Apgar test: Difference between revisions
mNo edit summary |
|||
| Line 37: | Line 37: | ||
{{Apgar table}} | |||
{ | |||
==Reassessment of Apgar Score== | ==Reassessment of Apgar Score== | ||
Revision as of 15:51, 2 June 2013
Introduction
A historic neonatal test designed by Dr Virginia Apgar[1] used in nearly all maternity clinics to assess the newborn infants well being assigned scores for each of 5 indicators: Heart Rate, Respiratory Effort, Reflex Irritability, Muscle Tone, Colour
Measured at one and five minutes after birth the Score values are totalled for all indicators: 7-10 is considered normal, 4-7 may require resuscitative measures, 3 and below require immediate resuscitation.
In recent years there has been some controversy of the relevance and accuracy of some of the criteria used in this test, though many feel it is still an invaluable initial assessment tool particularly where medical services are limited.
Some Recent Findings
|
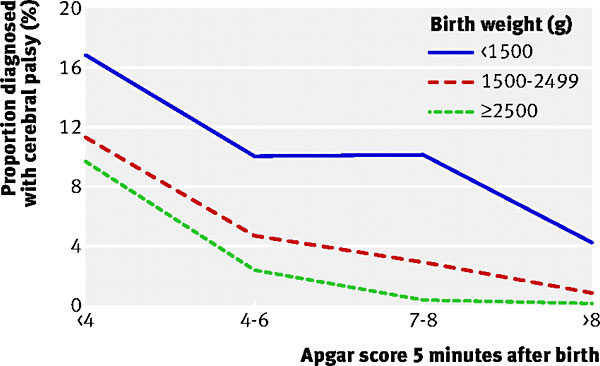
Low Apgar and cerebral palsy
Proportions diagnosed with cerebral palsy according to Apgar score in children with birth weight of less than 1500 g, 1500-2499 g, and 2500 g or more.
The Medical Birth Registry of Norway was used to identify all babies born between 1986 and 1995. These data were linked to the Norwegian Registry of Cerebral Palsy in Children born 1986-95, which was established on the basis of discharge diagnoses at all paediatric departments in Norway.
- "Low Apgar score was strongly associated with cerebral palsy. This association was high in children with normal birth weight and modest in children with low birth weight. The strength of the association differed between subgroups of spastic cerebral palsy. Given that Apgar score is a measure of vitality shortly after birth, our findings suggest that the causes of cerebral palsy are closely linked to factors that reduce infant vitality."
Reference: Association of cerebral palsy with Apgar score in low and normal birthweight infants: population based cohort study. Lie KK, Grøholt EK, Eskild A. BMJ. 2010 Oct 6;341:c4990. doi: 10.1136/bmj.c4990.
Apgar Test Scores
- Measured at one and five minutes after birth.
- The Score values are totalled for all indicators
- 7 to 10 is considered normal
- 4 to 7 may require resuscitative measures
- 3 and below require immediate resuscitation
| Indicator | Score 0 | Score 1 | Score 2 |
| Activity (muscle tone) |
Limp; no movement | Some flexion of arms and legs | Active motion |
| Pulse (heart rate) |
No heart rate | Fewer than 100 beats per minute | At least 100 beats per minute |
| Grimace (reflex response) |
No response to airways being suctioned | Grimace during suctioning | Grimace and pull away, cough, or sneeze during suctioning |
| Appearance (color) |
The baby's whole body is completely bluish-gray or pale | Good color in body with bluish hands or feet | Good color all over |
| Respiration (breathing) |
Not breathing | Weak cry; may sound like whimpering, slow or irregular breathing | Good, strong cry; normal rate and effort of breathing |
| Table data[3] Apgar test - Measured at one and five minutes after birth, the score values are totalled for all indicators: | |||
| Total Score: | 3 and below require immediate resuscitation | 4 to 7 may require resuscitative measures | 7 to 10 is considered normal |
|---|---|---|---|
Reassessment of Apgar Score
Two large 2001 neonatal studies have examined whether the Apgar score is still a relevant neonatal assessment tool.
- Low 5-minute Apgar score: a population-based register study of 1 million term births.[4] "Several obstetric risk factors are associated with low 5-minute Apgar score in term infants. Mortality and the risk of severe neurologic morbidity are increased in these infants."
- The continuing value of the Apgar score for the assessment of newborn infants.[5]"The Apgar scoring system remains as relevant for the prediction of neonatal survival today as it was almost 50 years ago."
References
Reviews
<pubmed>15680744</pubmed> <pubmed>15157595</pubmed> <pubmed>11949546</pubmed>
Articles
<pubmed>13083014</pubmed> <pubmed>17142501</pubmed> <pubmed>17011319</pubmed> <pubmed>17011319</pubmed> <pubmed>17011310</pubmed> <pubmed>11430958</pubmed> <pubmed>11172187</pubmed>
Search Pubmed
Search PubMed May 2010 "Apgar test" All (2327) Review (70) Free Full Text (294)
Search PubMed: Apgar | Apgar test | Virginia Apgar
Glossary Links
- Glossary: A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | Numbers | Symbols | Term Link
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, April 18) Embryology Apgar test. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/Apgar_test
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G