forms '''neural crest''' and outside of this again will contribute the epitheium of the skin. (this will be covered in more detail week 4). | ||
<br> | |||
< | {| | ||
File:Stage7-sem2.jpg| | ! Neural Plate | ||
File:Stage8_SEM1.jpg| | ! Neural Groove | ||
File:Stage9 sem4c.jpg| | |- | ||
| [[File:Mesoderm-cartoon1.jpg|300px]] | |||
| [[File::Mesoderm-cartoon2.jpg|300px]] | |||
|} | |||
<br> | |||
{| | |||
| [[File:Stage7-sem2.jpg|250px|link=Carnegie stage 7]] | |||
| [[File:Stage8_SEM1.jpg|250px|link=Carnegie stage 8]] | |||
| [[File:Stage9 sem4c.jpg|250px|link=Carnegie stage 9]] | |||
|- | |||
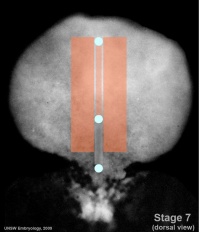
| [[Carnegie stage 7]] | |||
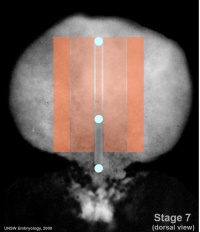
| [[Carnegie stage 8]] | |||
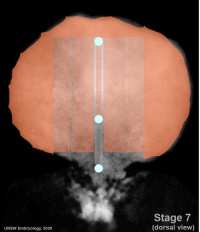
| [[Carnegie stage 9]] | |||
|} | |||
==Endoderm== | |||
{| | |||
| {{Week 3 movie}} | |||
| {{Amnion movie}} | |||
|- | |||
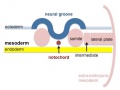
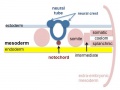
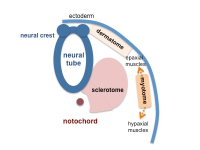
| The major folding processes that take place during this time, in relation to the notochord: | |||
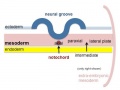
* '''Laterally''' (either side of the notochord) lies mesoderm. | * '''Laterally''' (either side of the notochord) lies mesoderm. | ||
| Line 39: | Line 54: | ||
* '''Dorsally''' (above the notochord) lies the neural tube then ectoderm. | * '''Dorsally''' (above the notochord) lies the neural tube then ectoderm. | ||
* '''Ventrally''' (beneath the notochord) lies the mesoderm then endoderm. | * '''Ventrally''' (beneath the notochord) lies the mesoderm then endoderm. | ||
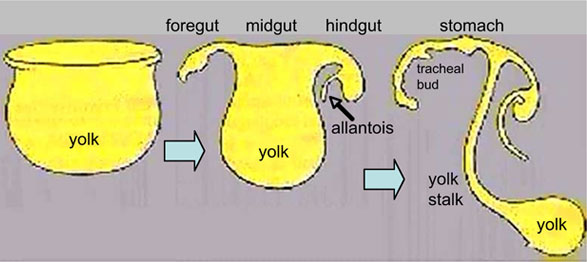
| The ventral endoderm (shown yellow) has grown to line a space called the yolk sac. Folding of the [[E#embryonic disc|embryonic disc]] "pinches off" part of this yolk sac forming the first primative GIT. | |||
[[File:Endoderm_cartoon.jpg]] | |||
|} | |||
==Mesoderm== | ==Mesoderm== | ||
| Line 58: | Line 74: | ||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
File:Mesoderm-cartoon1.jpg|trilaminar embryo | |||
File:Mesoderm-cartoon2.jpg|mesoderm regions | |||
File:Mesoderm-cartoon3.jpg|somite | |||
File:Mesoderm-cartoon4.jpg|somatic, coelom, splanchnic | |||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
===Mesoderm Development=== | ===Mesoderm Development=== | ||
{| | |||
| | |||
# [[E#epiblast|epiblast]] -> mesoderm + [[A#axial mesoderm|axial mesoderm]] ([[N#notochord|notochord]]) | # [[E#epiblast|epiblast]] -> mesoderm + [[A#axial mesoderm|axial mesoderm]] ([[N#notochord|notochord]]) | ||
# [[L#lateral plate|lateral plate]] + [[P#paraxial mesoderm|paraxial mesoderm]] + [[A#axial mesoderm|axial mesoderm]] | # [[L#lateral plate|lateral plate]] + [[P#paraxial mesoderm|paraxial mesoderm]] + [[A#axial mesoderm|axial mesoderm]] | ||
# [[L#lateral plate|lateral plate]] + [[I#intermediate mesoderm|intermediate mesoderm]] + [[S#somite|somites]] (body), [[P#paraxial mesoderm|paraxial mesoderm]] (head) + [[A#axial mesoderm|axial mesoderm]] | # [[L#lateral plate|lateral plate]] + [[I#intermediate mesoderm|intermediate mesoderm]] + [[S#somite|somites]] (body), [[P#paraxial mesoderm|paraxial mesoderm]] (head) + [[A#axial mesoderm|axial mesoderm]] | ||
# [[S#somatic mesoderm|somatic mesoderm]] + [[I#intraembryonic coelom|intraembryonic coelom]] + [[S#splanchnic mesoderm|splanchnic mesoderm]] + [[I#intermediate mesoderm|intermediate mesoderm]] + [[S#somite|somites]] (body), [[P#paraxial mesoderm|paraxial mesoderm]] (head) + [[A#axial mesoderm|axial mesoderm]] | # [[S#somatic mesoderm|somatic mesoderm]] + [[I#intraembryonic coelom|intraembryonic coelom]] + [[S#splanchnic mesoderm|splanchnic mesoderm]] + [[I#intermediate mesoderm|intermediate mesoderm]] + [[S#somite|somites]] (body), [[P#paraxial mesoderm|paraxial mesoderm]] (head) + [[A#axial mesoderm|axial mesoderm]] | ||
| [[File:Mesoderm cartoon.gif]] | |||
|} | |||
===Axial Mesoderm=== | ===Axial Mesoderm=== | ||
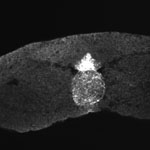
[[File:Sonic_hedgehog_expression.jpg|thumb|Notochord secreting sonic hedgehog]] | [[File:Sonic_hedgehog_expression.jpg|thumb|Notochord secreting sonic hedgehog]] | ||
| Line 80: | Line 98: | ||
# molecular role in patterning surrounding tissues | # molecular role in patterning surrounding tissues | ||
{{Week 3 notochord 1 movie}} {{Week 3 notochord 2 movie}} | |||
| Line 123: | Line 142: | ||
| | | | ||
* a "horseshoe shaped" space forms in the middle | * a "horseshoe shaped" space forms in the middle | ||
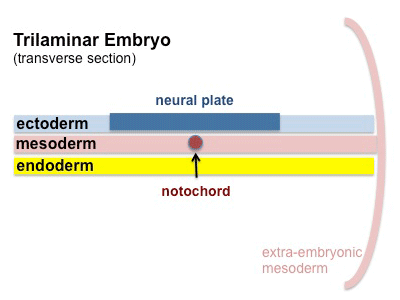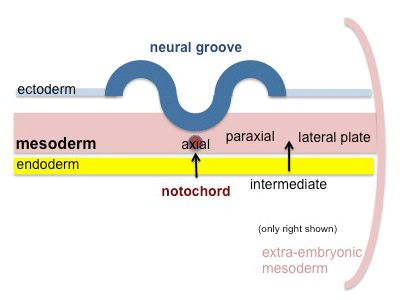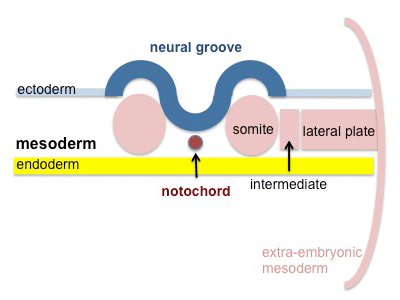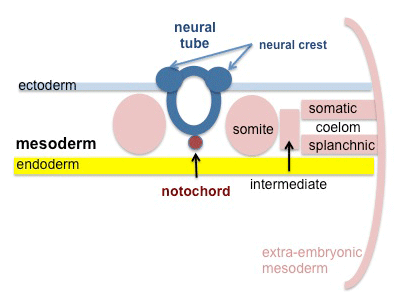
* [[S#somatic mesoderm|somatic mesoderm]] - closest to ectoderm | * [[S#somatic mesoderm|somatic mesoderm]] - closest to ectoderm, forms connective tissue of the body wall and the skeletal elements of the appendicular skeleton and sternum. | ||
* space - forms the 3 body cavities (pericardial, pleural, peritoneal) | * space - forms the 3 body cavities (pericardial, pleural, peritoneal) | ||
* [[S#splanchnic mesoderm|splanchnic mesoderm]] - closest to endoderm | * [[S#splanchnic mesoderm|splanchnic mesoderm]] - closest to endoderm, forms heart and blood vessels; connective tissue and smooth muscle of the gastrointestinal tract | ||
| Line 132: | Line 150: | ||
|- | |- | ||
|} | |||
===Heart Development=== | |||
{| | |||
| [[File:Early_Development_of_Heart_Tube.jpg|300px]] | |||
| Splanchnic mesoderm lying above the notochord (prechordal splanchnic mesoderm) forms a pair of simple tubes, that will fuse to form the primordia of the heart tube. | |||
More: [[Basic_-_Primitive_Heart_Tube|Primitive Heart Tube]] | |||
|} | |} | ||
===Somite Development=== | ===Somite Development=== | ||
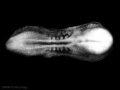
[[File:Stage11 | [[File:Stage11 sem100.jpg|400px]] | ||
Embryo ([[Carnegie stage 11]]) SEM | |||
Somite initially forms 2 main components | Somite initially forms 2 main components | ||
| Line 142: | Line 170: | ||
* dorsolateral - [[D#dermomyotome|dermomyotome]] forms dermis and skeletal muscle | * dorsolateral - [[D#dermomyotome|dermomyotome]] forms dermis and skeletal muscle | ||
{| | |||
|- | |||
| [[File:Somite cartoon1.png|200px]] | |||
| [[File:Somite cartoon2.png|200px]] | |||
| [[File:Somite cartoon3.png|200px]] | |||
| [[File:Somite cartoon4.png|200px]] | |||
|- | |||
| paraxial mesoderm | |||
| early somite | |||
| sclerotome and dermomyotome | |||
| dermatome and myotome | |||
|} | |||
{{Somite parts table}} | |||
===Sclerotome=== | ===Sclerotome=== | ||
{| | {| | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [[File:Vertabra 003 icon.jpg|200px|link= | | [[File:Vertabra 003 icon.jpg|200px|link=Vertebra Development Movie]] | ||
| | | | ||
* sclerotome from somites at the same segmental level contribute the right and left half of each vertebral and intervertebral element | * sclerotome from somites at the same segmental level contribute the right and left half of each vertebral and intervertebral element | ||
| Line 165: | Line 200: | ||
{| | {| | ||
| [[File:Somite cartoon5.png|left|200px|epaxial and hypaxial muscles]] | | [[File:Somite cartoon5.png|left|200px|epaxial and hypaxial muscles]] | ||
| | | [[File:Somite 001 icon.jpg|200px|link=Somite Musculoskeletal Movie]] | ||
Forms 2 muscle groups in body and limbs | |- | ||
| Forms 2 muscle groups in body and limbs | |||
* Body - [[E#epaxial muscle|epaxial]] and [[H#hypaxial muscle|hypaxial muscle]] groups | * Body - [[E#epaxial muscle|epaxial]] and [[H#hypaxial muscle|hypaxial muscle]] groups | ||
* Limbs - flexor and extensor muscles | * Limbs - flexor and extensor muscles | ||
| Development of the sclerotome and myotome components of the somite. | | Development of the sclerotome and myotome components of the somite. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 180: | Line 214: | ||
* spreads throughout the body | * spreads throughout the body | ||
'''Note''' - Dermatome is the term also used clinically postnatally to describe the region of skin supplied by a single spinal nerve. | '''Note''' - Dermatome is the term also used clinically postnatally to describe the [[:File:Dermatomes.png|region of skin supplied by a single spinal nerve]]. | ||
==Week 2 and 3 Movies== | ==Week 2 and 3 Movies== | ||
===Week 2=== | |||
{| | {| | ||
| {{Template:Week 2 implant movie}} | |||
| | | {{Template:Week 2 bilaminar movie}} | ||
| | |} | ||
| | ===Week 3=== | ||
{| | |||
| valign="bottom"|{{Week 3 mesoderm movie}} | |||
| valign="bottom"|{{Week 3 notochord 1 movie}} | |||
| | | valign="bottom"|{{Week 3 notochord 2 movie}} | ||
| | | valign="bottom"|{{Nodal cilia movie}} | ||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|- | |- | ||
| valign="bottom"|{{Week 3 movie}} | |||
| valign="bottom"|{{Amnion movie}} | |||
| valign="bottom"|{{Quail gastrulation ECM movie}} | |||
|} | |} | ||
{{BGDA Practical 6 - Week 3 Interactive}} | |||
{{BGDALab7}} | |||
==Additional Information== | |||
{{Med Prac additional Information}} | |||
===Timeline=== | |||
{{Week 3 Embryo Stages and Events table}} | |||
{{ | {{BGDAFooter}} | ||
[[Category:Week 3]] | [[Category:Week 3]] | ||
Latest revision as of 20:50, 12 May 2019
| Practical 6: Week 3 | Week 4 | Week 5 | Week 6 | Week 7 | Week 8 |
Introduction
Key events of human development during the third week (week 3) following fertilization clinical GA week 5.
Note that during this time the conceptus cells not contributing to the embryo are contributing to placental membranes and the early placenta. This page describes the mechanical events and changes occurring in each of the 3 germ layers (some concepts will also be covered in later weeks).
Gastrulation
Through week 3 the process of gastrulation continues, as cells to migrate through the primitive streak contributing to mesoderm.
As the embryonic disc grows overall in size, the primitive streak appears to become more caudal as it does not increase in size.
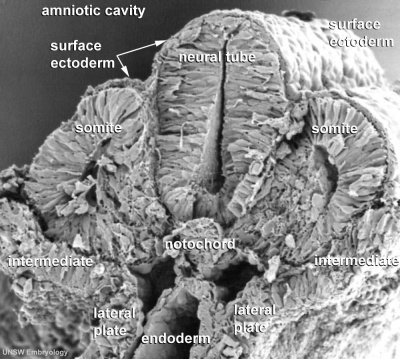
Folding
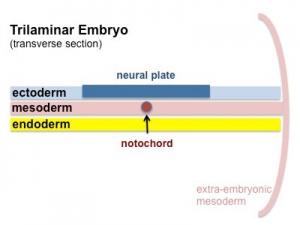
Endoderm, mesoderm and ectoderm layers. There are two major folding processes that take place during this time.
- Folding of the whole embryonic disc ventrally, separates the endoderm to form the epithelial lining of the gut. Folding of the embryonic disc occurs ventrally around the notochord, which forms a rod-like region running rostro-caudally in the midline.
- Folding of the ecoderm will form a neural groove, then closing to form a neural tube, separating the neural ectoderm from the embryo surface ectoderm.
Mesoderm Segmentation
Different regions of mesoderm form early intermediate structures.
- Cardiac development - forming the simple heart tube within splanchnic mesoderm.
- somitogenesis - when part of the mesoderm layer segments commences during week 3 to form balls of mesoderm called somites. The later migration of cells forms the mesoderm germ layer. An embryonic connective tissue (mesenchyme) which forms nearly all the connective tissues of the body (the head is different). Somitogenesis is when part of this layer segments during week 3 to form balls of mesoderm called somites, note that the majority of somites form during week 4.
- intra-embryonic coelom - Within the embryonic disc lateral plate mesoderm a space (coelom) forms, it lies within the embryo and so is called the intraembryonic coelom. This single "horseshoe-shaped" space will form the 3 major body cavities: pericardial (around the heart), pleural (around the lungs) and peritoneal (around the GIT and visceral organs).
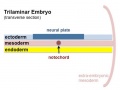
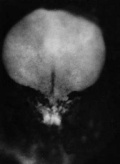
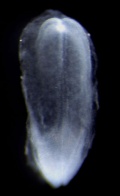
Ectoderm
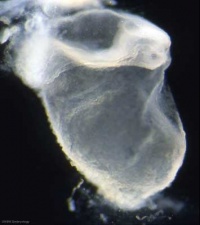
The central portion of the embryonic disc forms the neural plate, the edge of this plate forms neural crest and outside of this again will contribute the epitheium of the skin. (this will be covered in more detail week 4).
| Neural Plate | Neural Groove |
|---|---|
|
[[File::Mesoderm-cartoon2.jpg|300px]] |
|
|
|
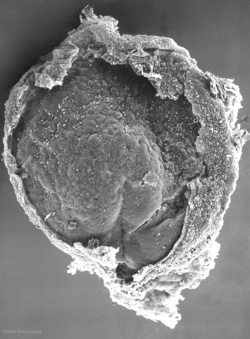
| Carnegie stage 7 | Carnegie stage 8 | Carnegie stage 9 |
Endoderm
|
| ||||||
The major folding processes that take place during this time, in relation to the notochord:
|
The ventral endoderm (shown yellow) has grown to line a space called the yolk sac. Folding of the embryonic disc "pinches off" part of this yolk sac forming the first primative GIT. |
Mesoderm
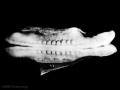
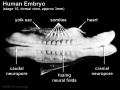
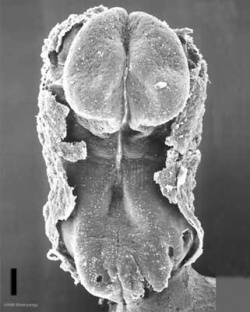
Mesoderm means the "middle layer" and it is from this layer that nearly all the bodies connective tissues are derived. In early mesoderm development a number of transient structures will form and then be lost as tissue structure is patterned and organised. Humans are vertebrates, with a "backbone", and the first mesoderm structure we will see form after the notochord will be somites.
Facts: Week 4, 22 - 23 days, 2 - 3.5 mm, Somite Number 4 - 12
View: This is a dorsal view of the human embryo, the amniotic membrane has been removed. Top embryo is an early stage 10, bottom is late stage 10.
Mesoderm Development
|
|
Axial Mesoderm
|
The notochord
|
Paraxial Mesoderm
Adult - contributes vertebral column (vertebra and IVD), dermis of the skin, skeletal muscle of body and limbs |
Intermediate Mesoderm
Adult - metanephros forms the kidney |
Lateral Plate Mesoderm
|
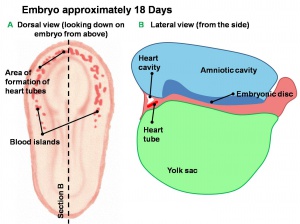
Heart Development
|
Splanchnic mesoderm lying above the notochord (prechordal splanchnic mesoderm) forms a pair of simple tubes, that will fuse to form the primordia of the heart tube.
More: Primitive Heart Tube |
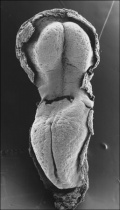
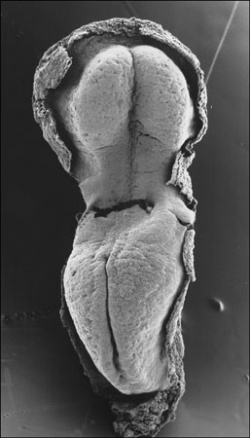
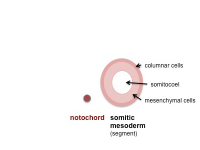
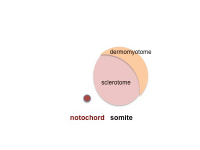
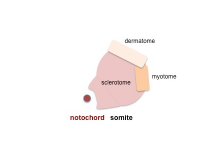
Somite Development
Embryo (Carnegie stage 11) SEM
Somite initially forms 2 main components
- ventromedial- sclerotome forms vertebral body and intervertebral disc
- dorsolateral - dermomyotome forms dermis and skeletal muscle
|
|
|
|
| paraxial mesoderm | early somite | sclerotome and dermomyotome | dermatome and myotome |
| Sclerotome | Dermatome |
|---|---|
|
|
| Myotome | |
|
Sclerotome
|
Myotome
Forms 2 muscle groups in body and limbs
|
Development of the sclerotome and myotome components of the somite. |
Dermatome
- connective tissue underlying epidermis
- begins as a dorsal thickening
- spreads throughout the body
Note - Dermatome is the term also used clinically postnatally to describe the region of skin supplied by a single spinal nerve.
Week 2 and 3 Movies
Week 2
|
|
Week 3
|
|
|
| ||||||||||||
|
|
|
Week 3 Interactive Component
| Attempt the Quiz - Week 3 | |
|---|---|

Here are a few simple Quiz questions that relate to Week 3 (GA week 5) from the lecture and practical. See your Quiz Result - Answer all the questions, then click "submit" to complete. The page will reload and you can then reopen this table to see your result and feedback.
|
| Practical 6: Week 3 | Week 4 | Week 5 | Week 6 | Week 7 | Week 8 |
Additional Information
| Additional Information - Content shown under this heading is not part of the material covered in this class. It is provided for those students who would like to know about some concepts or current research in topics related to the current class page. |
Timeline
| Week 3 - Human Embryo Stages and Events (GA week 5) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Embryo Week: Week 1 | Week 2 | Week 3 | Week 4 | Week 5 | Week 6 | Week 7 | Week 8 | Week 9 | ||
| Event | ||
| Stage 7 | Gastrulation primitive node (Hensen's node, primitive knot) The small circular region located at the cranial end of the primitive streak, where gastrulation occurs, and is a controller of this process. The process establishes the 3 germ cell layers: Endoderm, Mesoderm and Ectoderm. The second role is to act as an initial generator of the left-right (L-R) body axis. | |
| Stage 8 | Neural - neurogenesis, neural groove and folds are first seen | |
| Stage 9 | Musculoskeletal - somitogenesis, first somites form and continue to be added in sequence caudally (1 - 3 somite pairs).
Neural - the three main divisions of the brain, which are not cerebral vesicles, can be distinguished while the neural groove is still completely open Neural Crest - mesencephalic neural crest is visible[1] | |
| Heart - cardiogenesis, week 3 begins as paired heart tubes. | ||
| Note - the day timing of stages is only approximate, system names link to first page of that specific system, and events are based upon the literature cited below. | ||
References
| ||
BGDA: Lecture 1 | Lecture 2 | Practical 3 | Practical 6 | Practical 12 | Lecture Neural | Practical 14 | Histology Support - Female | Male | Tutorial
Glossary Links
- Glossary: A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | Numbers | Symbols | Term Link
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, April 16) Embryology BGDA Practical 7 - Week 3. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/BGDA_Practical_7_-_Week_3
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G